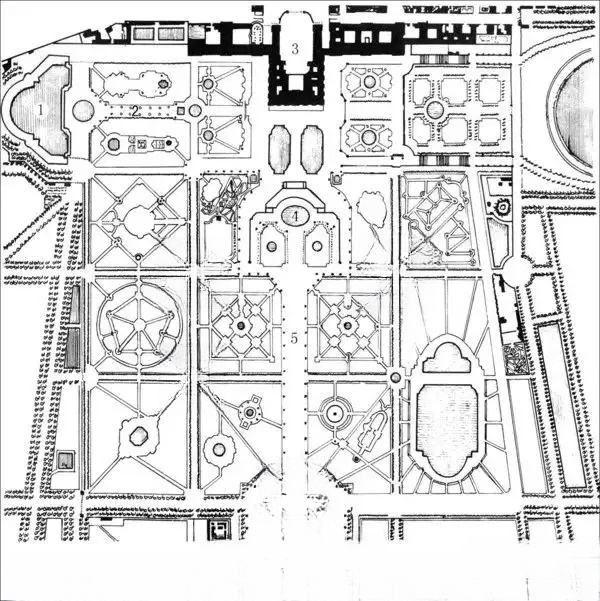
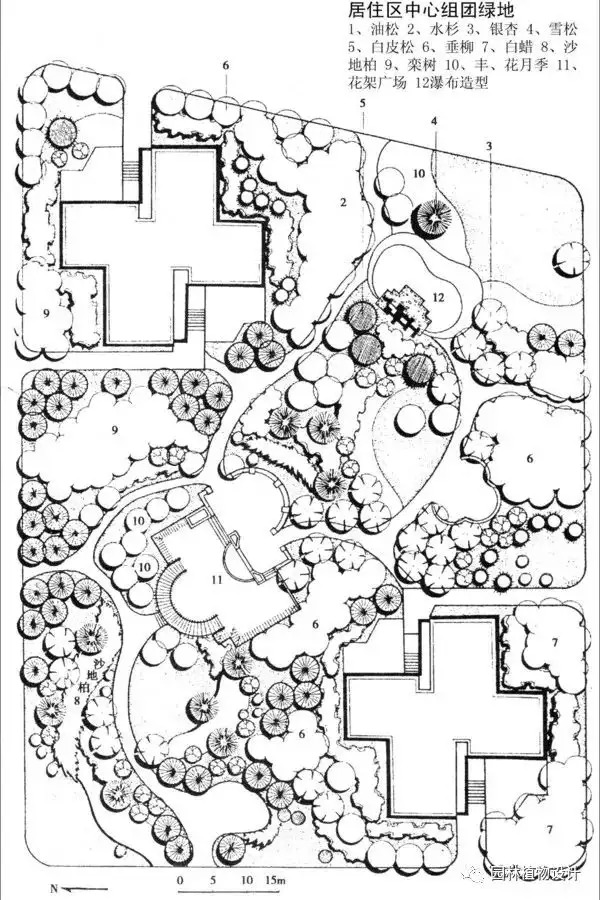
Detailed technical illustrations of garden plant design [Issue 2092]
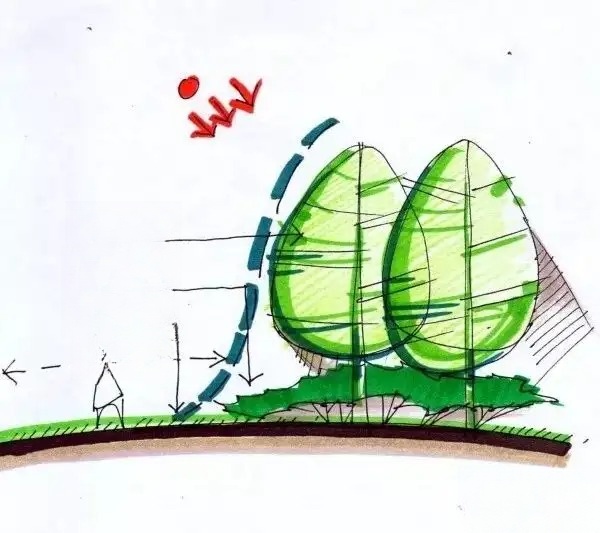
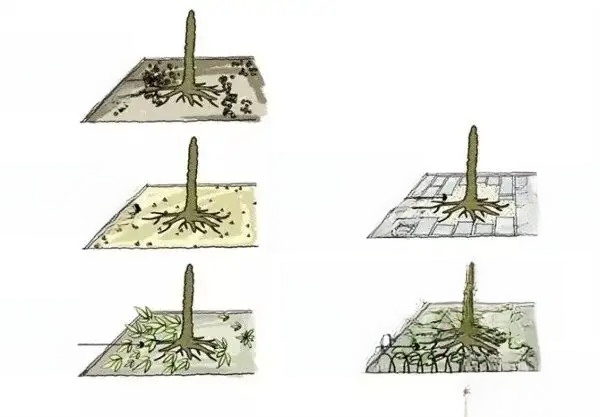










Planting technology requirements:
Greening is an important part of landscape engineering. In order to ensure that the greening construction can achieve the design requirements, special technical requirements for planting greening projects are formulated. All construction units should organize the construction in strict accordance with the construction technical requirements and design drawings to ensure the quality of the project and complete the greening project at a high level.
