Vegetable Soilless Cultivation Tutorial for Fools 20091210

1. It is relatively easy to get started and more convenient to manage than soil cultivation;
2. Good product quality and high yield;
3. Product safety and the ability to produce pollution-free food;
4. Improve local ecological conditions and create a suitable living environment. It is a good humidifier in the heating season and can evaporate more than n liters of water every day.
Nutrient solution should be stored in a cool place away from light and out of reach of children. Nutrient solution is acidic. If it splashes into your eyes, please wash it immediately with plenty of clean water.
Planting box : Do not overturn it to avoid large amounts of water spilling and causing losses.
Power supply: Keep sockets and adapters away from places where water may spill, or wrap them tightly with waterproof cloth.
Water pump: The household distribution box should be equipped with a leakage protector. The wires should have waterproof insulation sleeves. Make sure your hands are dry before plugging in the power supply, otherwise there is a risk of electric shock. Be sure to unplug the water pump plug when cleaning the planting box. Do not plug or unplug the plug when your hands are wet to prevent the risk of electric shock.
Climbing : When pruning, tying vines, and harvesting fruits, you should have a stable ladder or stool. If you step on a stool or ladder, please pay attention to safety to prevent slipping, falling, or muscle strain. It is best to have someone to assist.
Fixing: All planting support frames should be firmly fixed to prevent overturning.
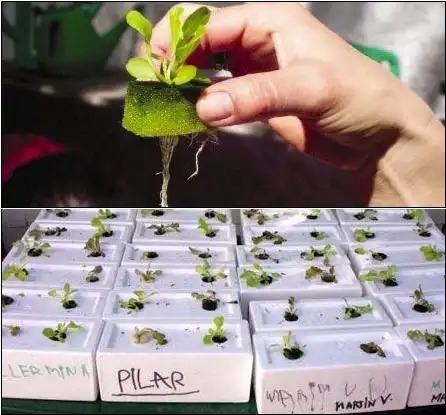




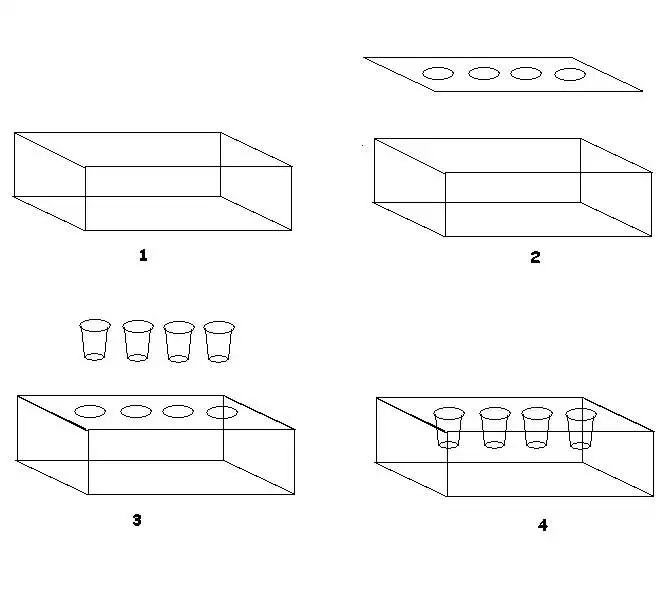
Lettuce is a crop that does not need to add oxygen to the roots, so you can use a pot or a foam box, put some nutrient solution in it, let the roots immerse in it, and it will grow well. You can plant it according to the diagram. If you don’t understand, or have more questions, please ask.
It should be noted that for leafy vegetables, you should stop adding nutrient solution one week before harvesting. You only need to add clean water to reduce the nitrate content inside the plant, thereby reducing the harmful nitrite content that may be generated in the human intestine. People are now only concerned about the pesticide problem for leafy vegetables sold on the market. In fact, unbalanced fertilizer ratios, too much nitrogen fertilizer, and too high nitrate content also need attention.
The article comes from
http:///php/viewtopic.php?p=77&highlight=kindergarten#77
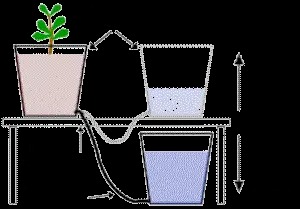
Following our suggestions, you can create a simple and inexpensive soilless cultivation system
1. Material list
(1) Planting system The planting system consists of two parts and is easy to assemble. (It is a bucket and a planting trough (if there is no planting trough, you can use a plastic pot, a thicker PVC pipe, a long strip of sealed bottom flower pot, etc.)
(2) Growth substrate The growth substrate must be inert and not react with the substances in the nutrient solution. It only serves to fix the plant. The substrate is looser than soil and can provide more oxygen to the roots.
(3) Two-component nutrient solution Any commercial nutrient solution for soilless cultivation can be used.
(4) PH adjuster If the PH is too high or too low, the planting will fail. You need a test strip or instrument to test the PH value of the nutrient solution. The adjuster can adjust the PH value to keep it within a reasonable range.
(5) Seed cabbage grows quickly, and lettuce is also good to harvest before flowering. Tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers grow and bear fruit too slowly, so it is best not to choose them.
(6) Bucket
(7) A piece of pipe to connect the planting system and the bucket
2. Rockwool planting block
The first step in the pretreatment of the rockwool planting block is to balance the pH of the rockwool planting block. (It is estimated that most people cannot get such things, so you can use fiberglass instead. If you don't like the prickly fiberglass, you can use a sponge or a small cup filled with ceramsite instead).
Friends who don't want to be too troublesome can just rinse it with clean water. Friends who are serious about doing things can look down: pH value represents the acidity and alkalinity of water. The value range is from 1-14. A pH value of 7 is neutral, greater than 7 is alkaline, and less than 7 is acidic. Tap water is generally alkaline, because the roots of plants like acidic, so we have to add a little acid to the water before watering the plants.
First take a cup of water and measure it with a test paper (agent). The general result is greenish, and you can know it by comparing it with the standard colorimetric plate (pH 7-8). Next, drop 2 drops of acidic pH regulator (phosphoric acid, please wash it with water immediately if it comes into contact with the skin), stir it and test it again until the result is yellowish (pH 6). If the color turns brown or red, it means that you have added too much acid. At this time, add tap water to increase the pH value.
3. Assemble the system
. Put the system in place. Once it starts, it will be difficult to move. Please put it in a level and firm place so that it will not tip over. If you install the bracket outside the window, please note that the bracket length should be greater than the system length. There should be a gap under the rock wool in the planting trough. Use a piece of pipe to connect the planting system and the bucket.
4. Planting seeds
Plant the seeds in the small eyes of the planting block. If there is no small eye, you can make one yourself (0.75cm). Gently cover the small eye so that the seeds have a dark environment to germinate, and cover it with a plastic bag to maintain humidity. Water every few days. Most seeds will germinate in 4-6 days. After germination, remove the plastic bag and water again.
5. Prepare nutrient solution
Nutrient solution is the food of plants. Too much or too little is not good. Nutrient solution provides plants with minerals originally provided by the soil. Use half the concentration during the seedling stage. The nutrient solution should submerge the bottom of the planting block.
6. Adjust the pH value
Adjust the pH value once after each addition of nutrient solution.
7. Tidal watering
Lift the bucket to let the nutrient solution in the bucket flow into the planting trough. The nutrient solution should submerge the bottom of the planting block, and then lower the bucket to let the nutrient solution return. Do not let the roots soak in water for more than 3 minutes. 3 times a day.
8. Management of nutrient solution:
Add clean water every day and adjust the pH value.
In the second week, you can use a normal concentration of nutrient solution.
9. About supplementary
light: Light is essential for plants. If there is insufficient sunlight, they will not grow well anyway.



Drill holes in the bottom of the small box above and make a window (you can ask a plastic steel window processing factory to do it)




Sea surface seedling blocks for seedling cultivation, leafy vegetables, fruit vegetables


When the seedlings grow to a certain stage, the nursery pot can no longer meet the growth requirements of the seedlings, so they need to be transplanted.

One week after planting, the roots will extend to the lower planting box.

