Plant Tips | Landscape Lawn Design and Technology

Application Examples
01
Residential Area Application Examples
In residential landscapes, the functions of lawns are mainly for recreation, appreciation, and exercise. They are often important places and spaces for people to relax, socialize, and interact.
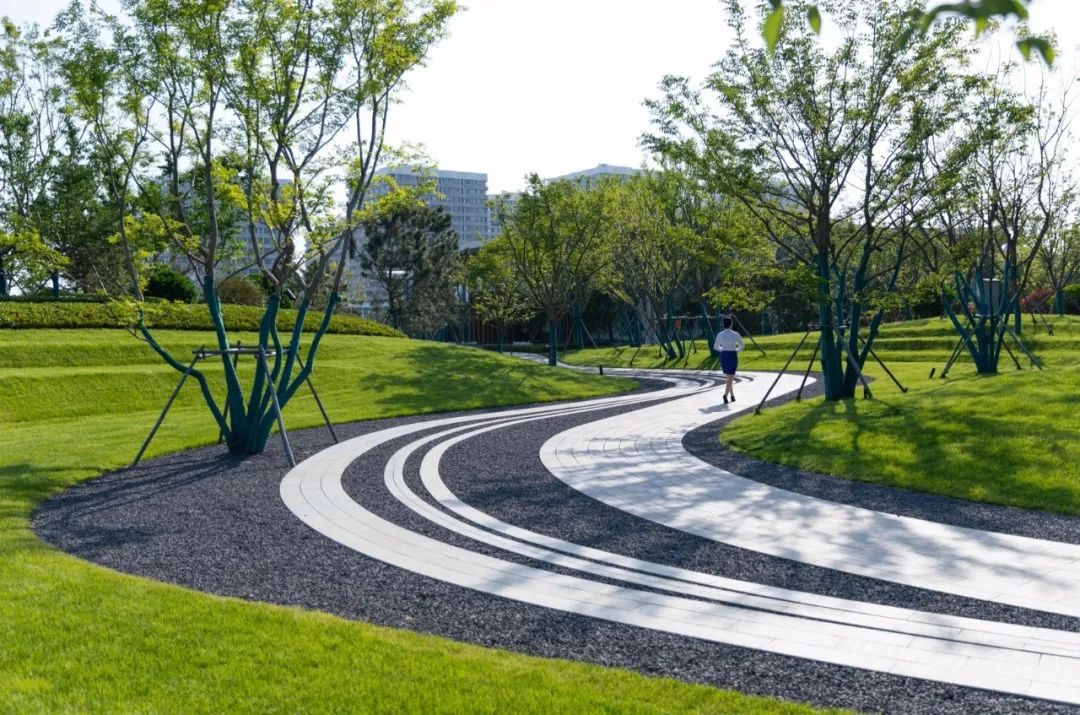
1. Layout of the lawn: There should be a resting platform around it , and the viewing angle on the platform should preferably correspond to a sunny lawn. A sunny lawn often has a main viewing point at or near its golden section point, which can be a main tree, a public artwork, or a terrain landscape. In short, a visual focus is needed.
2. Classification by form : generally divided into regular lawns and natural lawns .
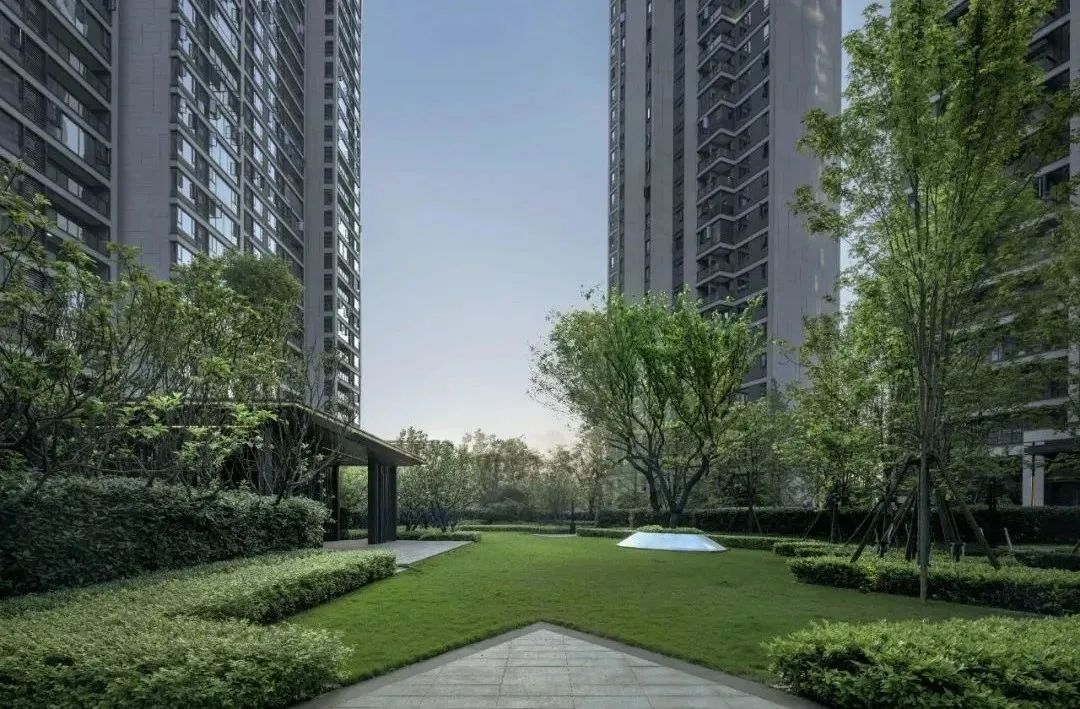
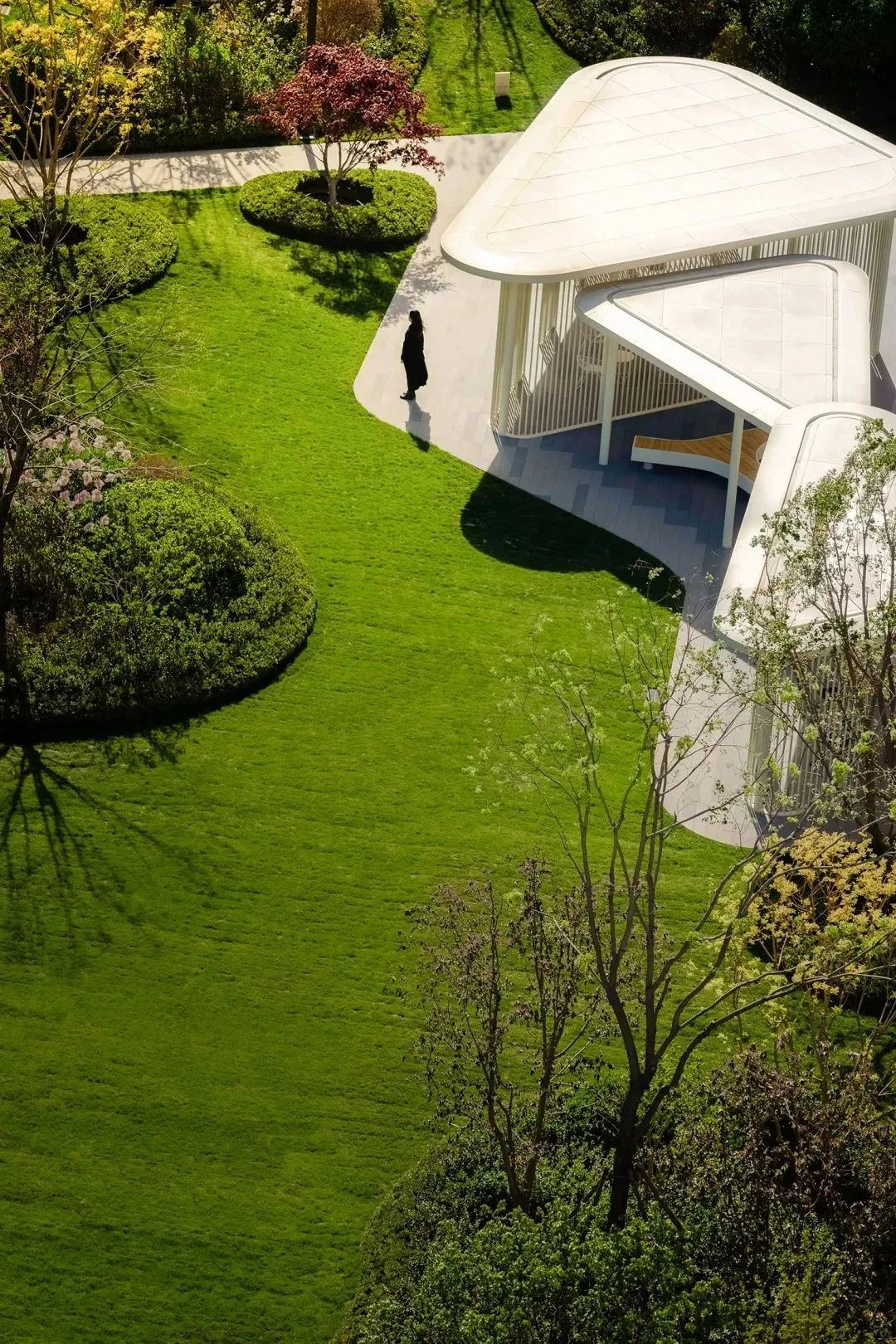