1. Earthwork:
1. Requirements for soil quality for planting:
Planting soil should be selected with good physical and chemical properties. It is required to use loam rich in organic matter and with a good aggregate structure. The planting soil should be loose, breathable, water-permeable and fertilizer-retaining. The soil pH (PH value) should be between 6-7. Clay or clay-like substances, coarse sand, stones, clods, weeds, harmful seeds and other objects are not allowed in the planting soil to ensure the consistency of the overall composition and structure of the planting soil. Garden planting soil should be tested according to the batches entering the site, and the testing content and physical and chemical indicators of the planting soil should comply with the "Quality Requirements for Garden Planting Soil".
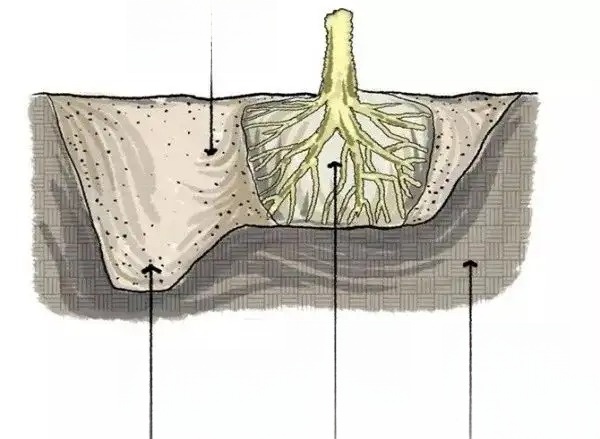
2. Backfill soil:
According to the actual situation on site, backfill soil can be divided into two levels:
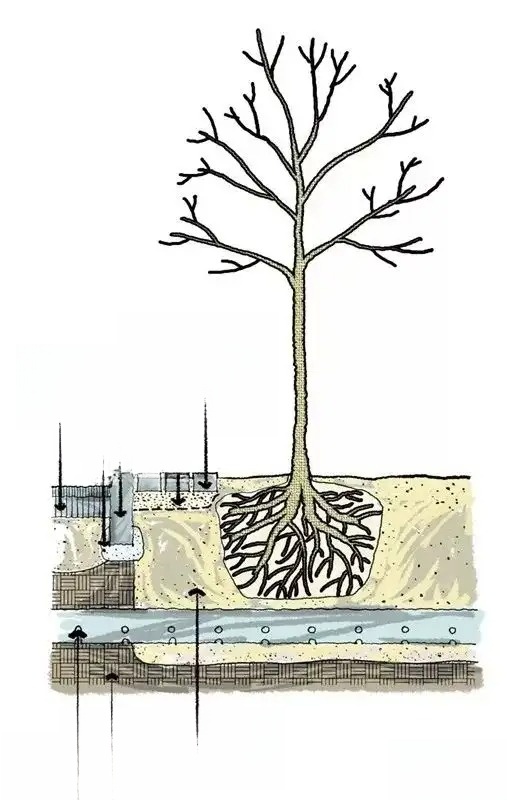
1. The thickness of the surface planting soil is required to be 100cm. Heavy machinery rolling should be avoided when backfilling the planting soil. The surface of the planting soil should be rolled flat with a stone roller, with a concave and convex no greater than 2cm, to meet the design elevation and slope requirements.
2. Backfill the mixed soil below the planting soil (mixed soil is soil that does not contain inorganic components and harmful components such as bricks, stones, cement blocks, etc.);
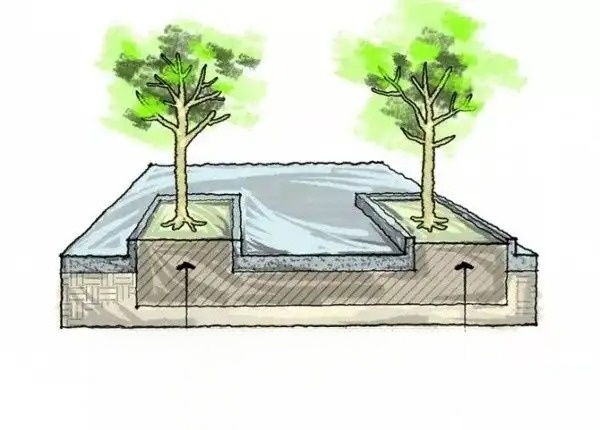
3. For garage roof greening, a root barrier layer should be set up on the garage roof to prevent the growth of plant roots from affecting the building structure.