After a while, you need to tie up the stems. If it is a leafy vegetable, this step is not necessary.

If you don't prune it in time, or if you are not ruthless enough when pruning it, it will grow wildly!

Specifically, the plants are overcrowded, the branches and leaves are so dense that no flowers bloom or the flowers do not bear fruit, and in severe cases, diseases and insect pests may occur.

The whole process of fruit from flowering to fruiting and then turning red

The process of fruit enlargement

Pick the fruits yourself, experience the joy of planting, and take a bite to enjoy the lingering fragrance!

12W water pump, water head (height to which water can be raised) 70cm

Environmental management
Light: direct sunlight for at least 4 hours per day
Temperature: 10-35 degrees Celsius
Humidity: 40-80%.
System installation sequence
Growth support Grid
Cultivation box
Support support rope Rope

Water pump, pipe or air pump for the lower cultivation box , water pipe for the aerated sand head

is punched with holes on the planting board according to the planting distance. The size of the holes is close to the size of the planting sponge block or planting cup for the seedlings. There are many ways to fix the roots of seedlings
in seedling blocks and seedling cups
. For sponge blocks or matrix blocks, sow the soaked and germinated tomato seeds in the cracks of the sponge block or the holes of the matrix block, and then pour a little nutrient solution every day until the seedlings emerge. When they grow to 10-15cm, they can be transplanted.
You can also use perlite and vermiculite to grow seedlings. Wrap a layer of sponge around the root and stem of the cultivated seedlings and implant them in the planting holes.
Friends who raise fish may know that there is a small planting basket for fixing the roots of water plants. There are many small slits on it. It is also good to use it in combination with ceramsite and pebbles to grow seedlings for leafy vegetable seeds. It is also OK to burn some small holes on the bottom and side walls of the disposable transparent plastic water cups sold in supermarkets.
Plant management (take tomatoes or cucumbers as an example)
Binding: tomatoes or cucumbers grow faster in a suitable environment, and their branches should be tied as they grow, so it is necessary to build a frame to fix the plants, so that the branches can stretch more and the branches are more beautiful. The main work of pruning is to prune and top, which can also be combined with twisting and pulling branches to achieve the same shaping effect as fruit trees. With single-stem or double-stem pruning, guide the branches to a reasonable direction so that the plants can get enough light and do not shade each other.
Pruning: Too many branches and leaves will cause the growth of plants to deteriorate, consume nutrients, reduce yields and easily attract diseases and insect pests. Therefore, it is necessary to remove old leaves, diseased leaves, and branches and leaves that grow too densely and too fast.
Thinning flowers and fruits: Too many flowers and fruits will cause the growth of plants to weaken and reduce the quality and yield of fruits. Management
of water and nutrient solution The purchased nutrient solution must contain trace elements. Tap water often causes reproductive disorders due to residual chlorine. In particular, if the tap water is not dechlorinated (aired for one day), residual chlorine will cause vegetable root rot. For nutrient solution management, mark the 3/4 of the depth of the inner wall of the container so that water can be added to the scale line in the future. Pay attention to check the water level. When the water level is lower than the marked water level line, you can add clean water or nutrient solution until it reaches the mark. Add nutrient solution 1-2 times a week. According to the instructions for use of nutrient solution preparation, prepare an aqueous solution with an EC value of 1.5-2 millisiemens and inject it into the container. Keep the solution conductivity around 2.0 millisiemens. If there is no detection tool, add 1 cup (250ml) of 50 times concentrated nutrient solution per week based on the actual plant growth situation, and only add clean water between every two additions of nutrient solution. The nutrient solution can be slightly more concentrated when it is replaced in the later stage of cultivation. The EC value of tomatoes is 1.4-1.6 millisiemens, and that of cucumbers is about 2.0. In home cultivation, for the convenience of use, the pre-prepared nutrient solution is usually placed in a large container according to the instructions. It can be scooped out when needed, but the container containing the diluted nutrient solution should be kept away from light to prevent the growth of green algae. Root oxygen management Oxygen is an essential element for root growth, and it is also the reason why soilless cultivation yields far more than soil cultivation. You can use a silent submersible pump for fish farming to circulate water and oxygenate it internally, or you can use an air pump to pump air into the water. The submersible pump consumes very little power and can be turned on all the time. The air pump is fixed outside the planting box, and the aeration sand head is placed in the nutrient solution to achieve aeration and oxygenation. Turn it on for at least 12 hours a day. If it is not turned on for a long time, the roots of the plant will grow weak due to lack of oxygen, the fruit will be reduced, or it will die. The growth cycle varies depending on the variety. Tomatoes and cucumbers are planted about one month after sowing, bloom one month after planting, and the fruit is harvested two months after flowering. The fruit harvest can last for 2 months or even longer. It takes about 6 months. From sowing to planting to harvesting, lettuce takes only 35 days in the warm season. Common diseases and pests Diseases Powdery mildew, gray mold, pests Whiteflies, aphids, spider mites, scale insects, leaf miners Solution, prevention first, frequent ventilation, pruning old leaves, diseased and insect-infested leaves, overcrowded leaves, use screens to cover the plants to prevent insects.

Instrument 2

pH meter to measure acidity and alkalinity

EC meter for measuring electrical conductivity

Data acquisition card for environmental>
Acid-base adjustment reagents

Various necessary fertilizers

Atomizer can be used for the ultimate way of soilless cultivation - aeroponics

Atomizer 2

PVC special glue is used to bond water supply pipes and planting supports.