3. The lawn as the background, whether in regular layout or natural layout, is very well integrated with other scenery that constitute the overall landscape, and plays a role of contrast and harmony.
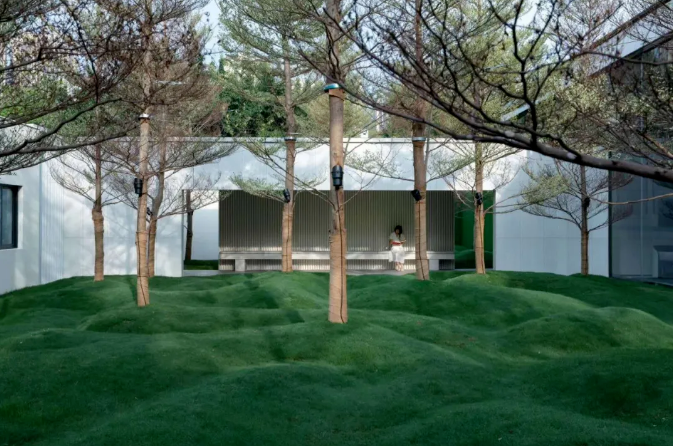
3-1. Lawns and other plants
1) Taking landscape psychology into full consideration, the ratio of lawn width to surrounding tree height should not exceed 10. In this case, tourists’ vertical viewing angle will be more comfortable and the aesthetic effect will be better.
2) The proportion of open lawns in large areas should not be too high. There should be a reasonable ratio between open lawns, sparse forest lawns, and dense forest lawns, generally controlled at 2:4:4, so that various planting types can be maintained in relative balance.
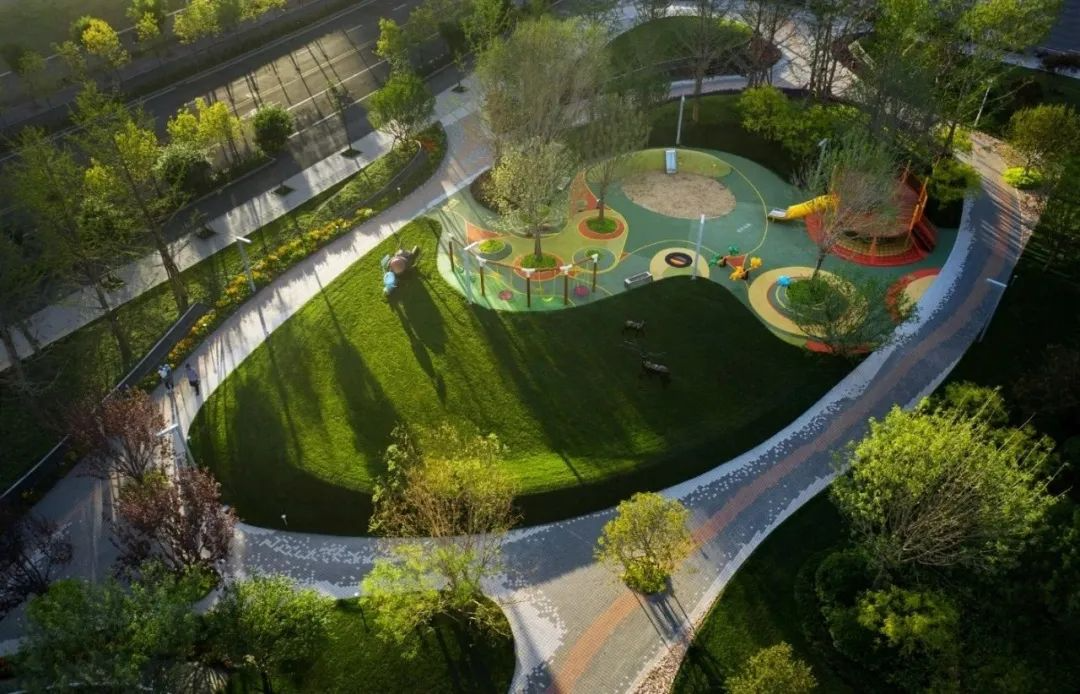
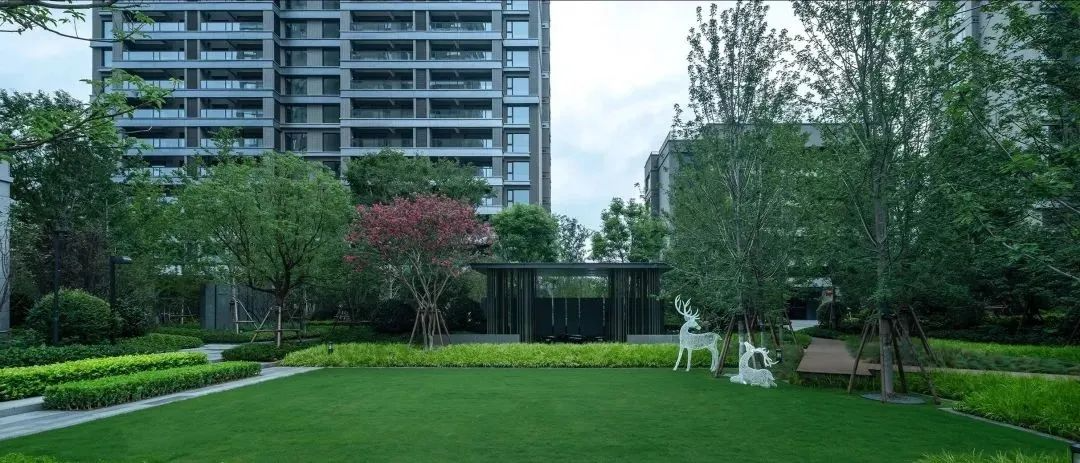
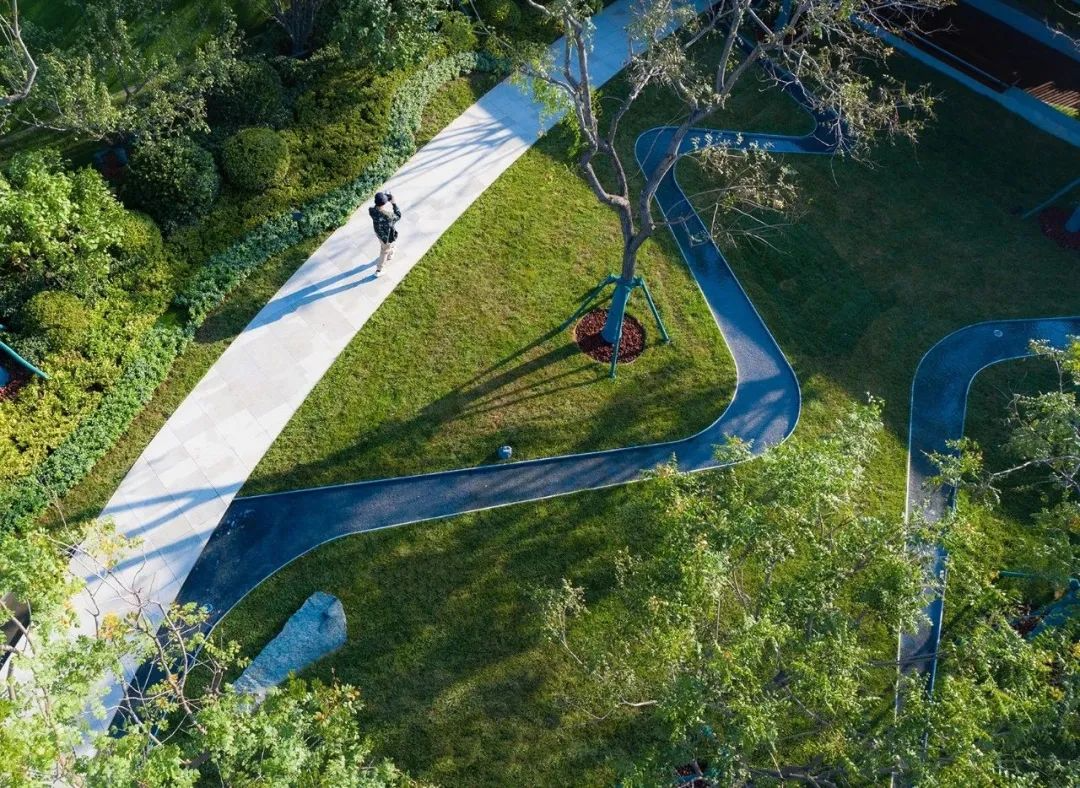




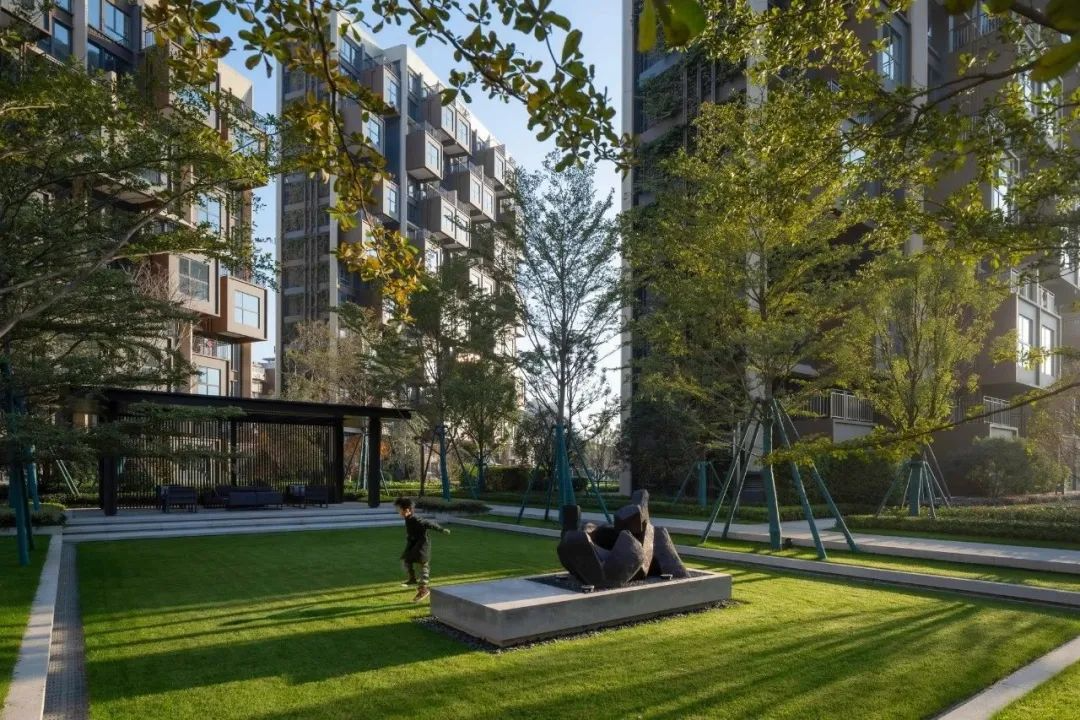
3-2. Lawns and landscape sketches
Dotting the lawn with small landscape pieces can appropriately increase the interest and interactivity of the landscape.
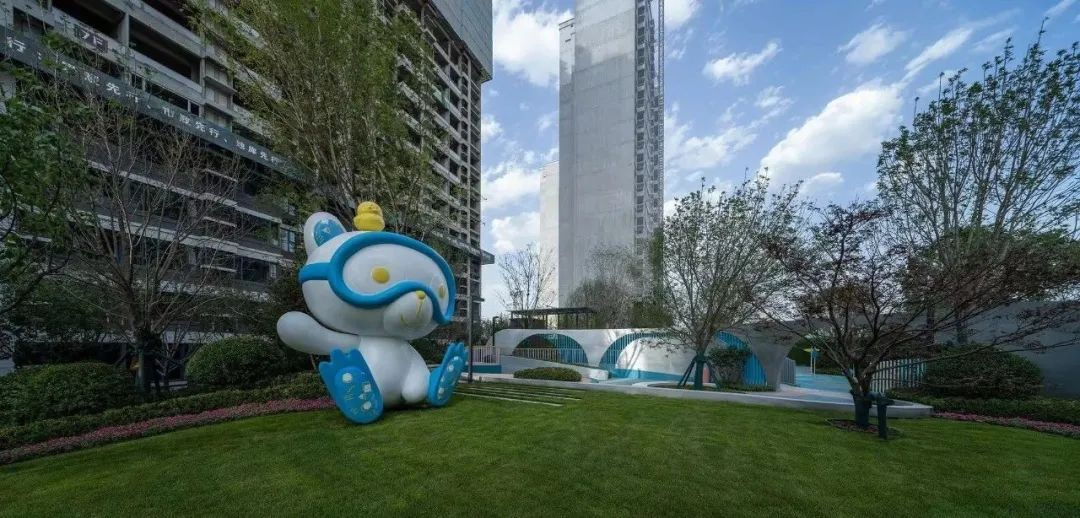
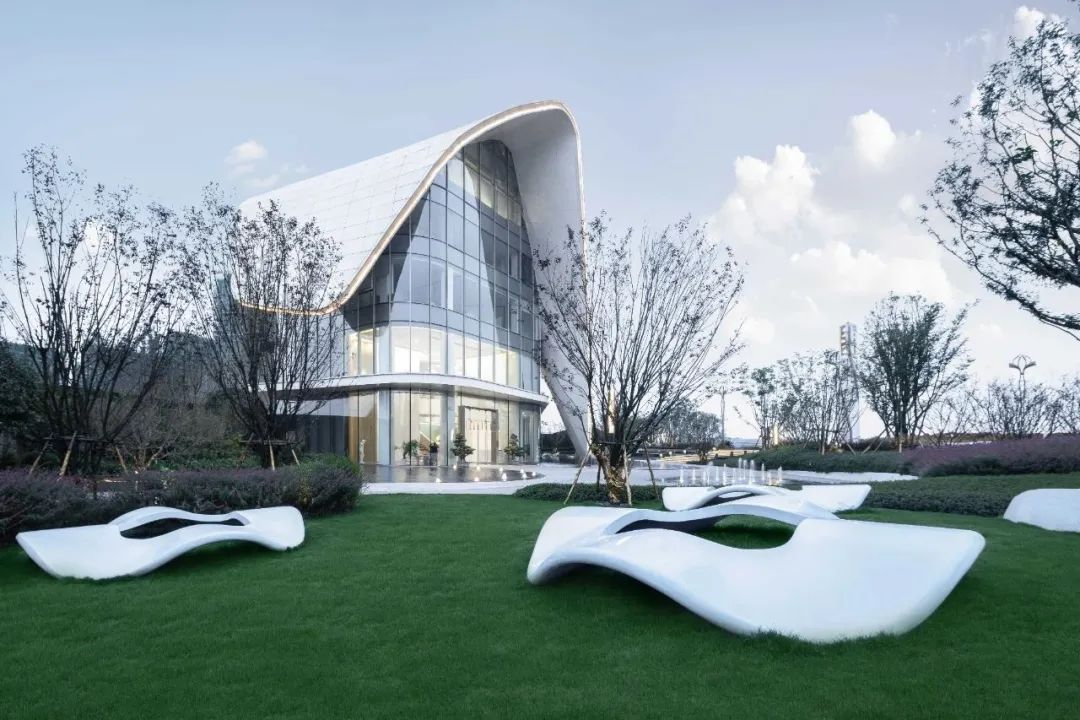
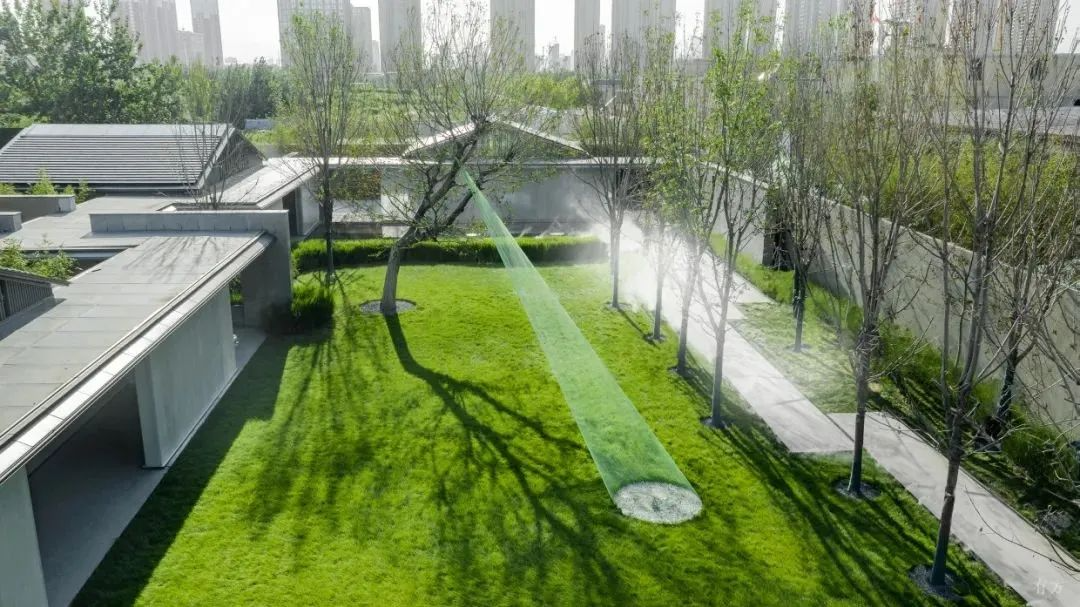
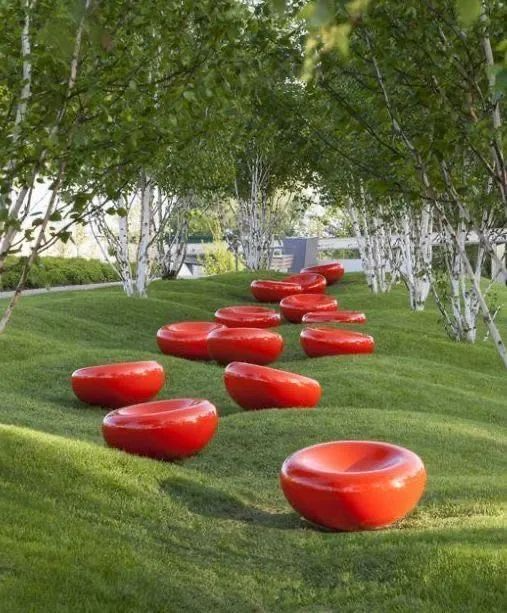




