Brief History of Furniture Development (Part 1)
The history of furniture is a history of development. It is the result of social, political, ideological, cultural and economic evolution. In order to study, examine and understand the overview of furniture in this period and the connection between periods, it is often summarized and classified according to historical years, and the characteristics of style are used as the main line for explanation and description in each historical period. In the process of studying the history of furniture development, it is important to grasp the style characteristics of furniture in each historical stage, and understand the historical reasons in society, culture, economy, science and technology that formed this style characteristic, so as to grasp the connotation and laws of furniture development and change, and serve the design innovation of furniture.
1. Foreign furniture
1. Foreign Classical Furniture
A. Ancient furniture
a. Ancient Egyptian furniture:
Around the 15th century BC, ancient Egypt was located in the lower reaches of the Nile River in eastern Africa. In 4000 BC, Menes unified Egypt and formed the earliest ancient civilization in the world. During its heyday in 1500 BC, ancient Egypt created a splendid Nile River Basin culture.
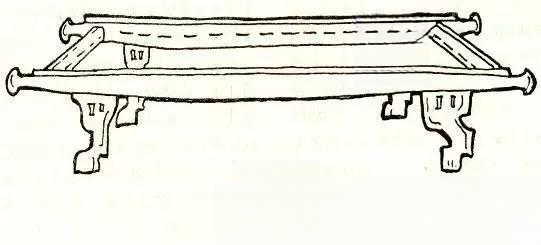
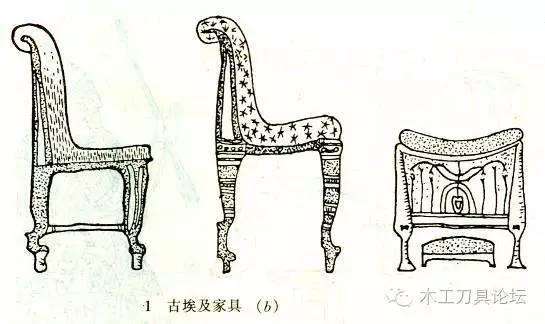
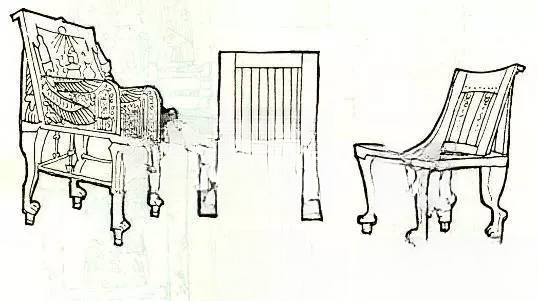
The wooden furniture that has been preserved today includes folding stools, armchairs, couches, boxes and tables.
The legs of chairs and beds are often carved into the shapes of animal legs, cow hooves, lion claws, duck beaks, etc. The two sides of the emperor's throne are often carved into images of lions, eagles, etc., giving people a feeling of majesty, solemnity and supremacy.
The decorative patterns are mostly drawn from common animal and plant images and hieroglyphs, such as lotus, reed, eagle, sheep, snake, beetle and some geometric shapes.
The decorative colors of furniture, in addition to the natural colors of gold, silver, ivory, and gemstones, common colors include red, yellow, green, brown, black, and white. The pigments are made of mineral pigments and plant gums.
The coverings used for folding stools, chairs and beds include: leather, rush and linen rope.
The woodworking technology of furniture had also reached a certain level. Egyptian craftsmen at that time were able to process some relatively perfect cutting and mortise and tenon joints and exquisite carvings, and their inlay technology had also reached a fairly skilled level.
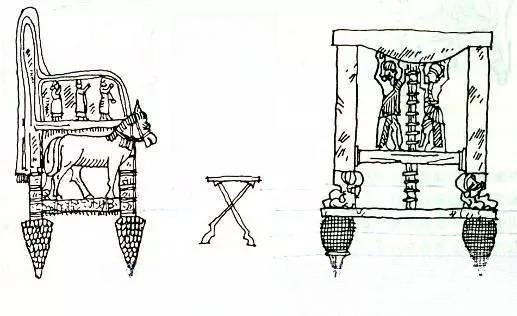
b. Furniture in the Mesopotamian region of ancient West Asia (10th century BC - 5th century BC):
In the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in western Asia, the ancient Babylonian Empire was established in 2000 BC. Then the Assyrian Empire emerged in the north and destroyed Babylon in the 8th century BC. In the 6th century BC, the Persians occupied the Mesopotamian region and established the Persian Empire. Babylon, Assyria and Persia all created splendid ancient cultures. From the excavated>
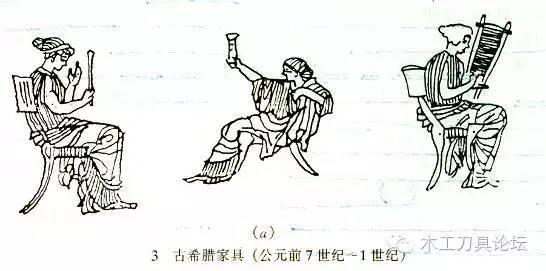
c. Ancient Greek furniture (7th century BC - 1st century BC):
The heyday of ancient Greek culture was from the 7th century BC to the 5th century BC. According to the records of stone carvings, there were already chairs, couches, boxes, altars, etc. Ancient Greek furniture was influenced by its architectural art. The legs of the furniture often adopted the column shape of the building, and the chair legs and backs were composed of light and graceful curves, forming the elegant and beautiful artistic style of ancient Greek furniture.