Table of Contents
Preparation before starting:
●Choose a suitable planting site;
●Nutrient solution
●Hardware
●Develop a planting plan
●Choose planting varieties
●Clean the site
and start planting
●Seedling raising
●Assembly and planting
●Crop management
●Harvest
●Main cleaning
Preparation before starting:
●Choose a suitable planting site;
1.Sunlight
Indoor balcony or window, outdoor roof or garden, as long as there is direct sunlight, you can consider it. Direct sunlight is required for 4 hours a day.
2.Temperature Plant roots grow well in the range of 15℃ -30℃, so the air temperature is best in this range. Depending on the variety, most plants can tolerate 10℃ -35℃ for a short time. Some heat-resistant or cold-resistant plant varieties may tolerate wider temperature changes. Humidity 40%-80%, too much humidity will cause diseases and insect pests, too little humidity will cause leaf curling and burning. 3.
The water quality is best to be soft water (sweet water). Moderately hard water is also acceptable, but the formula of the nutrient solution needs to be changed. Water that is too bitter and salty is absolutely not acceptable.
●Nutrient solution Full-price nutrient solution on the market (with all the required macro-elements and trace elements), or you can prepare it yourself according to the formula.
●Hardware
Vegetable cultivation can be done with a fully functional system or a simple and easy-to-operate method, as long as the cultivation principle conforms to the growth physiology of vegetables. Whether it is pipeline cultivation, floating cultivation, or aeroponics, it is to create sufficient fertilizer, water and air conditions for the plant roots. Only in this way can the plant take advantage of its rapid growth.
There are many ways to carry out simple hydroponics, which can be made at home using local materials. This is also a beautiful thing to entertain yourself. You can do it yourself and watch the vitality and growth of plants, vegetables or flowers every day.
Here I introduce a simple hydroponic box for vegetable cultivation. It consists of a hydroponic box or box, a foam floating planting board, a sponge block, a nutrient solution, a dropper, seeds, and a small oxygen pump and a microcontroller.
Hydroponic boxes or boxes can be made of some plastic containers discarded in family life. Planting boards can be made of foam boards from decoration material supply stores or foam pads lined with packaging of some household electrical appliances. Then, holes are punched on the foam according to the planting distance.
● Develop a planting plan and try to avoid unsuitable seasons. For example, the lowest heating temperature in the north is less than 10 degrees, which will cause some varieties to grow poorly or even die. In May, June and July of each year, the south-facing balcony will not have enough direct sunlight indoors due to the solar altitude.
● Choose suitable planting varieties. According to your own preferences and local climate, you can choose strawberries, passion fruit, tomatoes, cucumbers, beans, lettuce, peppers, etc. Disease-resistant varieties should be selected.
● Clean the site, remove and eliminate potential sources of infectious diseases and pests, such as sick potted flowers with a large number of flying insects. It is best to add screens to the balcony to effectively prevent the invasion of flying insects from the outside.
Officially start planting
●
The main function of the seedling sponge block is to serve as a carrier for seeds in soilless seedling cultivation. The sponge can be cut into squares and then a cross-shaped crack can be made on it. When raising seedlings, the germinated seeds can be sown into the gaps.
If conditions permit, light can be supplemented. Special attention should be paid to temperature and humidity during seedling cultivation. It is very important to cultivate strong seedlings, which can reduce pests and diseases and greatly increase yields.
● Assembly and planting Prepare clean water, add nutrient solution and leave it overnight. When the water temperature and air temperature are close, you can plant it.
● Crop management needs to point out that people who are often away from home will definitely not grow well. Plants do not need much, but they need to be cared for 2 to 3 times a week, 10 minutes each time, for watering, tying vines, pruning, auxiliary pollination, and harvesting fruits.
● When harvesting is the place where superiority is most reflected, the freshest fruits and vegetables can be picked at any time. You can wait for the fruit to be fully ripe before harvesting. Tomatoes in supermarkets and farmers' markets are picked when the fruit just changes color for the convenience of transportation. The fruit coloring period is exactly the most important to affect the quality of the fruit. Cucumbers can be harvested after the small protrusions on the surface are basically unfolded and the tomato fruit changes color and is fully colored.
●Major cleanup to prepare for the next cycle.
●Are there any books (or) materials on this subject
? ●Is the soilless cultivation nutrient solution environmentally friendly and harmless to the human body
? ●What are the factors that affect the quality of vegetables?
●Is soilless cultivation suitable for outdoor use?
●If an insect infestation occurs, won’t the room be full of insects?
●If a disease really occurs, how should it be solved
? ●If there is no conductivity meter, how to adjust the concentration of the nutrient solution?
●The cycle of adding nutrient solution
●Is the concentration the same in each period of the plant
? ●What are the ways to raise seedlings?
●What are the ways to fix plants?
●Nutrient solution ingredients
●Is it necessary to change the solution every once in a while, just like raising fish?
Tomato
Hoagland m mol/liter
2x concentrate
Macroelements
Ca(NO3)2 4H2O 3.00
KNO3 10.00
NH4H2PO4 2.00
MgSO4 7H2O 2.00
Trace elements
EDTA-FeNa2 24.00
H3BO3 1.24
MnSO4 H2O 2.23
MnCl2 4H2O
ZnSO4 7H2O 0.86
CuSO4 5H2O 0.13
(NH4)6Mo7O24 4H2O 0.12
PH 5.5-6.5
Because the water quality varies from place to place, this formula is designed according to the environment of the soft water area in the south, and is not suitable for the high calcium hard water area in the north. In the north, the content of calcium and magnesium can be reduced appropriately.
In addition, the concentration of macroelements can be halved or one-quarter, and the use of trace elements cannot be doubled or halved.
Metal containers cannot be used to prepare and store nutrient solutions.
You can first prepare a 50-fold concentrated nutrient solution and store it in a dark and refrigerated place. If there is a lot of precipitation in the nutrient solution, you must re-prepare it.
The above text is all from the lessons of personal failure.
Soilless cultivation does not rely on soil. It is the planting of vegetables and other crops in a certain cultivation device filled with nutrient solution, or in a planting bed made of non-natural soil matrix materials such as sand, gravel, vermiculite, perlite, rice husks, slag, rock wool, bagasse, etc. filled with nutrient solution. Because it does not use soil, it is called soilless cultivation. And because it does not use general organic and inorganic fertilizers, but relies on providing nutrient solution to replace traditional agricultural fertilization technology, soilless cultivation is also called nutrient solution cultivation, which is simply hydroponics or hydroponic cultivation technology.
Soilless cultivation is a major breakthrough in technology because it does not use soil. At the same time, due to the continuous improvement of technology, advanced facilities, and the application of new substrate materials, soilless cultivation can automatically adjust and control temperature, water, light, fertilizer, and air according to the growth and development needs of different crops, and implement factory production. Therefore, soilless cultivation is a high-tech modern agriculture and a new technology for modern facility cultivation.
2.What are the types of soilless cultivation?
There are many types and methods of soilless cultivation. Depending on whether solid substrate materials are used, soilless cultivation can be divided into two basic types, namely, substrate-free cultivation and substrate cultivation. Substrate-free cultivation means that there is no substrate to fix the root system, and the root system is in direct contact with the nutrient solution. It mainly includes the following types:
3.What are the advantages of soilless cultivation?
Soilless cultivation has advantages that cannot be matched by traditional soil cultivation, because it can monitor and regulate everything from cultivation facilities to environmental control according to the needs of crop growth and development. It can be summarized as follows:
4. Why is it said that soilless cultivation technology has broad development prospects in the cultivation of vegetables, flowers, etc.?
The development of facility agriculture has opened up new horizons for the application of soilless cultivation technology. Since the reform and opening up, with the continuous development of the economy, the continuous improvement of people's living standards and the development of the construction of the "vegetable basket project" in urban and rural areas, the demand for high-quality vegetables and flowers has increased. Therefore, the protected cultivation area of vegetables, flowers and other economic crops has expanded rapidly. According to statistics,
5. Why can soilless cultivation avoid continuous cropping problems?
In recent years, the area of facility cultivation such as greenhouses and greenhouses for cultivating vegetables and flowers has developed rapidly. However, due to the combined effect of multiple crops per year in facility cultivation, the same vegetables and flowers are frequently planted continuously, and the soil has continuous cropping obstacles, such as salinization, acidification, soil compaction, reduced soil fertility, serious root nematodes and soil-borne pests and diseases, and the yield and economic benefits are declining day by day. In serious cases, the fields cannot even continue to be used. Therefore, it is urgent to implement crop rotation, or change the soil, or disinfect the soil, irrigate and wash the salt, etc. However, the above measures are implemented on a large scale, and at the same time they are all restricted by fixed facilities such as greenhouses and greenhouses, and these facilities cannot be relocated on a large scale. In this case, soilless cultivation is adopted. Since there is no cultivation substrate that is replaced or disinfected every crop, there are no pests and diseases that harm crops. And planting troughs are easy to clean and disinfect. Therefore, soilless cultivation is an effective way to solve the problem of continuous cropping.