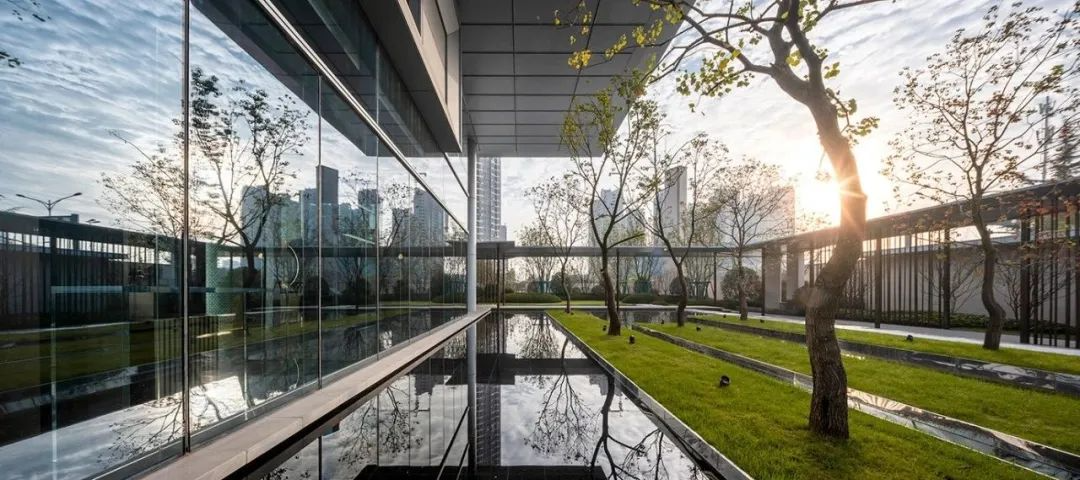
3-3. Lawn and waterscape
The contrast between stillness and movement highlights the artistic conception of "the mountain becomes more secluded when birds sing", which not only adds to the artistic beauty of the garden, but also adds a unique poetic and picturesque feeling.
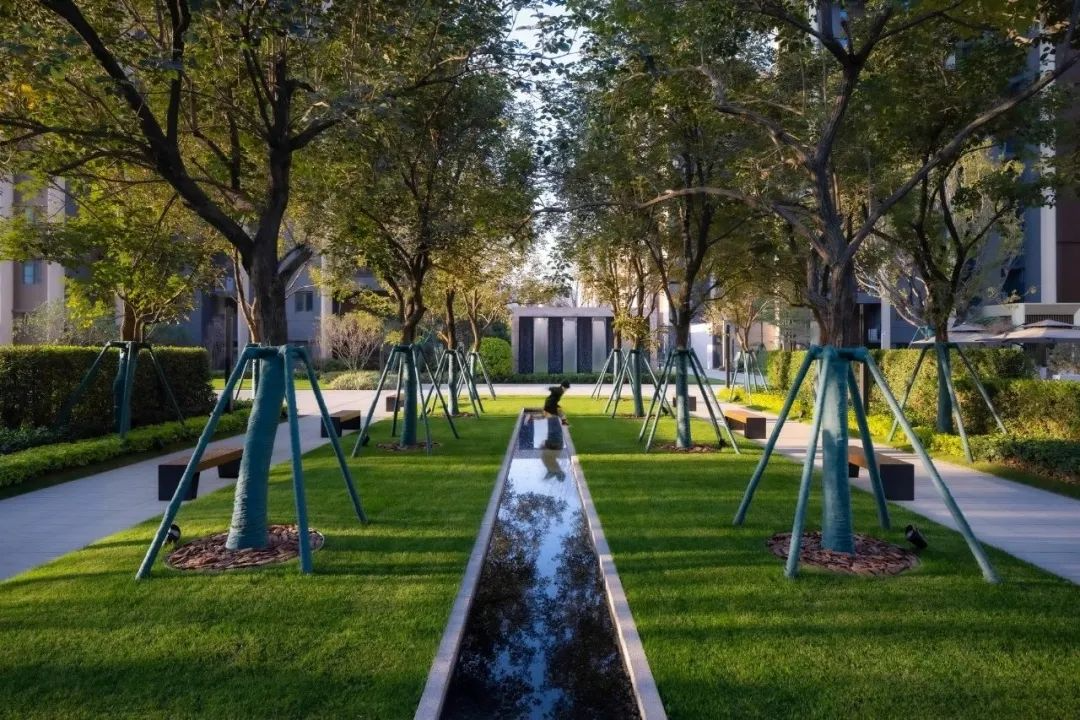