2. Plant materials:
Plant materials are the key to whether greening projects can achieve ideal results. During the construction of greening projects, all project staff should establish a basic consensus on the quality, morphology, and growth of seedlings, so as to better grasp the management scale and planting effect during the construction of the project. Therefore, we put forward the following specific requirements for seedling quality:
1. General requirements
1. The plants should be free of pests and diseases, and should not contain pathogens that can cause tree death.
2. There should be no prominent scars on the trunk and branches. If there are scars, they should be treated to prevent pathogens from entering. There should be no split stems or trunks at the branching points.
3. The root system of trees should be free of pests or pathogens. The root system should be stable and intact without split roots. The soil ball of seedlings with soil balls should be intact.
4. Deciduous trees are required to have a beautiful tree shape and retain their natural shape. After planting, they can be properly pruned to tidy up the tree shape and improve the survival rate, but the tree shape should be intact, the main trunk cannot be cut off, and single-pole trees are not allowed. Deciduous trees should have straight trunks, no mistletoe and other epiphytes, and no dead branches.
5. Evergreen trees should have a complete shape, full branches, no lopsided branches, and the lower branches should be full and not withered.
6. Regarding seedling specifications: The seedling purchasing size specification indicators are allowed to fluctuate within 10%, but for regular planting such as planting, row planting and tree array arrangement, the seedling specifications and tree shapes must be unified.
Height H (m): refers to the height of the seedlings after natural or artificial pruning during planting. It is required that the top growth point of the trees be retained as much as possible. The tree height listed in the seedling table is the minimum lower limit;
Diameter at breast height r (cm) refers to the diameter of the tree 1.2 meters above the root system soil mark;
Ground diameter D (cm) refers to the tree diameter 0.3 m above the root soil mark;
Crown width R (m): The crown width of the seedling tree should be measured based on the main crown surface of the leaf crown, excluding occasional branches. The crown width of shrubs refers to the main crown size of the shrub, and the crown width of trees refers to the size of the seedling crown at the branching point.
Branching point h (m): The height of trees and shrubs from the ground to the crown branch, which is the first main branching point.
7. Soil ball (m): The minimum average diameter of the soil ball required to ensure the survival and rapid growth of the transplanted trees. The soil ball should be intact when placed in the planting hole to be qualified. If the seedlings are transplanted or container seedlings, the specifications of the soil ball can be determined based on the actual situation, under the premise of ensuring the normal survival and rapid growth of the seedlings. The height of the soil ball is determined based on the actual distribution of the tree's root system.
(II) Special requirements
1. Specially selected large trees: refers to trees with a breast diameter greater than 20cm.
(1) Specially selected large trees must be confirmed by Party A and the designer before being transplanted to the site; the design shall determine the tree pruning requirements and branch point heights before the seedlings are brought to the site. The shape of the trees must not be damaged during digging and transportation.
(2) Large trees must retain their complete natural shape and be transplanted with their full crowns. Appropriate thinning may be performed to ensure survival, with the principle of maintaining an overall beautiful tree shape;
(3) A large tree should have a graceful posture and a straight trunk.
2. Evergreen trees:
A Conifers
(1) The tree has a full shape, pure color, and no missing branches or broken heads;
(2) The base of the plant should be full, the branch point of cedar should not be higher than 0.3 meters, only seedlings are allowed, and cuttings are not allowed; the branch point of cypress should not be higher than 0.3 meters;
B Evergreen trees with main trunks: such as Magnolia grandiflora, Ligustrum lucidum, etc.
(1) When selecting seedlings, determine the branching point. Generally, the branching point should not be higher than 2.2 meters. If used as a street tree, the branching point should be between 2.5-3.0 meters.
(2) The tree crown is full, the branches are evenly distributed, and the leaf color of the plant is pure and healthy.
3. Deciduous trees:
(1) The tree should have a complete and full natural crown and a straight trunk without obvious bends;
(2) The height of the branching point of the plant should strictly comply with the design requirements. The branching point of trees with obvious main trunks (such as Ginkgo, Ligusticum wallichii, Magnolia, etc.) should be below 2.2 meters. Only seedlings are allowed, and grafted seedlings are not allowed.
(3) If used as a street tree, the branching point should be between 2.5 and 3 meters.
4. Shrubs:
(1) The root system is well developed, the plant grows vigorously, the plant shape is perfect, the bush is symmetrical, and the crown is not skewed;
(2) Shrubs, whether evergreen or deciduous, should be pruned into a round shape, except for specially selected tree shapes. Seedlings with only a few branches are not allowed. For example, forsythia and redbud should be full bushes with the upper part pruned into a round shape.
(3) All shrub planting specifications required by the design refer to the specifications after being trimmed into a spherical or elliptical shape.