6. What is the development status of soilless cultivation technology abroad?
In the late 19th century, the famous German scientist Liebig proposed the theory of plant mineral nutrition, marking the entry of soilless cultivation technology into the experimental research stage. After that, German scientists such as Wegmann, Sacks and Knopp successively used nutrient solution to conduct experimental research on plant physiology. Since then, many scientists have conducted in-depth research on nutrient solution, and soilless cultivation technology has gradually moved from experimental research to production application.
At present, soilless cultivation has developed into an independent discipline, namely a high-tech of facility agriculture - soilless cultivation. Now, soilless cultivation has been widely used in production in the United States, Japan, the Netherlands, Denmark, the United Kingdom, Israel and other countries. For example, the area of soilless cultivation in the Netherlands has now developed to
7.What is the development status of soilless cultivation technology?
The application of soilless cultivation technology started late and is still in the development and testing stage.
8. What is the development trend of soilless cultivation in the future?
The development of soilless cultivation technology has a history of more than 100 years. From the initial experimental research to the current large-scale commercial production, the technology has become mature and perfect. Judging from the development of soilless cultivation in the past decade, the future development trend is in two directions: one is towards scale, intensiveness and automation, and the other is towards miniaturization and household use. As the advantages of soilless cultivation crop production are increasingly valued by people, at the same time, due to the improvement of greenhouse design, materials and production processes, modern control instruments and meters, especially the application of computer technology in soilless cultivation production, the production cost of soilless cultivation has been greatly reduced, while the output has been continuously improved, the economic benefits of growers have been higher, and in turn, the funds invested in soilless cultivation have also increased, prompting soilless cultivation production to develop in the direction of scale, automation and intensiveness, forming economies of scale. On the other hand, soilless cultivation technology can be regarded as a popular science and technology, and its use in families, primary and secondary schools has also been increasingly valued by people. With the improvement of housing conditions and the increase of people's income, many residents have adopted soilless cultivation technology, which is clean, convenient and practical, to grow flowers and plants on their balconies and rooftops to cultivate their temperament. Due to the intuitiveness and scientific nature of soilless cultivation of crops, it is very helpful to use it as a biology teaching aid in primary and secondary schools to cultivate students' ability to observe, analyze and solve problems. Therefore, it can be said that the future development prospects of soilless cultivation technology are very good.
9. How to consider and determine the soilless cultivation project?
As a modern agricultural production technology, soilless cultivation has advantages that cannot be matched by general soil cultivation. However, soilless cultivation is also a high-tech technology, involving multiple disciplines including crop cultivation, fertilizer, pest control, agricultural engineering, automatic control, etc., and its technical difficulty is also very high. Moreover, soilless cultivation requires certain facilities and devices, as well as water and power sources. Therefore, when developing soilless cultivation, the cost investment should be considered first, and then the technical strength and other social conditions should be considered. In places with poor economic conditions, soilless cultivation should not be developed blindly. Soilless cultivation can be developed when economic, technical and market conditions are good. However, the following points should be considered and clarified: First of all, the purpose and focus of developing soilless cultivation should be clarified, such as it can be used as an education base or agricultural tourism base for the popularization and promotion of new agricultural technologies. In areas where the development area of facility agriculture is large and soil-borne diseases and soil continuous cropping obstacles are serious, the above problems can be solved through soilless cultivation. In economically developed areas, open cities, and areas with serious soil pollution, soilless cultivation can be used to produce high-quality and high-end vegetables, fruits, and flowers to meet the special needs of hotels, export, and citizens. Soilless cultivation of vegetables can also be developed in places that are not suitable for soil cultivation, such as beaches, seashores, border defenses, islands, and industrial and mining areas. Secondly, it can be applied to small family balcony-style soilless cultivation devices in families and primary and secondary schools. There are many types and methods of soilless cultivation. Appropriate methods should be selected according to the economic, cultural, and technological conditions of different regions, using local materials to reduce costs. Thirdly, soilless cultivation should select high-value crops such as high-value vegetables, fruits, and flowers.
10.What are the basic conditions for soilless cultivation?
The development of soilless cultivation requires the following basic conditions: (1) There must be technical management personnel who are familiar with soilless cultivation and can carry out normal production management and operation and develop sales markets. (2) There must be a guaranteed power supply and water source, and the supply of nutrient solution will not be affected by power outages or water outages. (3) The atmosphere must not be seriously polluted, such as fluorine (FH), sulfur (SO2 ) , and nitrogen oxides (NOX ) . (4) There must be a high-quality water source. The quality of water affects the effect of soilless cultivation. The preparation of nutrient solution requires a high-quality water source: including no bacteria, no excessive chloride ions, sodium ions, calcium and magnesium ions, and no turbid water. (5) It must be carried out under certain protective facilities such as glass greenhouses and plastic film greenhouses covered with cultivation facilities. (6) An appropriate soilless cultivation system must be built. Regardless of the soilless cultivation method, it requires a suitable cultivation trough, drainage system, and control system. Ensure that the crop is in a suitable environmental condition without soil cultivation and can be controlled manually. (7) Suitable climate and season. In addition to fully automated modern soilless cultivation facilities, soilless cultivation of vegetables, flowers, etc. must be carried out under suitable climate conditions and seasons. Soilless cultivation can be carried out in any climate and season that is suitable for the growth of vegetables, flowers, and other crops.
11. How to plan a soilless cultivation production base?
When planning a soilless cultivation production base, the following aspects should be considered: (1) The area and scope should be determined based on the amount of investment and market demand, and the level of production management should be taken into consideration. It can be built in stages, such as in several phases, to leave room for development and expansion. (2) The overall planning is the same as that of a general facility cultivation horticultural farm, with a road system, drainage system, production area, seedling area, product processing and office logistics, drying yard, parking lot and other comprehensive areas. (3) The construction of greenhouses or greenhouses can be set to 8×42M2 ( square meters) or 6×30 square meters, with 10-20 seats as one area. If it is deep liquid flow hydroponics, two troughs can share a storage tank to supply nutrient solution. For substrate culture, 10 or more greenhouses can be used for centralized liquid supply, but the storage tank should be large enough to facilitate production arrangements and nutrient supply and other production management. Large greenhouses with multiple spans can also be built according to local actual conditions. (3) Deep liquid flow hydroponic planting troughs should be built with a stable cement trough structure, or polystyrene foam material pressed and molded planting troughs can be used, which can be spliced and moved, and can be used for hydroponic or substrate culture. However, the disadvantage is that it is easy to damage subsequent production materials and consumes a lot. Substrate culture can be based on specific conditions, with bricks stacked and covered with plastic film or cement troughs. Planting troughs in sheds or greenhouses can be set up in four rows of 8 or eight rows of 16. (4) The liquid storage tank can be located at the side of each group of sheds or in the shed. It is generally underground, but it can also be built above ground, and the liquid is pumped and supplied through the infusion pipeline with a water pump. The liquid storage tank and planting trough should be constructed strictly in accordance with the design requirements to prevent water leakage and meet other design requirements.
12.What are the theoretical basis and basic principles of soilless cultivation?
The essence of soilless cultivation is to replace soil with nutrient solution, and the production of nutrient solution is based on Liebig's theory of plant mineral nutrition. Therefore, the theory of mineral nutrition is the theoretical basis of soilless cultivation. As early as 1840, Liebig proposed the theory of mineral nutrition, believing that crops grow and develop by absorbing inorganic substances dissolved in water. Later, many scholars further confirmed, supplemented and improved this theory. In 1842, German scientists Wegmann and Postoloff and others successfully used container sand culture. From 1859 to 1865, Sachs and Knopp used chemical analysis methods to analyze plant bodies, clarifying that they contain nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and other nutrient elements, and first used inorganic fertilizers to prepare nutrient solution, and successfully cultivated crops. In 1935, American scientists Hogland and Anon and others analyzed and studied the composition and concentration of different soil solutions, and further clarified the necessity of adding trace elements. A lot of research has been conducted on the proportion and concentration of nutrient elements in nutrient solution, and many nutrient solution formulas have been published on this basis. Under the guidance of the above theory, after long-term research, soilless cultivation has finally developed into a new technology and made it practical. The basic principle of soilless cultivation is to design devices and cultivation methods that meet the necessary environmental conditions for the growth and development of different crops, especially the basic conditions for root growth, including nutrition, water, pH, ventilation conditions and rhizosphere temperature, to cultivate crops without soil without natural soil. Therefore, to master the technology of soilless cultivation, it is necessary not only to understand the relevant knowledge of crop cultivation, but also to master the management technology of nutrient solution.