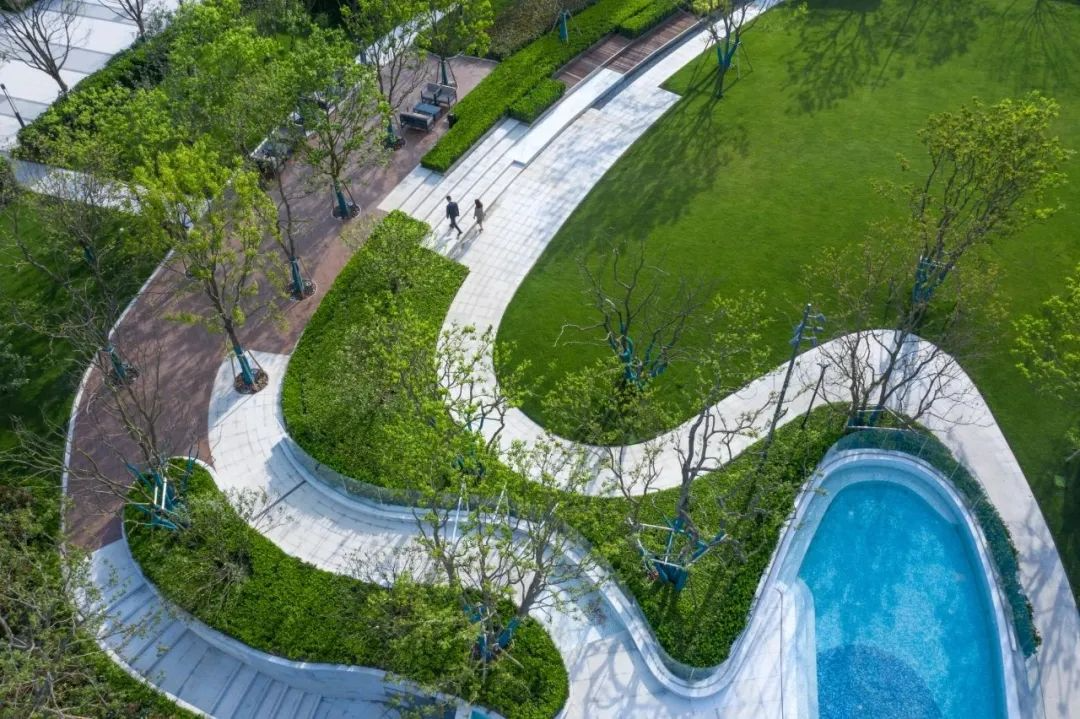
3-4. Lawn and Paving
In road greening, stones are embedded on the grass or grass is embedded in the cracks between the stones. The contrast between the light-colored stones and the lawn can enhance the visual effect.
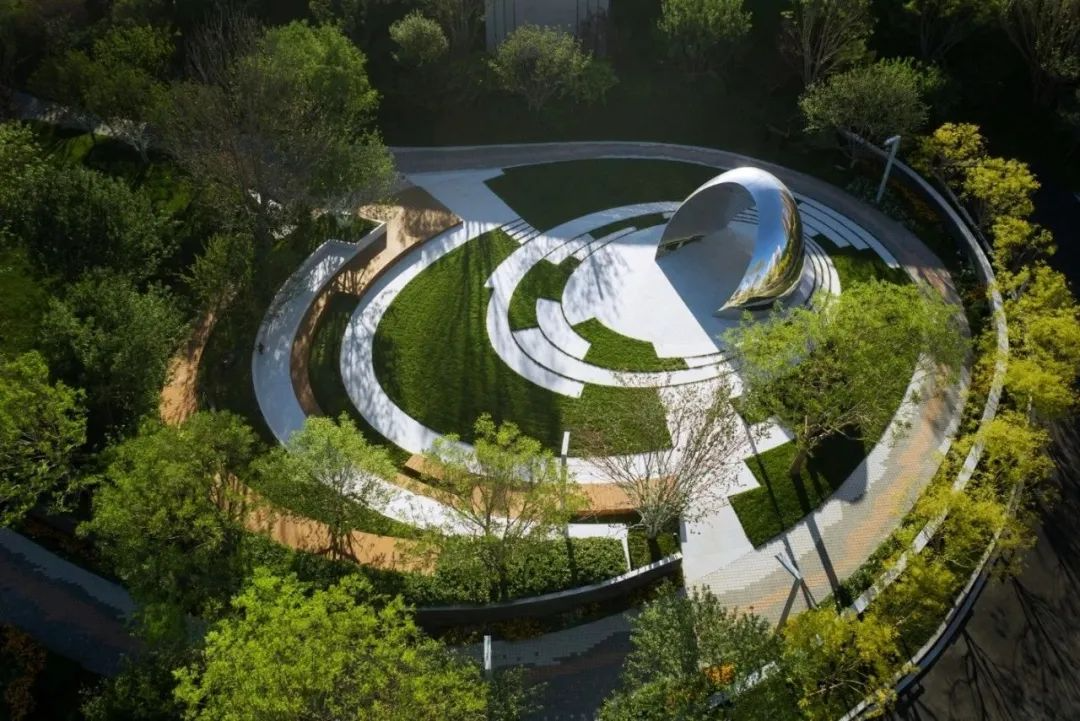
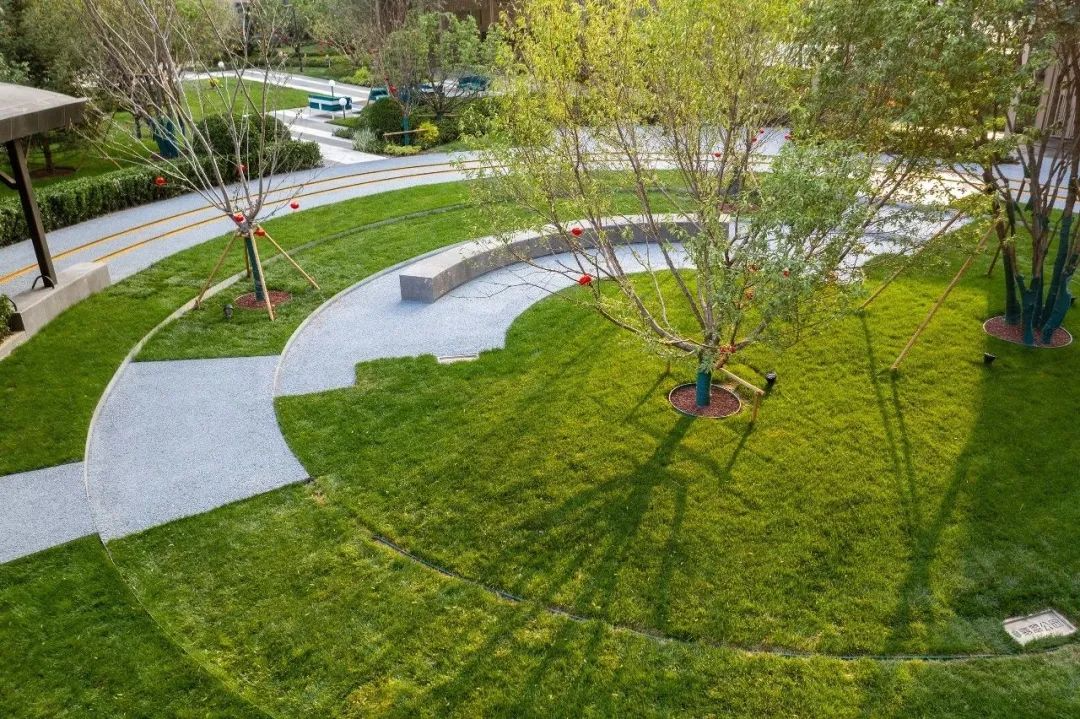
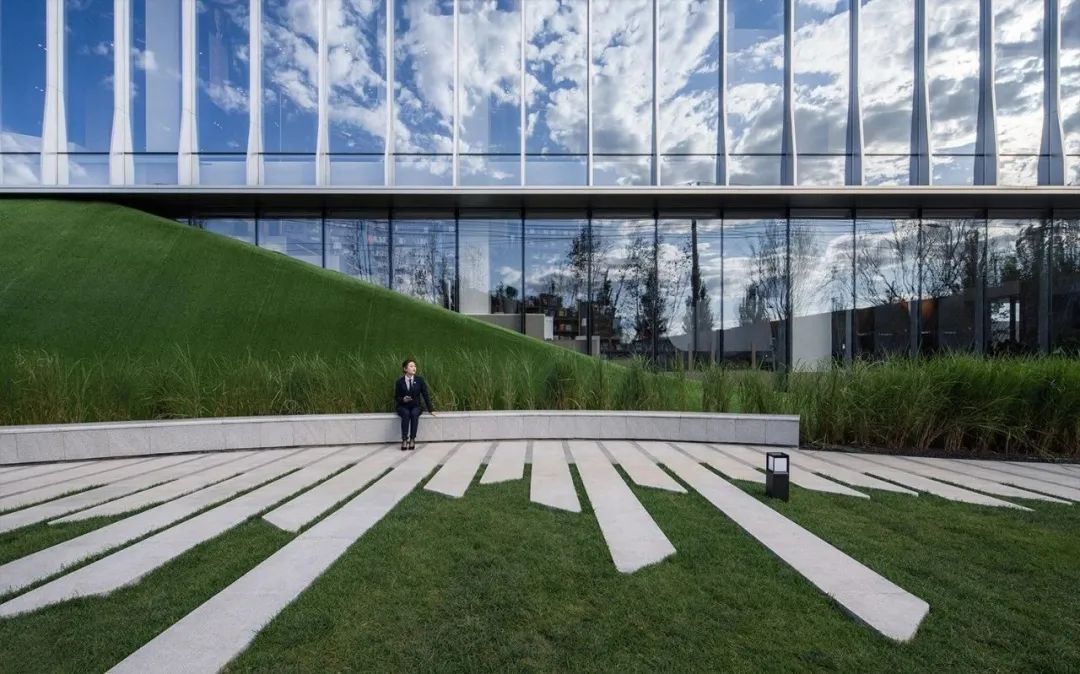



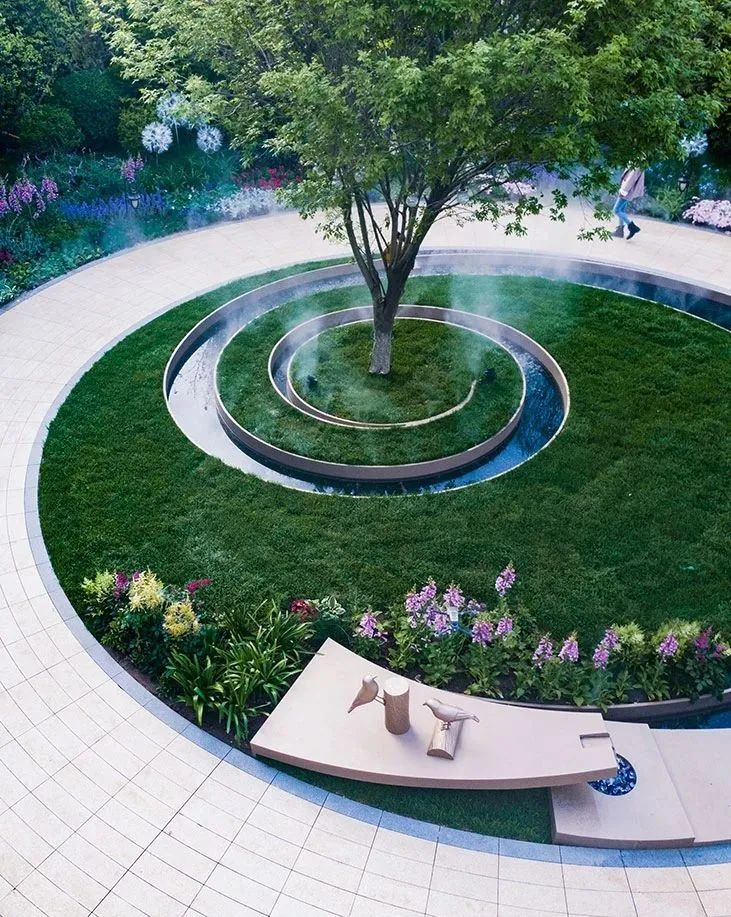
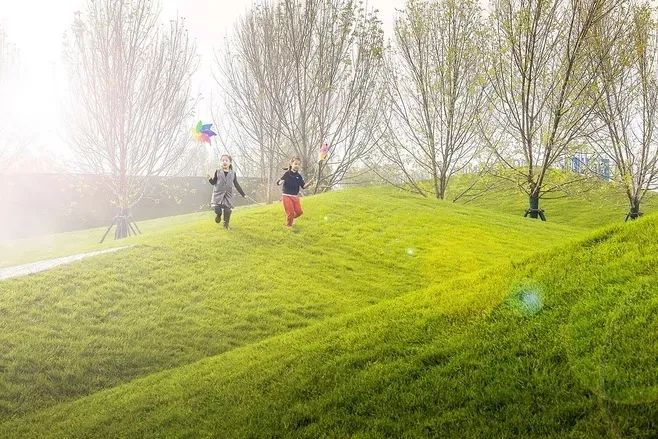
3-5. Lawn and terrain
Using the site as paper and the lawn as color, we can create an amazing landscape effect. With proper composition, we can achieve a landscape space that combines impact and interest.
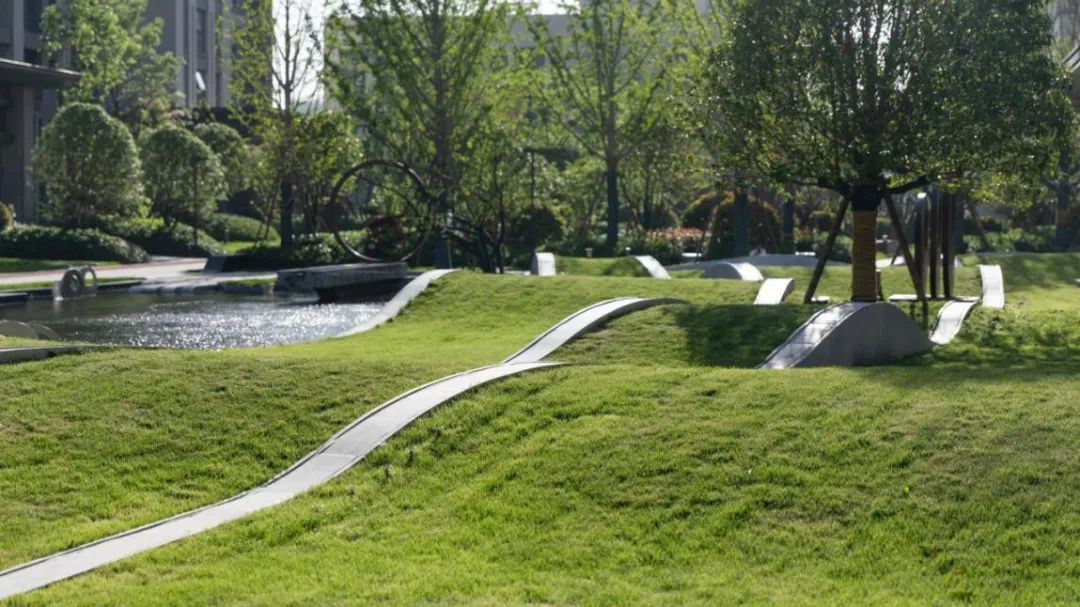