5. Quality standards for hedge plants:
(1) The heights specified in the seedling table are the heights after pruning, so when selecting seedlings, you should reserve a suitable pruning height;
(2) The support point of the base of the seedling should be less than 20 cm, with dense branches and leaves, no branch loss, and normal branch development.
6. Ground cover plants:
(1) The height of ground cover plants refers to the height after planting and pruning.
(2) Ground cover plants labeled as “hairy ball” are perennial plants that have been pruned and cultivated to have a fuller ball shape with no less than three levels of branches, and the base branching point is less than 15 cm; “seedlings” are natural plants that have grown for more than three years. Plants below 60 cm should have more than 6 branches, and plants between 60 cm and 100 cm should have more than 8 branches, and the base branching point is less than 15 cm.
7. Perennial flowers: Monocotyledonous perennial flowers must have a well-developed root system and three buds; perennial flowers such as chrysanthemums must be planted in nutrient pots to cultivate seedlings.
Seasonal flowers: Planting according to the seasons of the year, the variety and planting method, planting density are determined according to the specific seedling source. Generally, 2-inch pots and 4-inch pots are used for flower seedlings.
8. Tubers and bulbous flowers: Tubers and bulbs are intact, plump, free of rot, disease and insects, and have more than three buds or buds.
9. Bamboo: Choose 2-year-old marginal bamboo as mother bamboo. It must be transplanted with soil, retaining 40-50cm of whips and removing 80cm of whips. If transplanted nearby, the whips can be appropriately reduced, but the underground whips must have hidden buds, otherwise they will not sprout, delaying the completion of the bamboo forest.
10. The seeds of lawns, flowers and ground cover plants used for sowing should be marked with the variety, strain, origin, production unit, weight, harvest year, purity and germination rate, and must not be infected with diseases and insect pests. Seeds imported from other places must have a quarantine certificate. They can only be used if the germination rate is above 90%.
3. Plant pruning:
The root system of seedlings should be pruned before planting. Split roots, diseased and insect-infested roots, and excessively long roots should be cut off, and the crown should be pruned to maintain a balance between the above-ground and underground areas.
(I) Tree pruning should comply with the following regulations:
1. Tall deciduous trees with obvious main trunks should maintain their original tree shape and be thinned out appropriately. The main and side branches that are retained can be pruned back to strong buds, and 1/5 of the branches can be cut off.
2. For deciduous trees with dense branches and no obvious trunk, for trees with a trunk diameter of more than 10 cm, thinning can be done to maintain the original tree shape; for seedlings with a trunk diameter of 5 to 10 cm, several side branches on the trunk can be selected and pruned to maintain the original tree shape. Trees with weak germination ability (such as beech trees) only need to be properly thinned to retain at least one-third of the branches of the current year.
3. For evergreen trees with dense branches and round crowns, appropriate thinning can be done. Seedlings with branches and leaves clustered at the top of the trunk do not need to be pruned. For evergreen trees with whorled lateral branches, 2 to 3 layers or 1-2 layers of whorled lateral branches at the base can be cut off according to the height requirements of the branch point of the fixed trunk. The branch point of evergreen conifers with basal branches such as cedar, cypress, and white pine cannot exceed 30 cm.
4. Evergreen coniferous trees should not be pruned. Only diseased and insect-infested branches, dead branches, weak branches, overly dense whorled branches and drooping branches should be pruned.
5. The crowns of precious tree species should be lightly pruned.
(ii) Shrub pruning should comply with the following provisions:
1. Bare-root seedlings with soil balls or soil in humid areas and flowering shrubs with flower bud differentiation last year should not be pruned. Dead branches, diseased branches, and insect-infested branches should be pruned. The cut branches should be disposed of in time.
2. For large shrubs with dense branches, thinning can be done appropriately.
3. For grafted shrubs, the branches sprouting from the rootstock below the interface should be cut off.
4. For small shrubs with obvious branches and new branches bearing flower buds, appropriate strong pruning should be done according to the tree's vigor to promote the growth of new branches and renew old branches.
5. Trees and shrubs used as hedges can be shaped and pruned according to design requirements after planting. Hedges cultivated in nurseries should be trimmed after planting.
(III) The quality of seedling pruning shall comply with the following provisions:
1. The cut should be smooth and free of splitting;
2. When cutting branches short, the outer buds should be left, and the cut should be 1 cm above the bud position;
3. When pruning large branches and thick roots with a diameter of more than 2 cm, the cut must be flattened and coated with preservatives or paint to cover the cut.