13.What crops can be grown using soilless culture?
In theory, soilless cultivation can grow all kinds of crops that can grow in soil, including vegetables, flowers, fruit trees and other crops. Vegetables include leafy vegetables such as lettuce, water spinach, Chinese cabbage, cabbage, mustard greens, onions, amaranth, kale, fruit vegetables include tomatoes, cucumbers, wax gourds, wax gourds, bitter melons, loofahs, eggplants, etc., melons include watermelons, melons, etc., fruit trees include strawberries, etc., flowers include roses, chrysanthemums, carnations, gladioli, orchids, gerberas, tulips, evergreens, banyan trees, Brazilian wood, green giants, Schefflera arborvitae, and bonsai flowers such as Fujian tea and Osmanthus fragrans.
In actual production, the types of crops grown in soilless cultivation are mainly determined by the prices and seasons of crops in the market. Some places may grow certain types of crops, while other places may grow other types. At present, there are four main types of crops with the most soilless crops in the world, namely tomatoes, lettuce, cucumbers, and sweet peppers. There are many varieties of soilless crops in China. In addition to the above four crops, there are also many varieties such as melons, water spinach, celery, wax gourd, and strawberries. For example, in recent years, Guangdong, Hainan, Guangxi and other provinces and regions with tropical and subtropical climate conditions in the south have taken advantage of climatic conditions to plant thick-skinned melons on a large scale, making them go on the market earlier or later than their places of origin such as Xinjiang, which has achieved great success and obtained good economic benefits. For example, the use of greenhouses or greenhouses in the south to plant water spinach in off-season in winter and early spring can also achieve good economic benefits. In short, what crops to plant depends on the season and local market conditions, and cannot be forced to be consistent.
14.What are the similarities and differences between soilless cultivation and soil cultivation?
Soilless cultivation and soil cultivation both provide crops with sufficient nutrients, water, suitable root temperature, oxygen supply, solution concentration and pH value based on the environmental conditions necessary for the growth and development of crops, and obtain the products necessary for people through artificial cultivation. However, there are great differences between the two in terms of their respective cultivation methods and nutrient supply. The roots of crops cultivated in soil live in a soil layer with good buffering effect, which is full of aqueous solution and air. The water and nutrients needed by crops can be absorbed from the soil through the roots. The soil not only supports plants and provides an environment for root growth, but also continuously provides nutrients, water and oxygen for crop roots to absorb. The water and dissolved salts maintained in the pores of the soil constitute the soil solution, and the crop roots mainly absorb nutrients from the soil solution. The nutrients in the soil include two major categories: organic and inorganic. They must be decomposed into simple soluble compounds through the action of microorganisms and other factors, and dissolved in soil water before they can be absorbed and utilized by crops. The main source of soil nutrients is supplemented by fertilization. However, fertilization is mainly based on the three elements of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Soil air conditions, microbial activity, soil pH, etc. play an important role in the supply of nutrients to crop roots. Fertilizers applied to the soil have a low utilization rate due to the soil fixing the fertilizers, decomposition and volatilization of the fertilizers, and loss with runoff and infiltration of irrigation water and rainwater. The roots of crops in soilless culture grow in artificially prepared nutrient solutions or solid matrices, which have poor buffering properties. Therefore, they are easily affected by external conditions, such as pH, concentration, and the balance between nutrients, and require higher technology for regulation and management. However, since the nutrient solutions used in soilless culture are all made of soluble inorganic salts, they are easier to be absorbed by crops. It can meet the nutritional needs of crop growth in a timely and effective manner, and can promote rapid crop growth and increase yields, and the utilization rate of fertilizers is also high. Generally, the fertilizer utilization rate of soilless culture can reach more than 90-95%. The products of soilless culture are also more than twice that of soil culture. Soilless cultivation does not have the problems of water leakage and soil runoff like soil cultivation. Therefore, its water utilization rate is much higher than that of soil. Generally, the water consumption of soilless cultivation is only 1/10-1/5 of that of soil.
15.Why is soilless cultivation necessary to have appropriate planting facilities and what do they include?
Soilless cultivation does not use soil, but uses other materials as substrates to replace soil, and supplies nutrient solution containing essential elements at the same time, or does not use any materials as substrates, but only uses nutrient solution. Therefore, appropriate facilities must be taken to replace soil, fix the root system, support the plants, and continuously supply nutrient solution to ensure the crop's demand for nutrients and water and create a rhizosphere environment suitable for root growth and development. Due to the different forms of soilless cultivation, the planting facilities used are also different. At present, deep liquid flow and solid matrix cultivation are mainly used in Guangdong. However, no matter which form of soilless cultivation, it is necessary to have protective facilities such as glass greenhouses and plastic greenhouses, planting troughs, liquid storage tanks, liquid supply pipeline systems and control systems. Planting troughs are used to hold nutrient solution and substrates. To ensure the supply of nutrients and water, and to create a good rhizosphere environment for the growth of crop roots, planting troughs can be made of bricks and cement, or plastic and other materials. The liquid storage tank is a container for storing and supplying nutrient solution. It is made of bricks and concrete, and can also be made of non-toxic plastic containers or other materials. It is required not to leak and not to change the composition of the nutrient solution. The liquid supply system is to transport the nutrient solution from the storage tank to the planting trough to meet the needs of crops. There are two types of nutrient solution supply methods: circulation type and drip irrigation type. Each type consists of a water pump, a liquid supply main pipe, a branch pipe, a water faucet and a dripper or nozzle. The control system monitors and regulates the environmental factors of soilless crops through certain control devices. Domestic devices generally install a timer of appropriate model to control the supply time and interval time of the nutrient solution. The advanced control system uses a computer system to monitor and regulate temperature, light, air, water, fertilizer and the pH value of the nutrient solution.
16.What is deep liquid flow hydroponic technology and what are its characteristics?
Deep liquid flow technology (DFT) refers to a hydroponic technology in which the roots of plants grow in a relatively deep and flowing nutrient solution layer. The planting trough contains a nutrient solution of about 5-10 cm or sometimes even deeper, and the crop roots are placed in it. At the same time, a water pump is used to intermittently open the liquid supply to make the nutrient solution circulate, so as to replenish the oxygen in the nutrient solution and make the nutrients in the nutrient solution more uniform. The deep liquid flow hydroponic facility consists of a planting trough, a planting net or planting plate, a liquid storage tank, a circulation system and other parts. It is the earliest soilless cultivation technology developed for commercial production of agricultural crops. During its development, many countries in the world have made many improvements to it. It is an effective, practical and competitive type of hydroponic production. It is very popular in Japan and has a large area of use in Guangdong Province. It can produce fruits and vegetables such as tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, wax gourds, loofahs, melons, watermelons, and leafy vegetables such as Chinese cabbage, Chinese cabbage, lettuce, water spinach, and chives. It is a hydroponic type that is more suitable for the current national conditions, especially for the tropical and subtropical climate characteristics of the south. Its characteristics are as follows: (1) The liquid layer of the nutrient solution is deeper. The root system extends to a deeper liquid layer, and each plant occupies a larger amount of liquid. Therefore, the concentration of the nutrient solution, dissolved oxygen, pH, temperature and water storage are not prone to sudden changes, providing a relatively stable growth environment for the root system. (2) The plant is suspended on the horizontal surface of the nutrient solution, so that the root neck of the plant is away from the liquid surface, and the extended root system can touch the nutrient solution. Since the root neck is immersed in the nutrient solution, it will rot and cause the death of the plant, so the hanging plant should be done well. (3) The nutrient solution should be circulated. This increases the dissolved oxygen in the nutrient solution and eliminates the local accumulation of harmful metabolic products on the root surface, eliminates the difference in nutrient solution and nutrient concentration between the root surface and outside the root, so that nutrients can be delivered to the root surface in time and more fully meet the needs of the plant.