02
Public landscape application examples
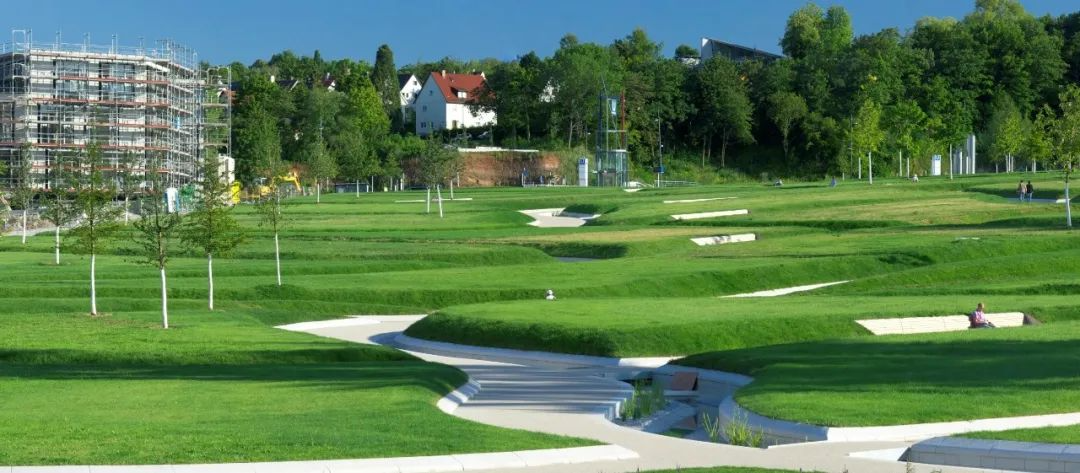
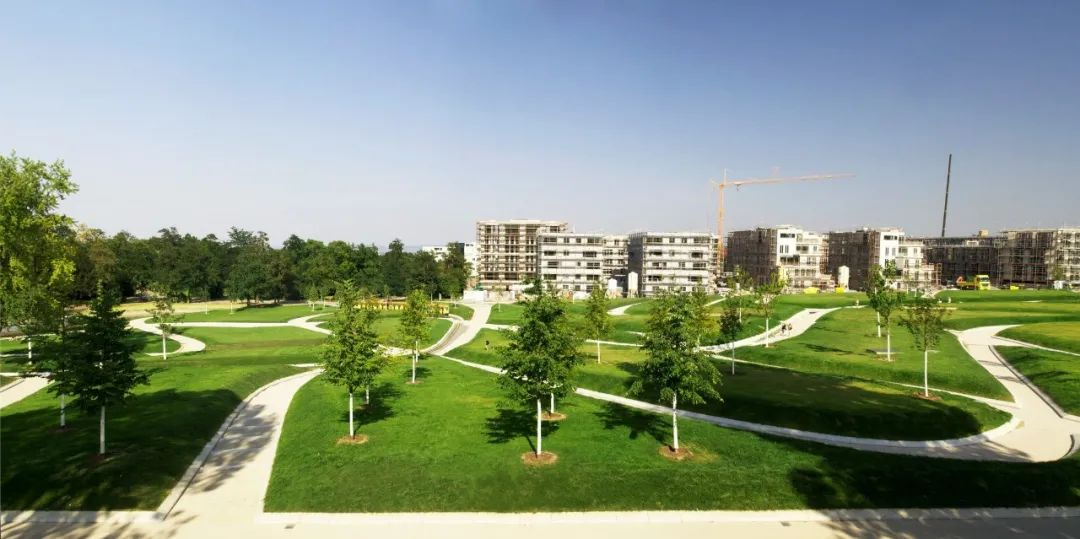
In addition to residential landscapes, lawns are also often used in public landscapes such as parks, schools, and commercial offices. The lawns in such landscapes are generally large in area, creating an open and "breathable" space, and are often designed in combination with terrain. In addition to viewing, lawns are often used as venues for sports, exhibitions, picnics, music festivals, and other activities.
1. Killesberg Park


2. Optus Office Centre Courtyard
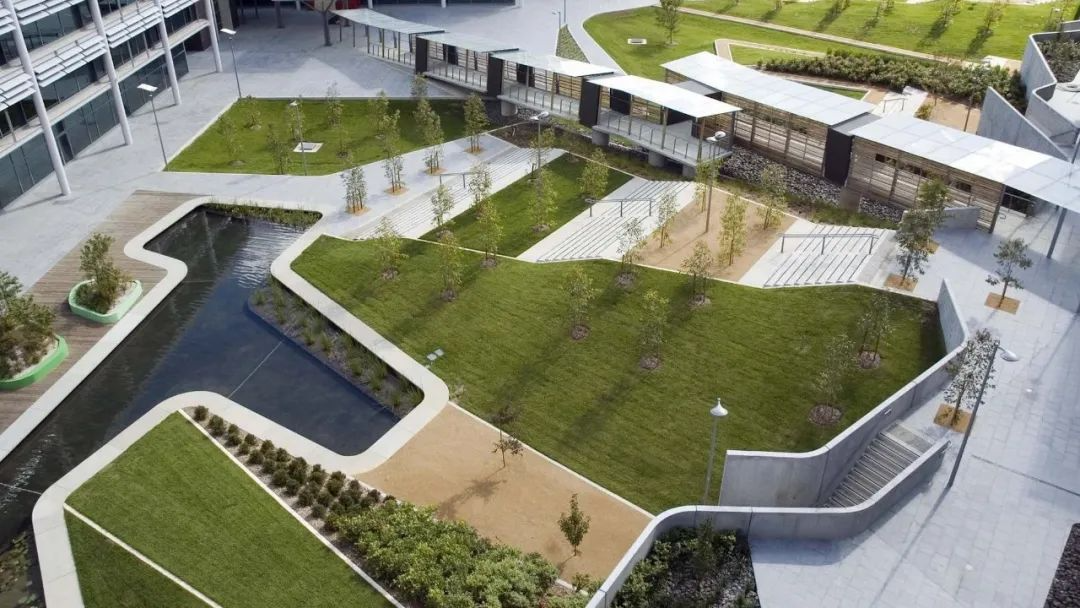
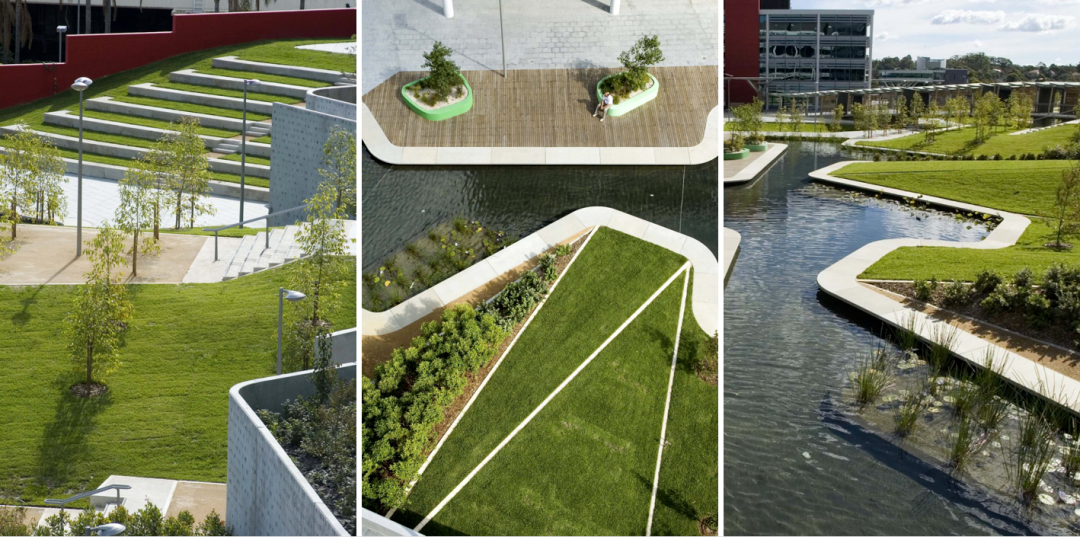


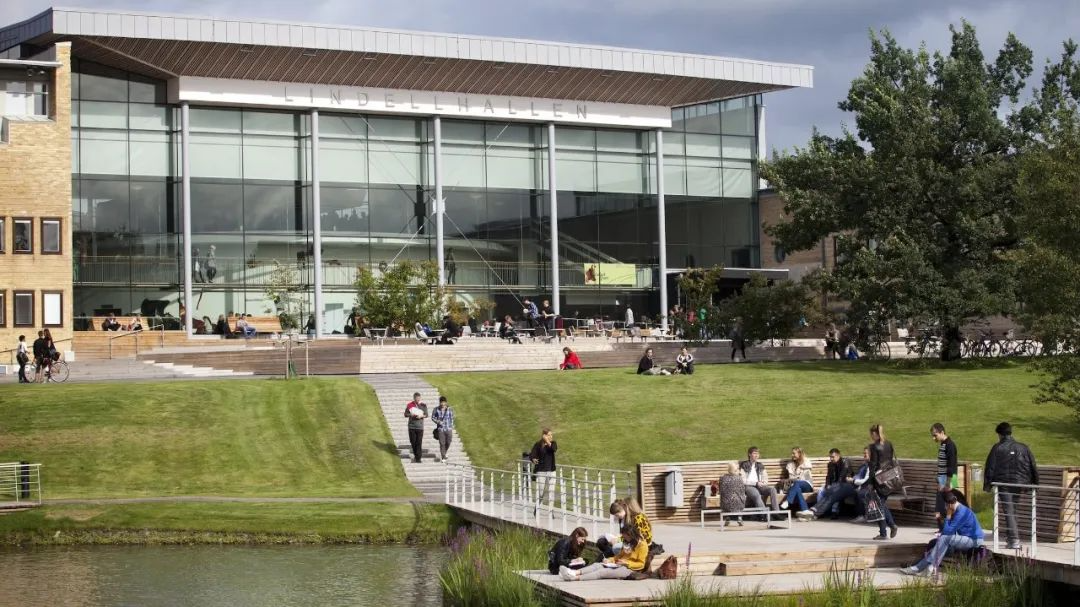
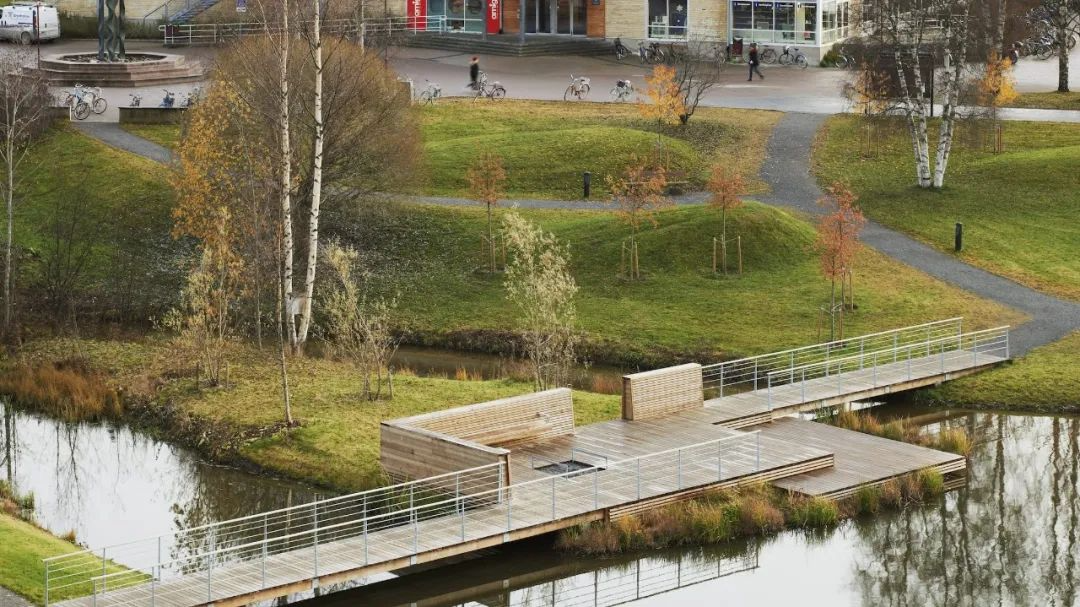
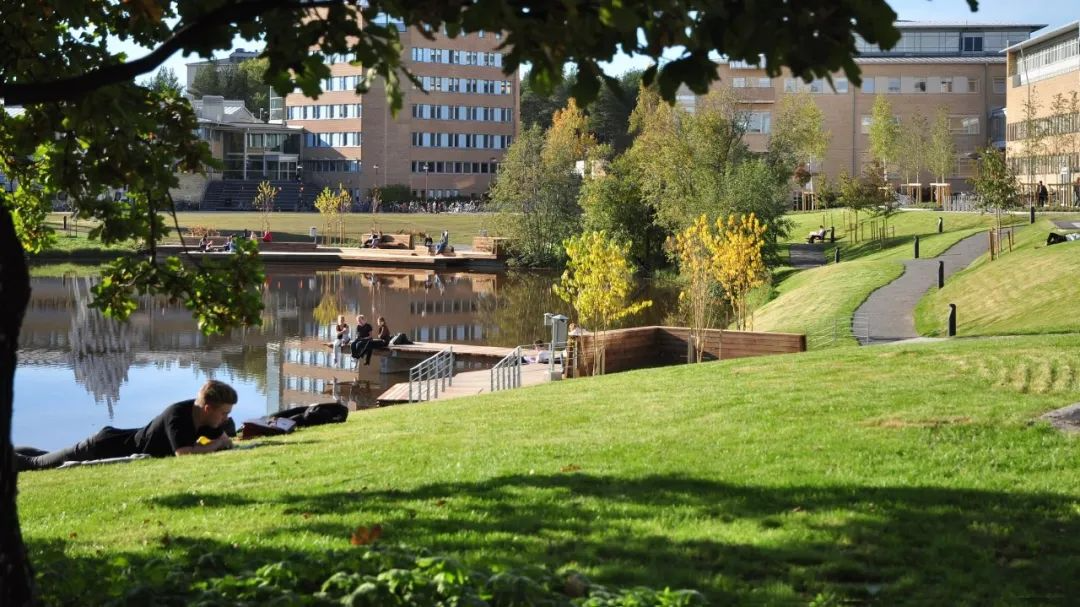
3. Lakeside landscape of Umeå University campus