4. Precautions for plant planting:
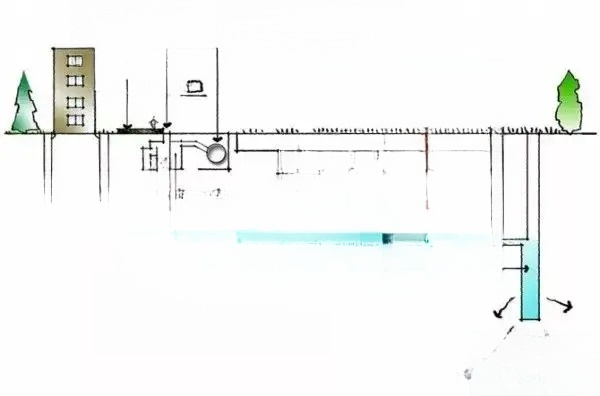
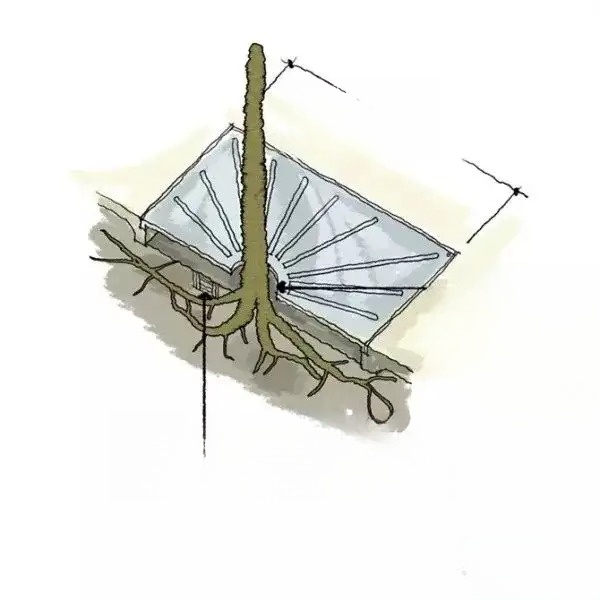
1. Tree planting and underground pipelines:
According to the Qingdao Urban Gardening and Greening Technical Guidelines, when planting plants and encountering conflicts between underground pipelines and the plant planting positions, the plants need to avoid the pipelines, adjust the plant planting positions according to the specifications in the table below, and communicate and negotiate with the designer in a timely manner to resolve the issue.
(II) Transplantation of large trees:
The transplantation of large trees needs to refer to the "Qingdao Large Tree Transplantation Construction Technical Regulations" issued by the Qingdao Quality and Technical Supervision Bureau. Before planting node trees or important plants, the contractor must provide pictures of seedlings (with seedling specifications as reference) to the landscape designer and obtain consent before planting.
(III) Tree (shrub) planting:
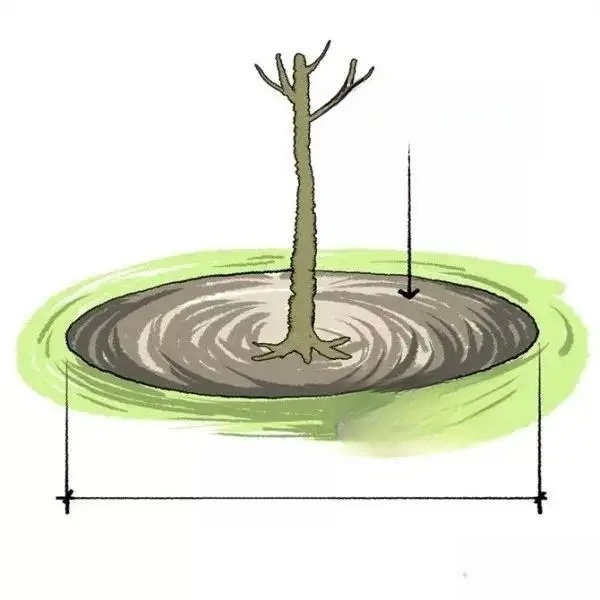
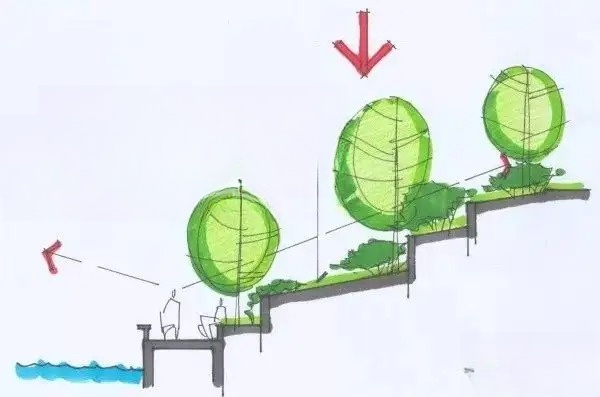
1. The orientation of tree planting should be full and complete, facing the main line of sight. Solitary trees should have complete crowns. The planting depth should ensure that after the soil sinks, the root diameter is at the same height as the ground surface.
2. The main trunk and first and second level main branches of trees with a diameter of more than 5 cm must be wrapped around a pole. The height of the pole varies according to the tree species. It must be tightly wrapped with soft materials such as straw rope or hemp, and must be guaranteed to be firm, neat and beautiful.