17.What is nutrient solution membrane core technology and what are its characteristics?
Nutrient film technology, referred to as NFT, was first developed by Cooper of the British Greenhouse Research Institute in 1973. It is a hydroponic method in which plants are planted in a shallow layer of flowing nutrient solution. After 1979, the technology was rapidly promoted worldwide. Grane in the United States, Adams in the United Kingdom, Douglas in India and others have made many improvements in the construction and daily management of nutrient film technology. Traditional soilless cultivation technology requires the setting of a deeper planting trough, and the placement of solid matrix or nutrient solution in the trough to plant crops. The planting trough needs to be made of cement, bricks, wood or metal, which is heavy and expensive, and the oxygen demand of the root system is difficult to solve. In contrast, the nutrient film technology does not use a solid matrix. In the inclined planting trough that requires a certain slope (about 1:75), the nutrient solution only flows through the crop root system in a thin layer of several millimeters deep. Part of the crop root system is immersed in the shallow flowing nutrient solution, and the other part is exposed to the moisture in the planting trough, which can better solve the root system's need for oxygen respiration. The planting troughs of this device are mostly made of plastic film or hard plastic sheet, which makes the structure of the equipment lighter and simpler. Users can design, install and use it by themselves, which greatly reduces the investment cost. However, due to the poor buffering performance of the root environment, the temperature around the rhizosphere is greatly affected by the outside world, and the ground level is strictly required. If the ground is uneven and the slope is different, the nutrient solution flow supply at the bottom of the cultivation trough is uneven, resulting in inconsistent growth between plants and affecting the yield. In addition, since the nutrient solution layer in the planting trough is relatively shallow and the total amount of nutrient solution in the planting system is small, the concentration and composition of the nutrient solution are prone to drastic changes. The liquid needs to be circulated continuously, and the energy consumption is large. If there is a long power outage or a water pump failure, it is easy to cause problems if it cannot be circulated in time. In high temperatures and the peak period of crop production, the plant leaves have a large amount of transpiration and consume a large amount of nutrient solution. Untimely supply can also easily cause the plant to wilt.
18.What is rock wool nutrient solution cultivation technology and what are its characteristics?
The rock wool nutrient solution cultivation technology was first developed by the Danish Grodan Company in 1969. It is a special substrate cultivation method. After the 1980s, it quickly became popular in European countries centered on the Netherlands. In 1986, the planting area of the Netherlands using this technology exceeded 2,000 hectares. Even the United Kingdom, the origin of nutrient film technology, turned to rock wool cultivation. Since then, other countries such as Japan have also adopted rock wool cultivation for soilless cultivation production. At present, the area of rock wool cultivation is not large. Rock wool is a loose and porous solid matrix made by melting a variety of rocks together to form magma, then spraying it into filaments and slightly compressing it after cooling. Because the manufacturing process of rock wool is carried out under high temperature conditions, it is completely sterilized and does not contain pathogens and other organic matter. The pressed rock wool block will not change its shape during the entire growth process of the crop, and the crop roots can easily penetrate it. It is breathable and has good water retention performance. It has a soft and uniform texture, which is conducive to the growth of the crop roots. There are two main types of rock wool cultivation: open rock wool cultivation that uses nutrient solution drip irrigation and does not recycle excess nutrient solution, and circulating rock wool cultivation that recycles nutrient solution. Compared with other solid substrate cultivation and hydroponic methods, the advantages of rock wool cultivation are: (1) It can better utilize the water retention and ventilation characteristics of rock wool to coordinate the relationship between fertilizer, water and air; (2) The device is simple, easy to install and use, and is not restricted by the ground level, power outages, or water outages. (3) It does not spread pests and diseases, and can be used continuously for 1-2 years or reused after disinfection if no serious diseases occur.
19. What is the sand culture nutrient solution drip irrigation technology? What are its characteristics?
Sand culture is a soilless cultivation technology that uses river sand as a growth matrix and supplies nutrient solution for crop growth in the form of drip irrigation. The sand particles for sand culture are preferably in the range of 0.5-3.0 mm in size. It is widely used as a water-saving agriculture in many places, especially in some areas with serious water shortages, such as deserts and semi-desert areas. The facility structure of sand culture includes two parts: planting troughs and drip irrigation systems. Planting troughs include fixed planting troughs and greenhouse full-ground sand culture. At present, fixed planting troughs are mostly used. This planting trough can be made into a V-shape or └┘-shape with bricks or wooden boards, and a layer of plastic film is lined in the trough. In order to facilitate drainage, some coarse gravel can be placed at the bottom of the plastic film, and then sand can be placed in the planting trough. The drip irrigation device consists of capillary tubes, drippers and drippers. Usually each plant has a dripper, so sand culture is more suitable for large-plant crops. In planting management, it is important to ensure that the sand culture is neither too dry nor too wet. Since the buffering capacity of the sand culture substrate is low and open drip irrigation is used for liquid supply, there is not much liquid stored in the substrate and no circulation is performed, so the concentration and acid-base reaction of the nutrient solution stored in the substrate vary greatly. Therefore, when choosing a nutrient solution formula, it is advisable to choose a low-dose formula with a relatively stable physiological response. In addition, the sand needs to be disinfected after each planting. Sand culture has the following characteristics: (1) The nutrient solution cannot be circulated, and the risk of cross-infection of pathogens is low; (2) The sand has a smaller particle size, a larger water holding capacity, and a larger diffusion range. The root system can fully absorb water and fertilizer, and the root system extends horizontally, so the drainage holes are not easily blocked; (3) Fresh nutrient solution is used each time, which better maintains nutrient balance and reduces the trouble of regulating the nutrient solution; (4) Equipment costs are low and management is easier; (5) The water holding capacity is large, so the number of liquid supplies can be less, and 1-2 times a day is sufficient; (6) It is more troublesome to disinfect the sand after each crop; (7) The drip irrigation system emitters are easily blocked; (8) The amount of water and fertilizer used is high, the absorption and utilization rate is not high, and salt accumulation is easy to occur.
20.What is mixed matrix nutrient solution drip irrigation technology? What are its characteristics?
Solid matrix can be divided into inorganic matrix and organic matrix as the material of matrix culture. The performance of the material has a great influence on the growth of crops, and the requirements for management technology are also different. For example, the water retention, permeability and buffering effect of the matrix are all related to the physical and chemical properties of the matrix. Therefore, before use, we should have a more specific understanding of the various physical and chemical properties of the matrix. For example, inorganic matrices such as bark and gravel have good functions of fixing, supporting and anchoring plants and good air permeability, but poor water retention and buffering effects, while organic matrices such as bark, sawdust, bagasse, peat, etc. have poor functions of fixing and supporting and anchoring plants, but good water retention and buffering effects. In order to overcome the disadvantages of single matrix such as too light or too heavy bulk density, poor ventilation or excessive ventilation, several matrices are often mixed to form a composite matrix for use. Generally, when preparing the composite matrix, it is best to mix two or three matrices. At present, in the matrix culture in Guangdong, many mixed matrices are used for soilless cultivation, and their cultivation facilities are similar to those of sand culture nutrient solution drip irrigation. The materials used also vary according to the requirements of the crops planted and the sources of the materials. Based on the principle of economy and practicality, they are prepared by yourself. For example, the bagasse mineral composite matrix developed by the Soilless Culture Technology Research Laboratory of South China Agricultural University is a mixture of 50-70% bagasse, sawdust, coconut bran, etc. and 30-50% sand, gravel or coal slag. It has an appropriate bulk density, a reasonable ratio of large and small pores, good water retention and ventilation, and has good effects whether it is seedling cultivation or full-term growth.
21. Why is nutrient solution the core of soilless cultivation technology?
The nutrients required by crops in soilless culture are generally not supplied by applying solid fertilizers, but by nutrient solutions. The so-called nutrient solution is a solution containing the nutrients necessary for plants, artificially prepared in a certain amount and proportion using inorganic salt fertilizers according to the demand characteristics of different crops for various nutrients and the characteristics of fertilizer absorption. Whether it is hydroponics or substrate culture, nutrient solution is needed to provide nutrients to crops. Therefore, nutrient solution is the core of soilless culture technology. Only by understanding and mastering it can we truly master soilless culture technology and use nutrient solution flexibly and correctly to achieve good results. When using nutrient solution, it is necessary to understand the types, quantities, and ratios of nutrients contained in the nutrient solution, as well as the solubility of various fertilizers and the pH of the nutrient solution, which are factors that affect the absorption of nutrients by crops, so as to timely and effectively provide the nutrients required for crop growth according to various crop varieties and different growth periods of various crops, so as to reduce costs, increase yields, and improve economic benefits. Therefore, nutrient solution management is the key to soilless culture technology. Only by mastering it skillfully can the level and economic benefits of soilless culture be improved.