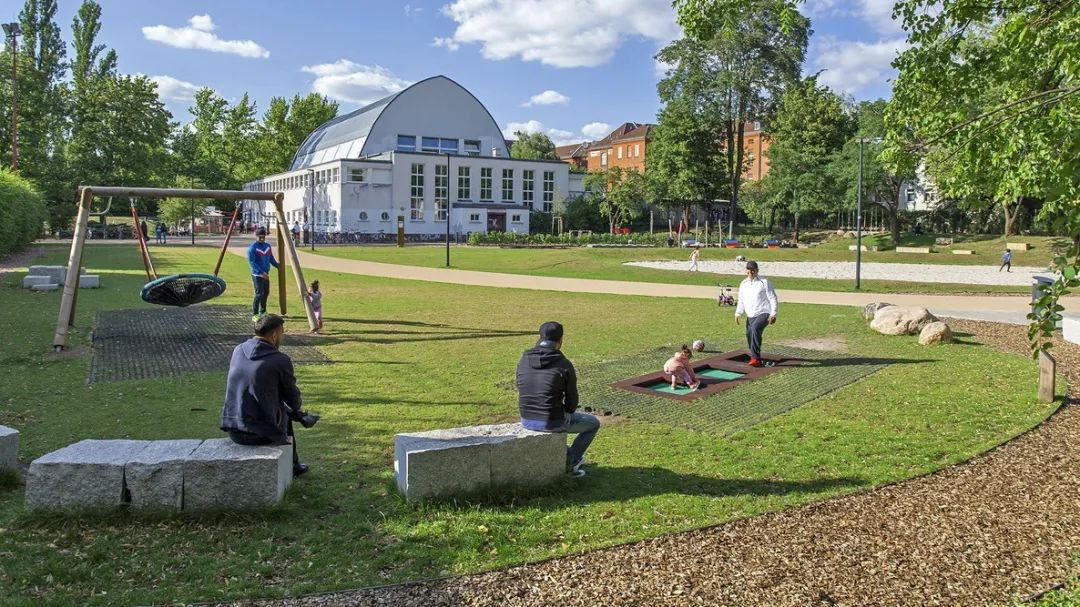
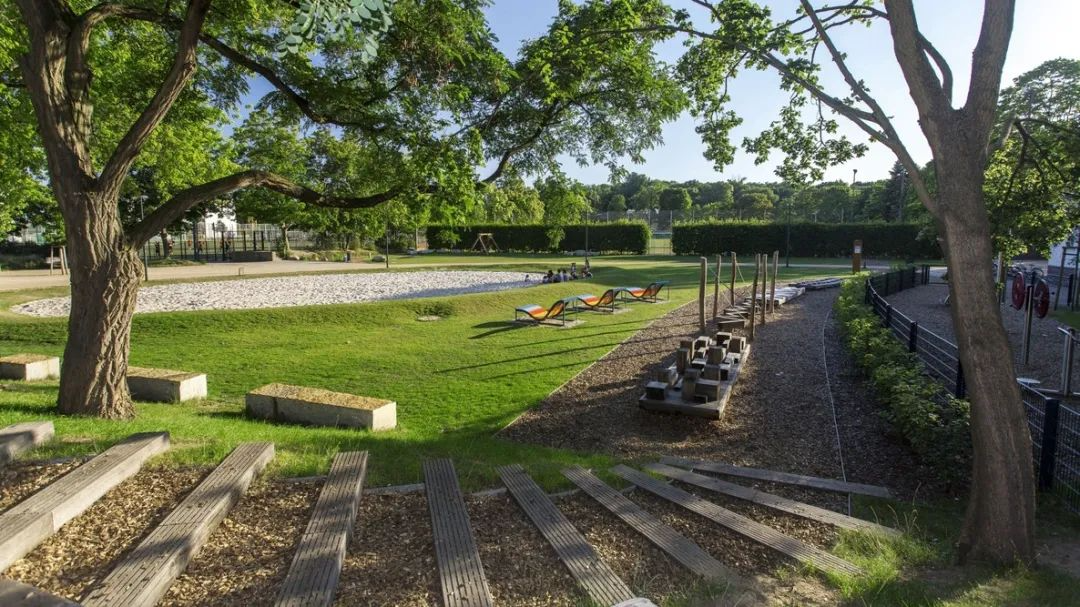
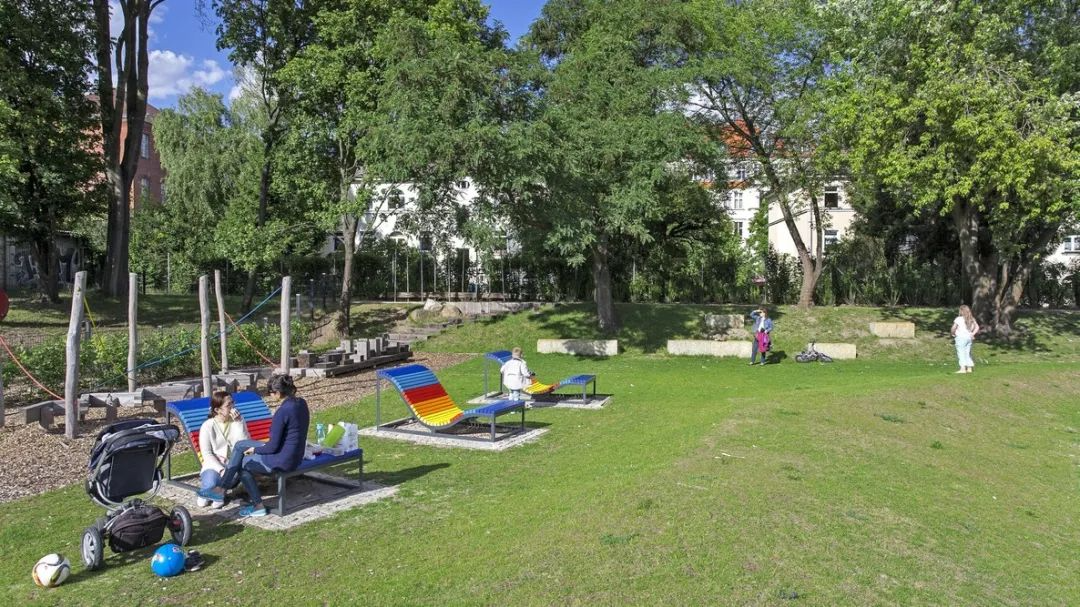
4. Urban Sports Park



Landscape lawn design technology sharing
Lawns are an important part of landscape design. In addition to purifying the air, conserving water and soil, and reducing noise, they can also beautify the environment and bring people a pleasant feeling. Large areas of flat lawns create an open and "breathable" space; the designed lawn space in the residential area adds functionality and artistry. To create a high-quality lawn space, its planting and subsequent maintenance management are very important.
01
Lawn grass classification and main varieties
1-1. Classification of lawn grass
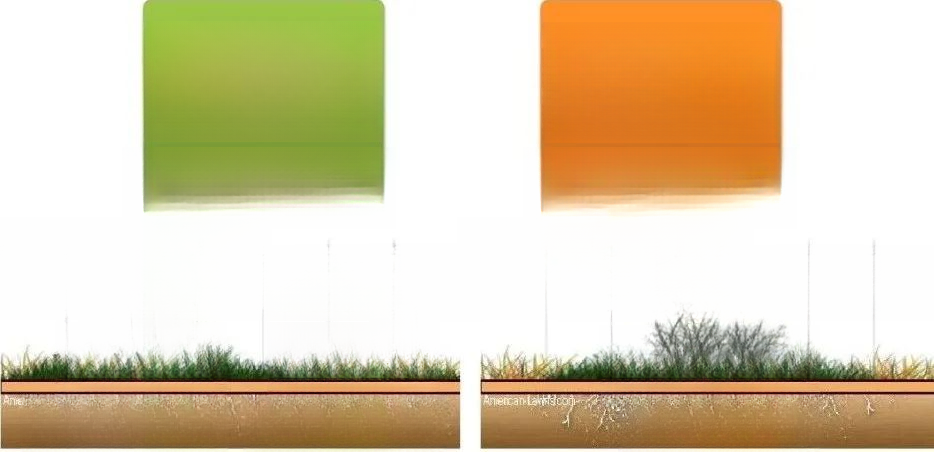
According to the growing climate: lawn plants are divided into cool season lawn grass and warm season lawn grass