3. Planting of trees with soil balls: fill the pit with planting soil to the height of the bottom of the soil ball, place the soil ball on the filling surface, open the soil ball packaging after orientation, take out the packaging (if the soil of the soil ball is loose, the packaging at the bottom of the soil ball can be left in). Then, add soil from the edge of the pit to the sides of the soil ball, and compact it layer by layer. When the height of the soil increases to 2/3 of the depth of the soil ball, build a cofferdam, water it sufficiently, and level it after the water penetrates. If the soil sinks, add planting soil within three days, and then water it and level it.
4. When planting bare-root trees, first fill the pit with planting soil of appropriate thickness according to the root system, stretch the roots in the pit, evenly add soil around them, and lift the trunk tip upward or move left and right. After straightening it, add soil and tamp it layer by layer. Then build a cofferdam along the outer edge of the tree pit and water it until the water no longer seeps downward.
5. During the entire process from digging to planting trees, if the temperature is high, the branches and leaves should be thinned out appropriately, or a shed should be built to provide shade to keep the trees moist. When the weather is cold and windy, windproof and heat-insulating measures should be taken.
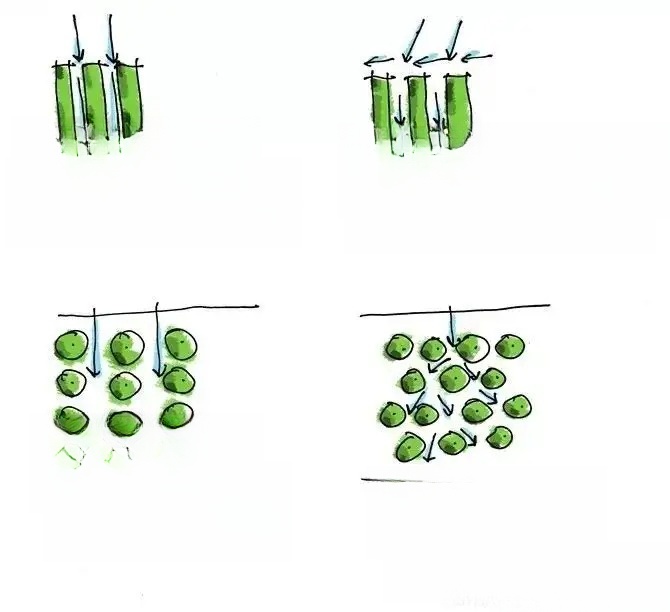
4. Planting density of ground cover and hedge plants:
1. The planting density of ground cover plants is related to the quality of seedlings. In this figure, the morphology of ground cover plants is described as hair balls and seedlings. In the design, the planting density is determined based on the quality description of hair balls and seedlings.
2. When selecting seedlings for ground cover, the height and density after construction are the main control indicators of the design effect. On the premise of meeting the above design effects, the construction unit can increase the planting density, adjust the planting techniques and use seedlings instead of hair balls without increasing the cost.
3. The effect of hedge planting is greatly affected by the quality of seedlings. The construction unit should pay attention to the design requirements for the crown width of individual seedlings to ensure the effect. If the seedlings are weak, the planting density can be adjusted according to the seedlings to achieve the designed effect without increasing the cost.
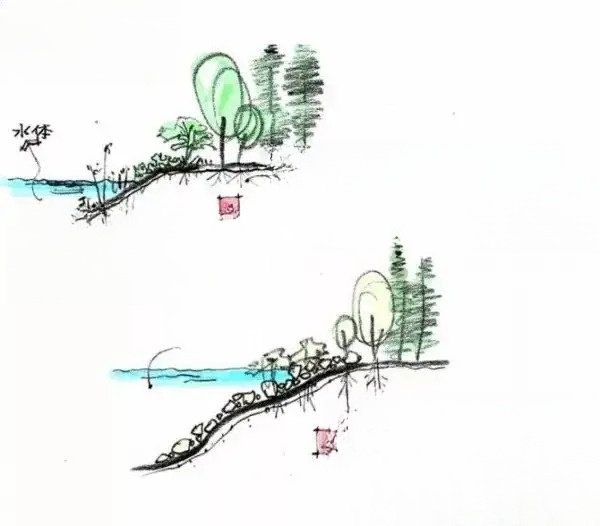
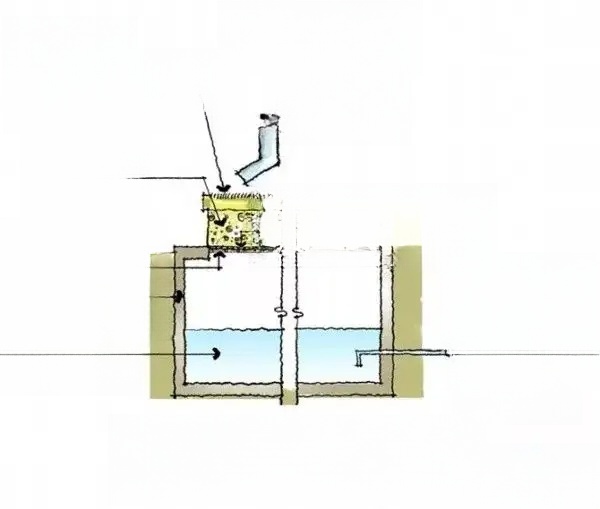
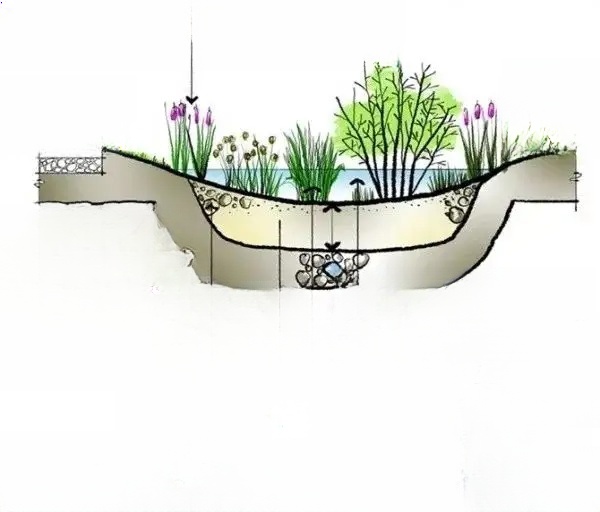
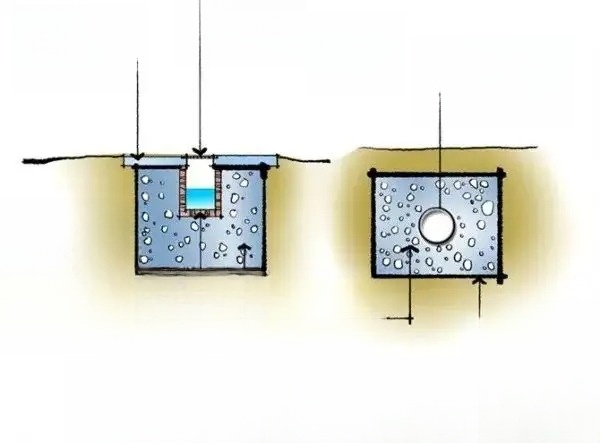
(V) Aquatic plant planting - container planting method:
First plant the aquatic plants in a container, then sink the container into the water. For some plant species, the container must be taken out and stored in winter to protect against the cold; change the soil and add fertilizer in spring. Use a permeable pottery pot for the planter. Choose a container of appropriate size and placement according to the different requirements of different aquatic plants for water depth and soil. To prevent the container from floating in the water, tie the container with two water-resistant ropes, then fix the ropes on the shore and press them under the stones to hide the ropes to avoid affecting the landscape effect.
(VI) Support frame: To prevent man-made damage and windfall, support frames should be provided for newly planted trees. Support frames can be provided with one-corner support, three-corner support (three), or four-corner support (four). Supports should be provided with stakes according to the tree. It is strictly forbidden to pass the wooden poles through the soil ball or break the root plate. Electric drills are used to drill holes between wooden poles and iron wires are used to connect them. To ensure that the trees are not damaged, straw ropes are required to be wrapped around the trunks and then tied to the wooden poles. Electric drills are used to drill holes between wooden poles, and iron wires are used to connect and compact them. Support frames at the same location are required to be of the same material, form, method, and direction to ensure overall beauty.
5. Street trees:
(1) Fill the tree hole with planting soil: length x width x depth = 1.8 x 1.5 x 1.8.
2. Pruning of roadside trees:
The root system of seedlings should be pruned before planting. Split roots, diseased and insect-infested roots, and excessively long roots should be cut off, and the crown should be pruned to maintain a balance between the above-ground and underground areas.
1. Pruning of street trees should comply with the following regulations:
(1) For street trees, all branches below the first branch point should be pruned according to the fixed trunk height, and branches above the branch point should be thinned or shortened as appropriate, and the original crown shape should be maintained;
(2) Street trees with obvious trunks should maintain their original shape and be thinned appropriately. The main and side branches that are retained can be pruned back to the strong buds, and 1/5 of the branches can be cut off;
(3) For street trees with weak germination ability (such as Liriodendron tulipifera), only appropriate branch thinning is required, retaining at least one-third of the branches of the current year;
(4) The crowns of precious street trees (such as Ginkgo biloba and Liriodendron chinense) should be lightly thinned.
2. The quality of pruning of roadside tree seedlings should comply with the following regulations:
(1) The cut should be smooth and free of splitting;
(2) When pruning branches, the outer buds should be left, and the cut should be at least 1 cm away from the bud position;
(3) When pruning large branches and thick roots with a diameter of more than 2 cm, the cut ends must be flattened and coated with preservatives or paint.