22.How to determine and select the nutrient solution formula?
(1) The relationship between root absorption of mineral elements and absorption of water. Mineral elements can only be absorbed by plants when dissolved in water. Water directly affects the absorption and transportation of mineral elements, but the two are not in direct proportion and each has relative independence.
(2) Plant roots have the characteristic of selective absorption of mineral elements. The amount of salt ions absorbed by the roots is not proportional to the ions in the solution. Even the anions and cations of the same salt enter the plant body in different proportions, causing the composition and pH of the nutrient solution to gradually change. (3) Antagonism between single salt toxic ions. Any plant cannot grow in a nutrient solution containing a single salt, which is called single salt toxicity. If a small amount of other salts is added to it, the single salt toxicity can be eliminated. This phenomenon that ions can eliminate each other's toxicity is called antagonism. Therefore, when determining and selecting the nutrient solution formula, the nutrient solution formula should be selected according to the characteristics of different species. Now, there are a wide variety of nutrient solution formulas for people to choose from.
23.What are the requirements for nutrient solution for soilless cultivation?
(1) It must contain all the nutrients necessary for crop growth and development, including macroelements and trace elements.
(2) These mineral elements should be mixed into a balanced nutrient solution in appropriate proportions according to the needs of different crops.
(3) The prepared inorganic salts should have high solubility in water and be in ionic state, which can be easily absorbed by crops.
(4) It should not contain harmful or toxic ingredients, and maintain a pH and ion concentration suitable for root growth and conducive to nutrient absorption. (
5) The application effect should be good, enabling crops to grow well and to obtain high quality and high yield. (6
) It should be easy to obtain materials, with small amounts and low costs.
Therefore, in order to prepare a nutrient solution that meets the requirements, its raw materials, including water sources, compounds containing nutrient elements and auxiliary substances, should meet the requirements. First of all, the water quality requirements, the water used in production usually comes from rainwater, well water and tap water, etc., and its general requirements are equivalent to drinking water that meets hygienic standards. The main thing is that the hardness cannot be too high. Generally, it is appropriate not to exceed 10 degrees, the pH value is between 6.5-8.5, the sodium chloride content is less than 2 mmol/L, and the content of heavy metals such as mercury, cadmium, lead, etc. and elements that are harmful to health are within the allowable range. For the requirements of inorganic salt compounds, since the dosage indicated in the nutrient solution formula is expressed as pure products, when preparing the nutrient solution, the dosage of the raw materials should be calculated according to the actual purity of the raw materials of various compounds. Raw materials with unclear commodity labels and unclear technical parameters are prohibited. If a large number of raw materials purchased lack technical parameters, samples should be taken for inspection and only allowed to be used when confirmed to be harmless. In addition, the purity of the raw materials must meet the requirements, and a small amount of harmful elements should not exceed the allowable limit. Otherwise, it will affect the balance of the nutrient solution.
24.What should we pay attention to when preparing nutrient solution?
When preparing nutrient solution, care should be taken to avoid the precipitation of insoluble substances. A nutrient solution prepared with a qualified balanced nutrient solution formula should not produce precipitation of insoluble substances, but any nutrient solution formula must have the possibility of producing precipitation of insoluble substances. Because the nutrient solution must contain cations such as calcium, magnesium, iron, and manganese and anions such as phosphate and sulfate, if the preparation process is well controlled, no precipitation will occur, but if it is not well controlled, precipitation may occur. The concentration product law of insoluble electrolytes should be used as a guide during preparation to avoid precipitation. For this reason, when preparing concentrated stock solutions or working nutrient solutions, the order of mixing and dissolving fertilizers should be strictly followed. Calcium ions and sulfate ions and phosphate ions should be separated, that is, calcium nitrate cannot be mixed with sulfates such as magnesium sulfate and phosphates such as potassium dihydrogen phosphate to avoid the precipitation of calcium sulfate or calcium phosphate. If concentrated stock solutions are prepared, they are generally divided into three types: A, B, and C, called A mother solution, B mother solution, and C mother solution. A mother solution is centered on calcium salts, and all salts that do not react with calcium to produce precipitation can be put together. The B mother liquor is centered on phosphates, and anything that does not form a precipitate with phosphate can be put together. The C mother liquor is prepared by combining iron and trace elements; because of its small dosage, it can be prepared into a mother liquor with a very high concentration multiple. The concentration multiple of the mother liquor should be based on not being oversaturated and precipitating, and it is better to prepare an integer multiple for easy operation. If the mother liquor needs to be stored for a long time, it should be acidified to prevent precipitation. The mother liquor should be stored in a dark container. When preparing the working nutrient solution with concentrated stock solution, the three stock solutions A, B, and C must be diluted before adding, and the speed of addition should be slow. After adding one stock solution, it must be circulated for a period of time before adding another stock solution. If the working nutrient solution is prepared by directly weighing the fertilizer and dissolving it in the planting system, about 70% to 80% of clean water should be added to the planting system before adding the dissolved fertilizer. Moreover, each type of fertilizer should be diluted before adding it, and after adding it, it should be circulated for a period of time before adding another type of fertilizer to avoid precipitation. In addition, when weighing and preparing fertilizers, attention should be paid to the consistency between the name and the actual situation to prevent weighing the wrong fertilizer, and repeated checks should be made to confirm that they are correct before preparation. At the same time, detailed records should be filled out.
25.What are the fertilizers that can be used as nitrogen sources for soilless cultivation?
Nitrogen mainly includes nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen. The fertilizers include calcium nitrate, which contains 4 crystal waters, is a white small crystal solid, easily soluble in water, easy to absorb moisture, and should be stored dry. The acidity and alkalinity are chemically neutral and physiologically alkaline. It contains 11.86% nitrate nitrogen and calcium required by plants. Potassium nitrate is a white small crystal solid with a molecular weight of 101.10 and contains 13.85% nitrate nitrogen. It is a chemically neutral compound with physiological weak alkalinity and a solubility of 31.6 grams/100 grams of water at 20 degrees Celsius. Potassium nitrate is a strong oxidant that can explode when exposed to fire and is often easily damp and agglomerated. Safety should be paid attention to during storage and transportation. Ammonium nitrate is a white small crystal solid with a molecular weight of 80.05. It contains nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen at the same time. The total nitrogen content is 35%, of which ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen each account for half. It is chemically hydrolyzed acidic and physiologically acidic. Sodium nitrate is a white small crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 5.01 and contains 16.5% nitrate nitrogen. It is chemically neutral and physiologically strongly alkaline. Ammonium sulfate has a molecular weight of 132.15, is easily soluble in water, contains 21.20% ammonium nitrogen, is a white small crystalline solid, is chemically hydrolyzed acidic, and is physiologically strongly acidic. Ammonium chloride is a white small crystalline solid with 37.2% ammonium nitrogen, is chemically hydrolyzed acidic, and is physiologically strongly acidic. Urea is a white small crystalline solid with 46.64% nitrogen, which is easily soluble in water, chemically neutral, and physiologically acidic. Monoammonium phosphate is a grayish white powder with 12.18% nitrogen. It is chemically hydrolyzed acidic, and the physiological acidity and alkalinity are not obvious. It can also provide phosphorus nutrition. Diammonium phosphate is a grayish white powder with 21.22% nitrogen. It is easily soluble in water, chemically hydrolyzed alkaline, and the physiological acidity and alkalinity are not obvious. In soilless cultivation production, the most commonly used fertilizers include calcium nitrate, potassium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, and diammonium phosphate. Nitrate nitrogen is more commonly used because nitrate nitrogen is mostly physiologically alkaline, and the physiological alkalinity caused by nitrate nitrogen changes in a small range and is easy to control; while ammonium nitrogen produces stronger physiological acidity, changes more drastically, and is difficult to control. However, nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen sources have the same nutritional effects. In production, as long as appropriate measures are taken to overcome the adverse effects of their physiological acid-base properties, both can be used as nitrogen sources.
26.What are the phosphorus fertilizers for soilless cultivation?