1-2. Main varieties of lawn grass

02
Turf Grass Variety Selection
2-1. Basic
Should adapt to local climate and soil conditions (water content, pH value, soil properties, etc.)
The availability and level of irrigation equipment, construction costs and management fees
Ease of obtaining seeds or seedlings
Resistance to external forces (pruning resistance, trampling resistance, etc.)
Required lawn quality, aesthetics and practical use quality
Turfgrass life span (annual, biennial or perennial)
Resistance to stress (drought, cold, heat), resistance to diseases and insects
Accumulation and formation of organic layer
2-2. Selection of varieties for use in different regions and seasons
It is generally selected based on its geographical distribution and adaptability to temperature conditions.
03
Lawn Planting & Maintenance
1. Lawn Planting
Lawn planting methods: seeding, vegetation belt, large-angle slope planting technology, lawn paving, etc.; lawn paving methods can quickly meet landscape requirements.
Lawn establishment period:
① The most suitable time to sow cool-season grass is early spring and autumn. Spring-sown lawns are under great watering pressure and are more susceptible to weeds. In contrast, autumn is the best time to plant.
②The most suitable sowing time for warm-season lawn grasses is mainly in summer.
③Grass stem planting of warm-season grasses is best carried out in summer and rainy seasons
④ Vegetation belts, paving of grass blocks or grass rolls should be carried out in spring, summer and autumn.
Lawn Planting Flowchart
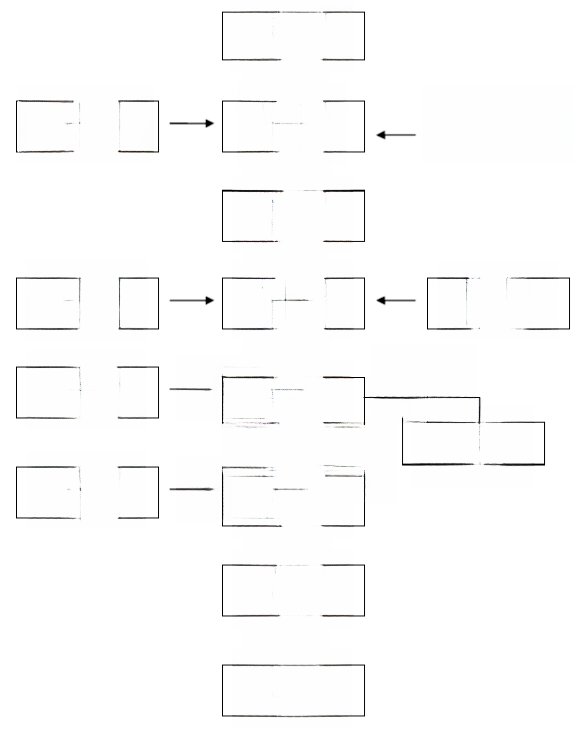
Take dwarf Bermuda as an example (warm season lawn grass):
① Planting in April, single season type is enough, it is 3-6 yuan/㎡ more expensive than Manila, but in mid-November, ryegrass seeds are added, which is about 3-5 yuan per square meter.
② Planting in October, using double-season turf, is 7-8 yuan/㎡ more expensive than Manila.
Process requirements:
① Add ryegrass and trim the grass to 2.5cm. Spread a thin layer of sand after sowing. If sowing in December, cover with non-woven fabric.
② The terrain needs to be leveled and sand needs to be spread. For large-scale paving, blind pipes need to be added to the base layer.
Maintenance details:
① Pruning is more frequent in summer than in Manila, usually once every 4-5 days
② Sow ryegrass seeds in November every year to ensure that the grass is evergreen all year round. Cut the rye off in March every year to allow the Bermuda grass to grow.
Planting details:
1. Drainage settings - lawn drainage
1) Design a flat field with no slope and an area of ≥500 square meters, and bury pipes in the middle of the flat field as drainage pipes;
2) If the design is for a sloped field, blind pipes or culverts can be used directly along the roadside as drainage pipes;

No slope, area ≥500m²: buried drainage pipe in the middle
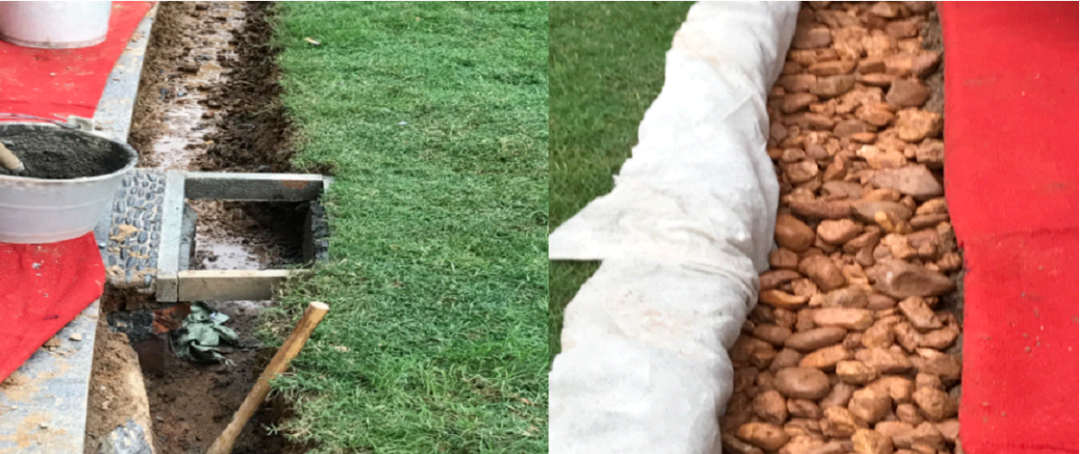

Slope: roadside blind pipe/ditch drainage
2. Site terrain treatment
2-1. Finishing the terrain
1) Clean up all tiles, gravel, construction waste and debris. Generally, it should be no less than 30cm below the lawn bed.
2) Further break up the matrix soil into smaller pieces less than 2 cm.
3) Fill soil gaps with coarse sand (particle size 0.5~1mm) to ensure that fine sand in the surface layer does not flow away.
4) Finely level the lawn surface.

Cleaning up the garbage

The matrix soil is broken into pieces less than 2 cm
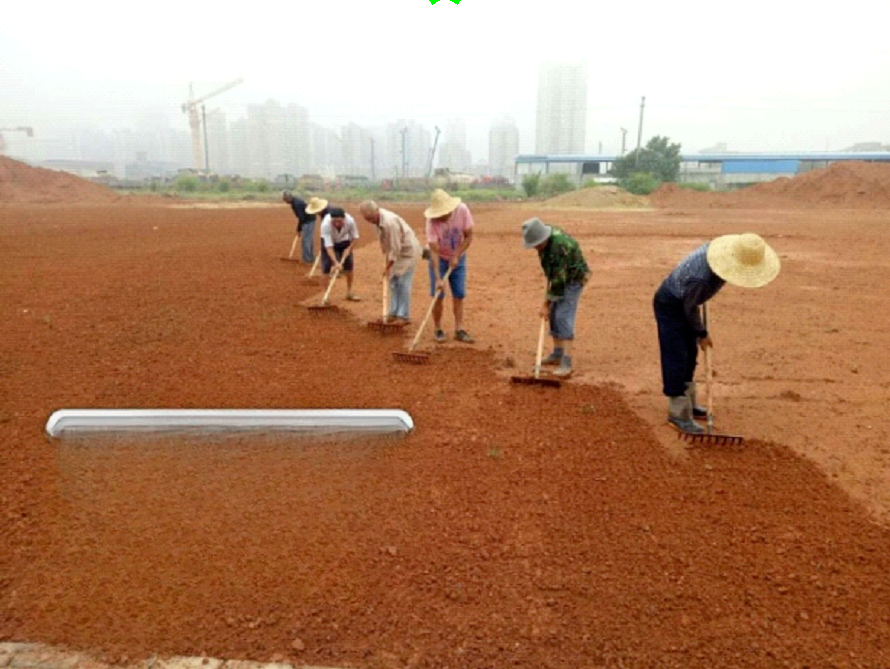

Coarse sand filling, fine leveling
2-2. Lawn bed
The construction of the ping bed is divided into five layers:
1) Lay the first layer of gravel or pebbles (2x4cm) about 15cm from bottom to top;
2) The second layer uses coarse sand to fill the gaps between the pebbles in the first layer and then compacts it (to prevent settlement);
3) The third layer is made of planting soil (preferably sandy soil), organic agricultural fertilizer and coarse sand, and spread to about 30 cm on the lawn bed, then roll it (to promote the development of turf);
4) The fourth layer of coarse sand with a thickness of about 3-5 cm is used for leveling, and then rolling (to reduce uneven areas);
5) The fifth layer is paved with turf;


3. Lawn paving process standards
1) First, go to the turf base to check the quality and growth density of the turf, and require the turf to be trimmed before planting, leaving a stubble height of 3-4cm.
2) Acceptance upon arrival must be strictly in accordance with lawn standards.
3) The edges of the turf blocks should not be broken. Tearing of the turf blocks is prohibited and they should be cut with a sharp knife.

4) Closely lay the turf, with no gaps between the turf blocks and no exposed soil at the joints. The edge should be 2-3 cm lower than the stone pavement. If it is necessary to lay backwards, use thick wooden strips to scrape the sand surface while laying. It is strictly forbidden to step on it immediately after laying. If the lawn needs to be adjusted and it is necessary to step on it, wooden boards must be laid before stepping.
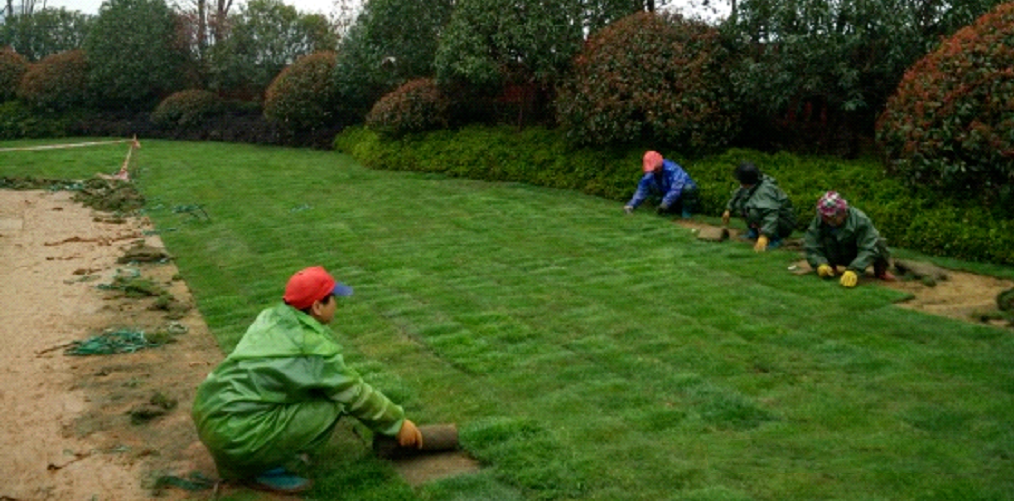
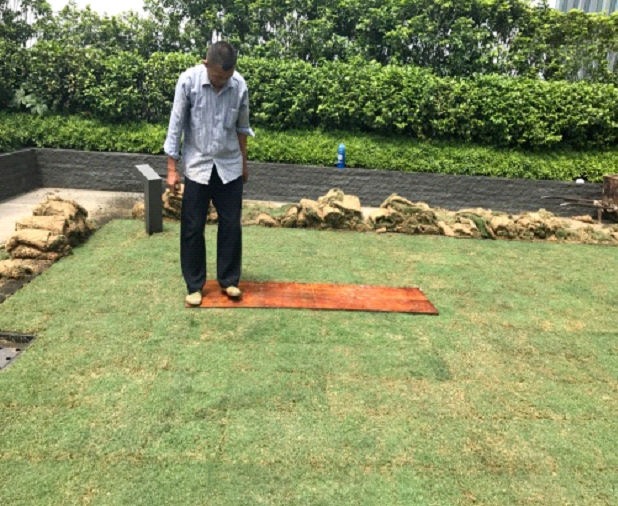


5) Water promptly after laying: After laying, it is necessary to ensure that the soil is watered thoroughly within 4 hours, even on rainy days, so that the roots are in close contact with the sand.
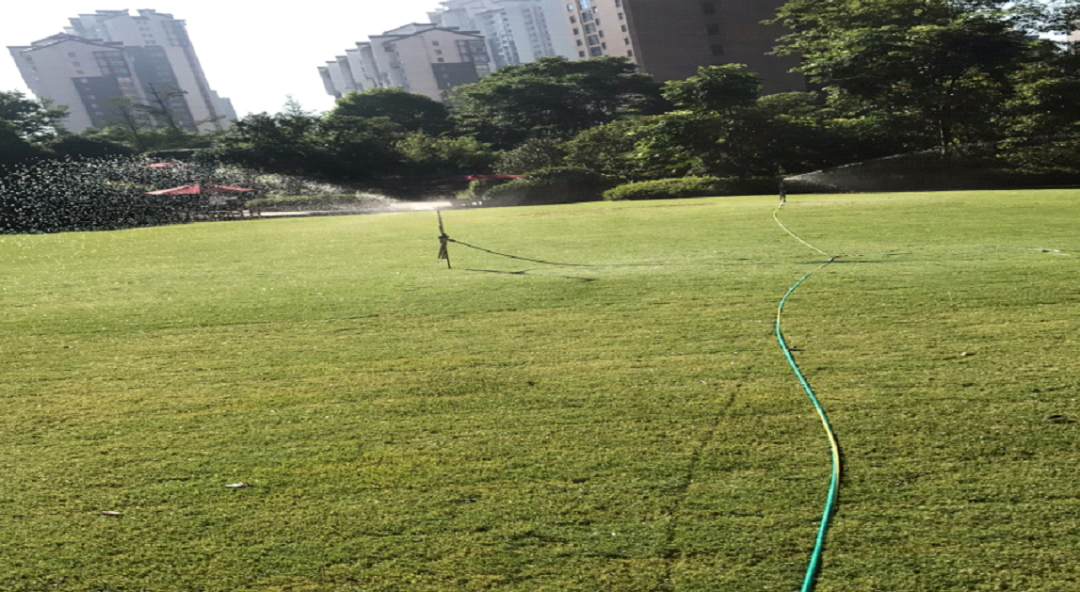