Ancient Greek furniture often uses blue as the base color, with decorative patterns such as honeysuckle, laurel, and grapes painted on the surface, and inlaid with ivory, tortoise shell, gold, silver and other materials.
d. Ancient Roman furniture (5th century BC - 5th century AD)
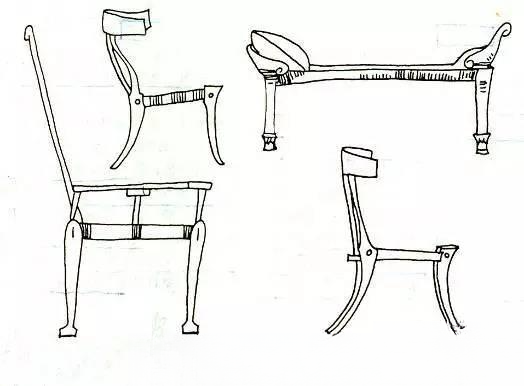
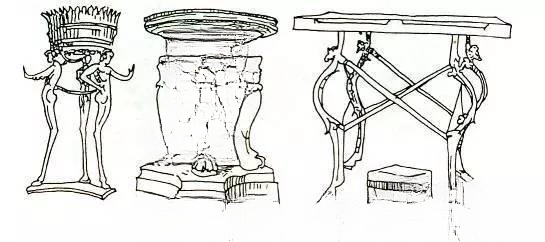
In the 3rd century BC, the ancient Roman slave state was established in the central part of the Italian peninsula. After that, with the continuous expansion of the Romans, a consolidated Roman Empire was formed. Most of the remaining objects are bronze and marble furniture. Although they were influenced by Greece in shape and decoration, they still have the solid and solemn style characteristics of the ancient Roman Empire.
The legs of animal-footed furniture are more substantial than those of Egyptian furniture.
Wood is also a widely used material, and is often decorated with inlays.
Commonly used patterns include eagles, winged lions, goddess of victory, laurel wreaths, honeysuckle, palm trees, and curlicues.
B. Medieval Furniture
a. Byzantine furniture (328-1005 AD)
In the fourth century AD, the ancient Roman Empire was divided into two parts, the East and the West. The capital of the Eastern Roman Empire was Constantinople, known as the Byzantine Empire. Byzantine furniture inherited the formation of Roman furniture and integrated the artistic styles of West Asia and Egypt, with carving and inlay being the most common. Some furniture is covered with shallow carvings.
The decorative techniques often imitate the arch forms used in Roman architecture.
Ivory, gold and silver are commonly used for inlay, and gemstones are occasionally used.
Decorative patterns include leaf ornaments and flowers, combined with Christian symbols such as crosses, wreathes, lions, horses, etc. Geometric patterns are also often used.
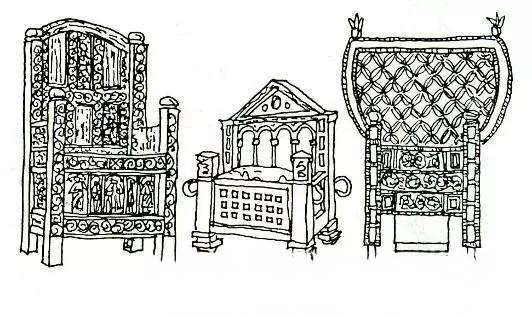
b. Imitation Roman furniture (10th-13th century AD)
After the fall of the Roman Empire, Italian feudal states combined Roman culture with folk art to form an art form called Romanesque, which was later spread to countries such as Britain, France, Germany and Spain, and became popular in Western Europe from the 11th to the 13th century.
The most prominent feature of the woodturning technique is the imitation of the arches of the building. There are armchairs made entirely of woodturning, and the top of the cabinets is in the form of two-slope spires. Some surfaces are attached with metal accessories and round rivets, which are both reinforcement parts and good decorations. The panels are decorated with relief and shallow carvings, and the decorative patterns include: geometric patterns, woven patterns, curling grass, crosses, Christ, saints, angels and lions, etc.