In addition to potassium dihydrogen phosphate, phosphorus source fertilizers in soilless cultivation can also use ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, diammonium hydrogen phosphate and superphosphate. The molecular weight of potassium dihydrogen phosphate is 136.09, and the pure product contains 22.76% phosphorus and 28.73% potassium. It is white crystal or powder, stable in nature and easily soluble in water. It can provide both phosphorus and potassium, and is a high-quality phosphorus-potassium compound fertilizer. The molecular weight of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate is 115.05, and it is a gray-white powder with a nitrogen content of 12.18% and a phosphorus content of 26.92%. The molecular weight of diammonium hydrogen phosphate is 132.07, and it is a gray-white powder with a nitrogen content of 21.22% and a phosphorus content of 23.45%. The general fertilizer ammonium phosphate is a mixture of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and diammonium hydrogen phosphate. Its nitrogen and phosphorus content should be understood before use. Superphosphate is a gray granule or powder, which is made by adding sulfuric acid to phosphate rock powder and dissolving it. Its effective phosphorus-containing component is monocalcium phosphate, which is easily soluble in water. However, since superphosphate contains insoluble calcium sulfate and a large amount of free sulfuric acid, it is rarely used directly in the preparation of nutrient solution and is generally only applied directly to the substrate.
27. What are the potassium, calcium and magnesium fertilizers for soilless cultivation? What are their characteristics?
Commonly used potassium fertilizers include potassium nitrate, potassium sulfate, potassium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate. Potassium nitrate is a white small crystal solid with a solubility of
28. What fertilizer is the source of iron in soilless cultivation? Why is it necessary to chelate the iron?
In the early days of soilless cultivation, the iron source was inorganic salts such as ferrous sulfate and ferric chloride. The molecular weight of ferric chloride is
29.What kinds of fertilizers are used for trace elements in soilless cultivation?
The so-called trace elements are classified according to the content level in plants, generally those with an average content of less than one thousandth. Among the 16 essential nutrients for plants, 7 are trace elements, namely chlorine, iron, boron, manganese, zinc, copper, and molybdenum. Since the special performance of iron has been mentioned, and chlorine has a wide range of allowable existence, there is enough chlorine in the production water for plant growth, so it is not specially added. Therefore, the trace elements usually mentioned refer to boron, manganese, zinc, copper, and molybdenum. Boron fertilizers are mostly made of boric acid or borax. Boric acid is the main source, containing 17.48% boron, with a molecular weight of 61.83. It is a colorless or white crystalline powder, easily soluble in hot water, and presents a colorless aqueous solution. Borax is another boron source fertilizer, containing 11.34% boron, in a colorless or white crystalline state, easily soluble in water for plant absorption and utilization. Manganese fertilizer uses manganese sulfate as the main source of manganese, containing 23.5% manganese, in the form of pink crystals, with a solubility of 62% per 100 grams of water at 20 degrees Celsius, and hydrolysis is acidic. Zinc sulfate is the main source of zinc in soilless cultivation, containing 22.74% zinc, in the form of colorless or white crystalline particles or powder, which is very soluble in water and hydrolyzed in acid. Copper fertilizer uses copper sulfate, containing 5 crystal waters, as the main source of copper for soilless crops, containing 25.45% copper, in the form of blue crystalline substances, with a solubility of 20.7 grams per 100 grams of water at 20 degrees Celsius. Ammonium molybdate is the main source of molybdenum fertilizer in soilless cultivation, containing 4 crystal waters and 54.3% molybdenum, in the form of white, colorless, light yellow or light green crystalline particles or powder, which is easily soluble in water. In addition, sodium molybdate can also be used as a source of molybdenum fertilizer, containing 39% molybdenum, in the form of white powder, which is easily soluble in water.
30.How is the concentration of nutrient solution expressed?
(1) The weight of a certain compound contained in each liter of solution. The weight unit can be expressed in grams or milligrams. For example, each liter of nutrient solution contains 0.81 grams (or 810 milligrams) of potassium nitrate. This expression is usually called working concentration or operating concentration. The specific preparation is carried out according to this method.
(2) The weight of a certain nutrient element contained in each liter of solution. The weight unit is usually expressed in milligrams, such as 210 milligrams of nitrogen per liter. Using element weight to express concentration is a need for scientific research comparison and cannot be used for direct operation.
(3) The number of moles of a substance contained in each liter of solution. A substance can be an element, molecule or ion. Mole represents the amount of a substance, and its value is equal to the atomic weight or molecular weight or ionic weight of a substance.
Using moles to express concentration helps to understand the exact chemical composition of the solution, but it cannot be operated directly and needs to be converted before weighing and preparing. There are two indirect expression methods:
(1) Electrical conductivity method (EC). The water-soluble inorganic salts usually used to prepare nutrient solutions are strong electrolytes. Their aqueous solutions have conductive properties. The strength of the conductivity can be expressed by conductivity. Within a certain concentration range, the salt content of the solution, that is, the concentration, is closely positively correlated with the conductivity. The higher the salt content, the greater the conductivity of the solution. Therefore, the conductivity of the nutrient solution can reflect the salt content in the solution, but the conductivity only reflects the total salt concentration of various salts in the nutrient solution and cannot reflect the individual concentrations of various salts. However, this can meet the needs of controlling the nutrient solution in soilless cultivation and is currently the most commonly used measurement method in production.
(2) Osmotic pressure is the water pressure generated when two solutions of different concentrations are separated by a semipermeable membrane. Water generates pressure when it passes through a semipermeable membrane from a solution with low concentration to a solution with high concentration. The higher the concentration of the solution, the greater the osmotic pressure. The unit of osmotic pressure is usually expressed in Pa. 270.30, containing 20.66% iron, in the form of yellow-brown or orange-yellow block crystals, with a slight smell of hydrochloric acid, very easy to deliquesce in the air, and easily soluble in water. Ferrous sulfate, commonly known as green vitriol, can provide iron and sulfur, containing 20.09% iron, in the form of blue-green crystals, with unstable properties, easy to lose water and oxidize to brown iron sulfate, and even more unstable under high temperature and strong light or in the presence of alkaline substances. Since ferrous sulfate is a by-product of some industries, it has a wide source and is cheap. It is an important iron source for soilless crops and a raw material for making other iron fertilizers such as ammonium ferrous sulfate and chelated iron. Since inorganic iron salts such as ferric chloride and ferrous sulfate can easily become ferric phosphate or ferric hydroxide precipitation and become ineffective when the alkalinity is high, and can even be oxidized into basic salt precipitation under neutral conditions, and low-valent ferrous sulfate can be easily oxidized into high-valent iron by oxygen in the air and become ineffective, often causing iron deficiency in plants, the iron salts in cultivation were later changed to organic acid iron, such as ferric citrate and ferric tartaric acid. Although these compounds are more effective than ferric chloride and ferrous sulfate, they are very unstable, so their effects are not ideal. With the development of modern chemical science, it is clear that organic compounds that can form chelate rings can be used to react with iron or chelate iron. This type of chelated iron is used as an iron source in soilless culture nutrient solution, and the effect is very good, so it is now used to replace the inorganic iron salts and organic acid iron used initially. Iron chelate is a light brown or dark brown powdery substance. In the soilless culture nutrient solution, iron can form stable compounds and can maintain its effectiveness for a long time. The main iron chelates include disodium iron ethylenediaminetetraacetate (Na 2 FeEDTA), disodium iron diethylenetriaminepentaacetate (Na 2 FeDTPA) and many others. Since disodium iron ethylenediaminetetraacetate is cheap and has good stability, disodium iron ethylenediaminetetraacetate is the most commonly used one. When preparing, ferrous sulfate and disodium iron ethylenediaminetetraacetate are dissolved separately before mixing them together for chelation. 31.6%, chemically neutral salt, physiologically weak alkalinity. Potassium sulfate is a white small crystalline solid with a solubility of 11.1%, chemically neutral, and physiologically strongly acidic. Potassium chloride is a white small crystalline solid with a solubility of 34%, chemically neutral, and physiologically strongly acidic. Potassium dihydrogen phosphate is a white small crystalline solid with a solubility of 22.6%, chemically hydrolyzed acidic, and physiologically neutral. Calcium source fertilizers generally use calcium nitrate, calcium chloride, calcium sulfate, and superphosphate. Calcium nitrate is a white small crystal solid, containing four crystal waters, easily soluble in water, with a solubility of 129.3%, chemically neutral salt, physiologically alkaline, and a calcium content of 16.97%. Calcium chloride is a white small crystal solid, with a solubility of 74.5%, chemically neutral salt, and physiologically acidic. Calcium sulfate is a white powder with a very low solubility of 0.204%, a chemically neutral salt, and physiologically acidic. Superphosphate is a gray powder with strong chemical acidity. It is rarely used directly in nutrient solution formulas, but is mostly directly mixed into the matrix. Magnesium fertilizer is mainly magnesium sulfate, which contains 7 crystal waters, is a white small crystal solid, has a solubility of 35.5%, is chemically neutral in acidity and alkalinity, and is physiologically acidic, and contains 9.86% magnesium.