6) Rolling and compaction (to make the turf roots closely integrated with the bottom layer): When the moisture is slightly dry and the soil shrinks, carry out manual compaction. For large lawns, use a 0.5-1 ton roller to flatten them. For small lawns, use a pressure plate to flatten them to ensure that the lawn surface is smooth, without depressions, depressions, or ridges.
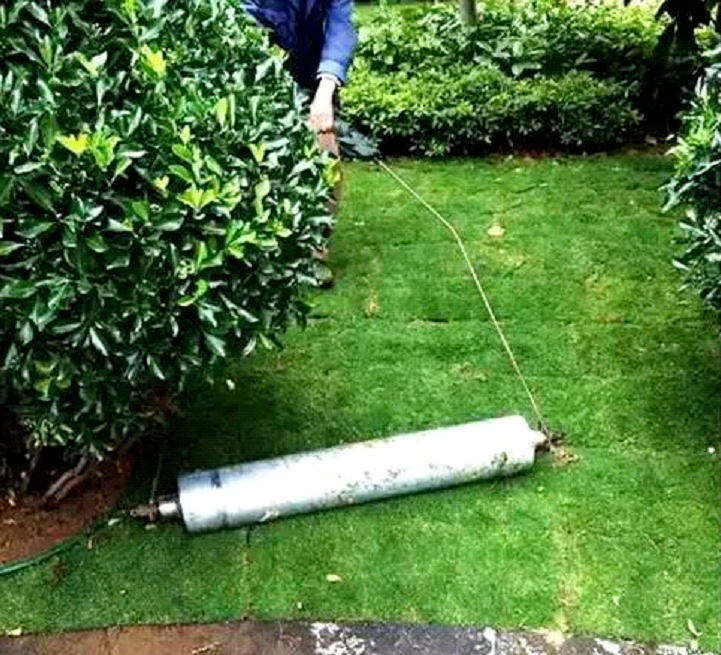

(II) Lawn maintenance and management
1. Lawn mowing
① Lawn grass grows rapidly, and generally it should be mowed when the grass grows to a height of 5 cm.
② Mowing work is often done on sunny days and when the soil is hard. The blade of the lawn mower should be sharp and the height should be adjusted appropriately.
③To avoid excessive damage to the seedlings, pruning is best done in the afternoon (avoid dew).
④ The frequency of pre-pruning is generally related to maintenance. For example, here it is usually once every 5 days. After pruning, fungicides should be sprayed in time to prevent infection of the incision and cause diseases. (Note: The trimmed grass should be removed in time to prevent the occurrence of diseases and insect pests).
⑤Trim the edges neatly (by hand).

2. Watering the lawn
The principle of maintenance irrigation is not to water unless the soil is dry, and to water thoroughly when it is used. It should be done in the morning and around dusk; watering should be controlled during the high incidence period of diseases; watering should be done in time during the early spring greening period.
Warm-season grasses have shallow roots and grow quickly. When the climate is dry, timely irrigation is required. The root layer should be wet to about 10-15 cm. This will prevent the lawn grass from wilting and turning yellow, or even dying, due to lack of timely water supply. Watering again in early December will help the lawn grass to turn green again next year.

3. Fertilizing the lawn
As an important means of lawn maintenance and management, fertilization is an indispensable measure to provide nutrients for lawn grass. Like irrigation and pruning, it is also a decisive factor in improving the durability and quality of lawns. However, it is more expensive, but it is one of the measures with the fastest effect. Fertilization is determined according to specific conditions each year, and generally granular fertilizers and foliar fertilizers are applied.
Spreading: It is mainly used for the application of organic fertilizer and inorganic fertilizer, which can be done by mechanical or manual operation. Spreading should be done when the lawn grass leaves are dry, the fertilizer should be spread evenly, and water should be applied in time after fertilization.
Spraying: Use low concentration solution and spray on a sunny and windless day.

4. Loose lawn
Turf thinning should be done during the most vigorous growth period for lawns, which should be spring or fall for cool-season lawns and late spring or early summer for warm-season lawns.
In order to prevent the soil from becoming compacted after being trampled, the lawn should be frequently loosened and aerated. Loosening the soil can promote water penetration, improve the aeration of the root system, maintain moisture in the soil, and promote lawn growth. Fine lawn management should be perforated 1 to 2 times a year, and the lawn can be scratched or punctured and vertically cut as needed; other lawns can be perforated as needed.
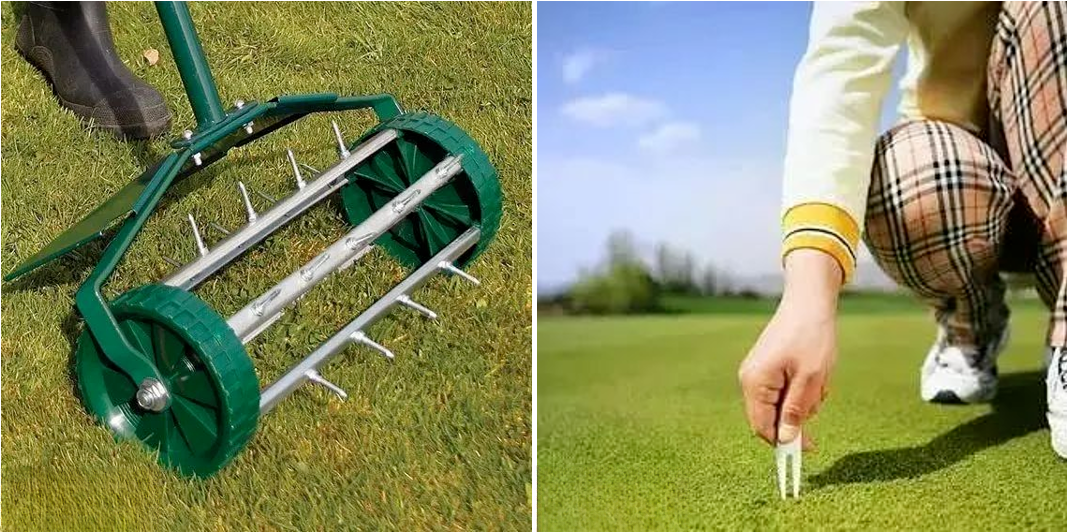

5. Weed removal on lawn
Weed control for Bermudagrass lawns is usually done with closed-type herbicides and manual weeding.
6. Lawn pest control
Common ones include armyworms, grass moths, cutworms, and fall armyworms, which can be prevented by mixing 300m²/1kg of Dihaiping with an appropriate amount of fine sand and spraying 1000 times of Kuangsha on the leaves. During fertilization, pruning and irrigation, try to avoid providing a suitable environment for the occurrence of diseases and pests.
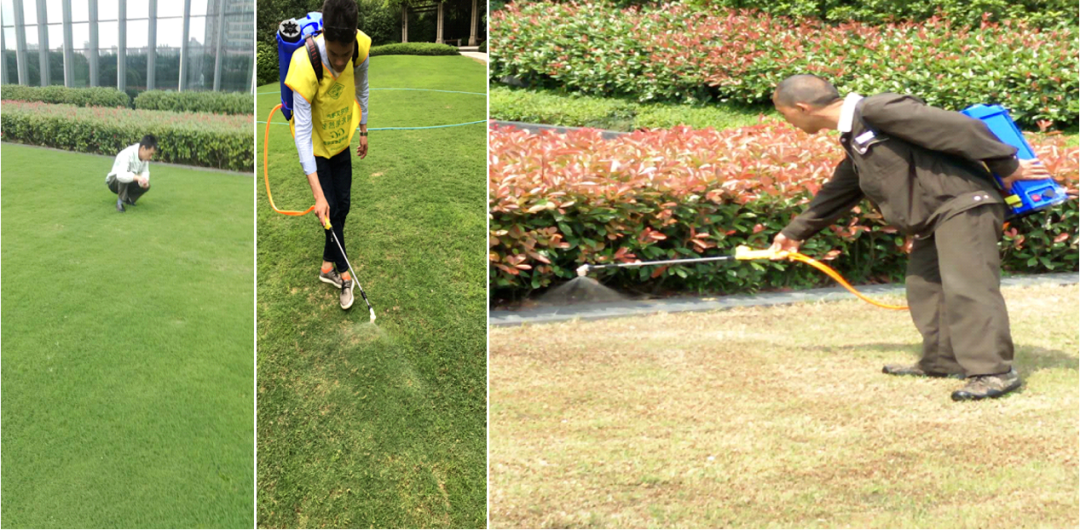

7. Lawn soil improvement
Common problems with garden soil
①Reduction of soil organic matter, microbial content and activity
②Soil structure damage and severe compaction
③The soil is too acidic or alkaline
④Soil tillage layer becomes shallower
⑤ There are fillers in the soil. Without soil replacement, the garden soil is mostly covered with construction waste and domestic waste.
⑥ Various municipal facilities are buried in the street greening soil
⑦Poor soil, lack of organic matter
Lawn soil improvement
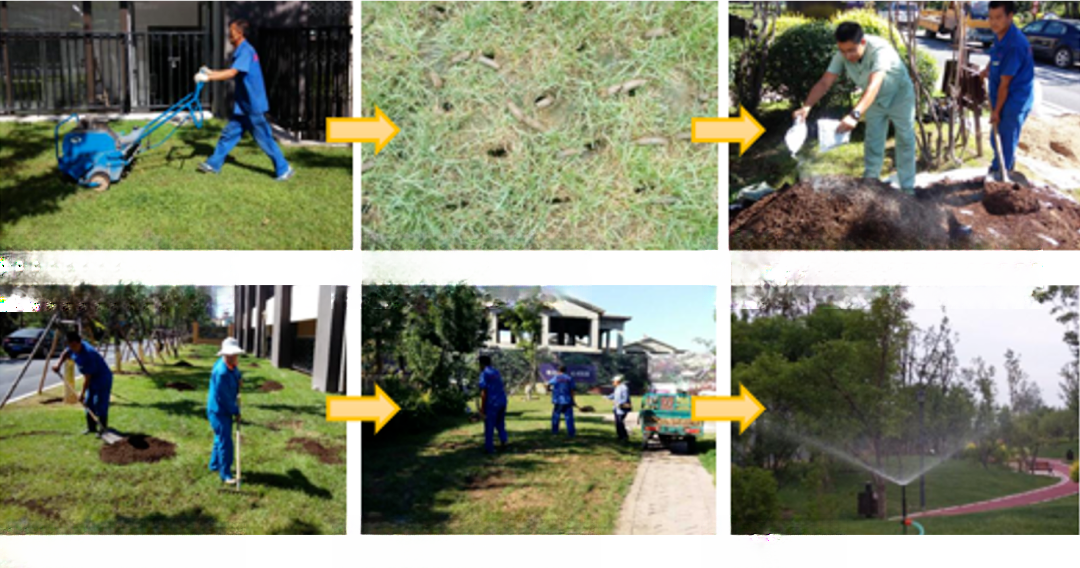

Shared from Shangjing General Engineering Office