6. Fertilization requirements:
(I) Fertilizer selection
Organic fertilizer: finished organic fertilizer (product specified by Party A, the amount of fertilizer to be applied is determined according to the specific planting season).
(II) Fertilization method:
1. Organic fertilizer: Before planting, base fertilizer should be applied to the bottom of the tree pits of trees and shrubs. The method of fertilization is to mix high-quality organic fertilizer with the planting soil before construction and apply it to the bottom of the tree pit. The fertilizer should not come into direct contact with the roots, that is, a layer of planting soil should be covered on the fertilizer before planting.
2. Topdressing: Determined according to normal maintenance and planting. Use chemical fertilizers during the plant growth period. Chemical fertilizers should be dissolved before application, generally applied at a concentration of 0.5%-1%. Dry fertilizers must be applied evenly, with less rather than more. After application, water must be applied promptly and fully to avoid damaging the roots and leaves.
3. Covering fertilizer: For perennial flowers, after the plants dry up in winter, cut off the above-ground parts and spread the covering fertilizer - pine scale exquisite type 3# (product specified by Party A) evenly on the ground surface.
7. Requirements for laying finished lawns
1. Site leveling: Fine leveling is carried out before laying the turf according to the existing site. The surface soil is laid at a ratio of peat, fine soil and fine sand of 5:3:2 with a depth of 3 to 4 cm, and then compacted with stone rollers to prevent settlement.
2. Turf selection: The variety and formula of the finished lawn should be reported to Party A for confirmation. Choose varieties and formulas suitable for growth in the north, with a long green period, easy maintenance, and few diseases and insect pests. The root layer of the finished turf should be greater than 2.5cm, uniform in color, free of diseases and insect pests, and weeds, and the grass length should be less than 5cm.
3. Laying the turf: Before laying, cut the four sides of the turf evenly to ensure seamless connection. Ensure that there are no obvious gaps, missing corners, or missing edges. Use a greens fork or a knife to pierce the edges of the lawn joints back and forth between the two pieces of turf to level them to avoid warping.
4. Turf laying and maintenance: After the turf is laid, cover the surface with a layer of fine sand, and rake the sand into the roots with a broom in time, and use a 0.5-ton stone shovel to compact it. The newly laid lawn should be evenly watered with a mist sprinkler (do not cause erosion of the surface soil). The newly laid turf should be kept moist within two weeks.
8. Live broadcast of evergreen lawn
1. Laying requirements:
1. Site leveling: Before laying the turf, the existing site should be leveled carefully to ensure that the soil on the bed is as dry as possible and to minimize traces on the soil surface.
2. Grass seed selection: According to the seed formula determined by the professional seed company determined by the construction unit according to the local climatic conditions, the green period of 8 months required by the design should be met. Select the seed source with a seed quality label, and check the purity of the seeds to avoid weeds. Cold-season grasses should be sown at 16-30℃, and warm-season grasses should be sown at 21-35℃ (late spring and early summer are suitable for warm-season grasses, and late summer and early autumn are suitable for cold-season grasses). Confirming the planting time is crucial for the rapid formation of the lawn and the uniformity of the lawn.
3. Seed direct seeding: Avoid sowing on windy days as much as possible. Use a spreader to evenly spread the surface according to the seed sowing requirements. The sowing depth is 6mm. Immediately after sowing, lightly press the seeds so that the seeds are in close contact with the soil. (For example, if the creeping bentgrass seeds are small, fine soil can be added to the seeds and mixed and sown). After the overall direct seeding is completed, it should be immediately covered with white non-woven fabric and fixed with bamboo sticks.
(II) Management of young lawns:
1. Watering: After direct seeding, water in small amounts and multiple times to keep the surface sand and seeds moist. Each time you water, adjust the nozzle to a fine mist to prevent surface runoff;
2. Fertilization: When the new buds grow to 2 cm, start fertilizing every 15 days with a nitrogen application rate of 2-3 g/m2;
3. Rolling: The purpose of rolling is to compact the soil layer and make the lawn surface smooth;
4. Sanding: The purpose of sanding is to repair the surface damage during lawn construction, to repair the small pits left by uneven watering, and to ensure the smoothness of the lawn bed;
5. Replanting: There may be a lack of seedlings in some areas during planting due to many factors. In order to achieve a consistent lawn, replanting should be done in a timely manner, and water control in the replanting area should be strengthened;
6. Pruning: When the lawn coverage rate reaches more than 90% and the seedling height is 10-15cm, pruning should be carried out. Pruning should be carried out according to the two-thirds principle when there is no dew. In the early stage, it should be controlled at 8-12cm. Pay attention to timely cleaning of grass clippings to prevent the spread of pests and diseases.
7. Weeds and pests: The amount of weeds in the lawn bed will increase day by day in the early stage. They should be pulled out manually and the use of herbicides is strictly prohibited.