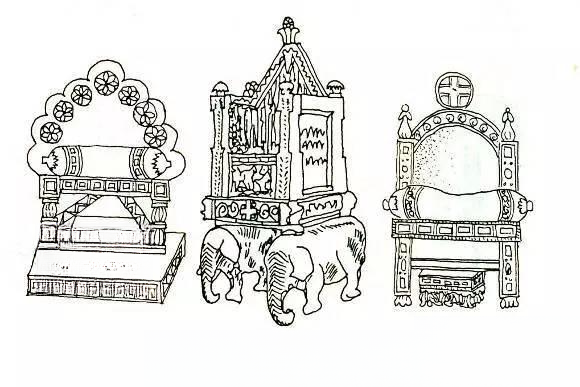
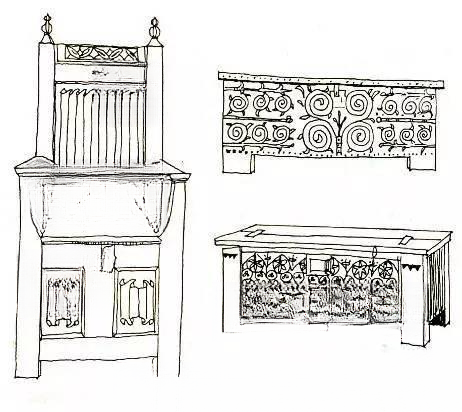
c. Gothic furniture (12th-16th century AD)
A form of furniture that first originated in France in the late 12th century and then became popular in Europe in the 13th and 14th centuries.
The main feature is that it is consistent with the Gothic architectural style of the time, imitating certain architectural features, such as: using spires, pointed arches, thin columns, pendant covers, shallow carvings or openwork panel decorations. The artistic style is also reflected in the exquisite carvings and decorations. Almost every space in the plane of the furniture is regularly divided into rectangles, which are filled with vines, flowers, roots and geometric reliefs. Most of these patterns have symbolic meanings of Christ, such as the "three-leaf decoration" (a pattern composed of three pointed leaves) symbolizing the Trinity of the Father, the Son and the Holy Spirit; the "four-leaf decoration" symbolizes the four gospels; the "five-leaf decoration" represents the five apostles, etc. Gothic furniture is also often inlaid with metal decorations and additional rivets.

C. Modern furniture
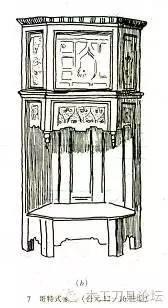
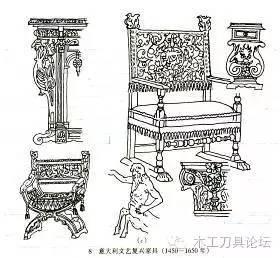
a. Italian Renaissance furniture (1450-1650)
In the 14th and 15th centuries, due to the development of the urban commodity economy, capitalist production relations had gradually formed within the European feudal system, and culture began to reflect the interests and demands of the emerging bourgeoisie. The ideological trend at that time was humanism, which opposed the asceticism and religious views of the Middle Ages and got rid of the church's constraints on people's thoughts. The characteristics of furniture at that time were: heavy and solemn appearance, rough lines, ancient Roman architectural features, and the human body as a decorative subject appeared in large numbers on furniture. The main materials used were oak, walnut and mahogany. It was particular about appearing in the room in the form of a set of furniture, and at the same time, a box-shaped long couch appeared, which prompted the prototype of the later "sofa". The surface of the furniture is often made of very hard plaster floral decorations and gold foil, and some are also painted on the gold base to increase the decorative effect. By the 16th century, it was popular to use polished marble, agate, tortoise shell, gold and silver, etc., inlaid into floral decorations composed of gorgeous branches and vortices.
b. British furniture in the modern century (1485-1830)
Starting from the Renaissance in Britain, furniture entered a period of continuous development and change.
① Tudor furniture (1509-1603)
A type of furniture named after the British Royal Tudor family. It is characterized by its simple and clumsy shape. In the early days, it was a unique form that included late Gothic decorations, Renaissance carvings, and Tudor rose decorations. Later, it formed British Renaissance furniture, such as paneling in uniform rectangles, table legs and bedposts in the shape of turned wood cylinders, and giant bottle-shaped pillars and groove-shaped decorations. The main material is oak. Therefore, it is also called the "Oak Period".
②Jacobin style furniture (1603-1689)
This is also a type of furniture named after James, the first king of the Stuart dynasty, another family of the British royal family. With the political changes in different periods, its style has slightly changed, and the furniture has changed from high to low. The characteristics are: the chair back is vertical, generally wide and low, and the wooden legs continue to be used. The most obvious is the appearance of Dutch ball feet and Flemish scroll-shaped openwork pulls. The cabinet doors are also influenced by the Dutch inlay technology, with ivory or bone inlaid into beautiful patterns. In addition to oak, walnut has begun to be used.

③ William and Mary furniture (1689-1702)
Furniture increasingly uses curves to replace Jacobin's straight lines, gradually becoming lighter and more lively. Spiral, spherical and bread-shaped feet are very popular, and the footrests are mostly X-shaped curved cross structures. The outlines and decorations of furniture are relatively simple. Walnut is used extensively. As carved decoration tends to decline, inlay work becomes more popular. Influenced by the oriental style from the Netherlands, China began to imitate the Chinese painting process of tracing gold on black, blue, green and red lacquer, and sometimes even covered the entire piece of furniture with gold foil.
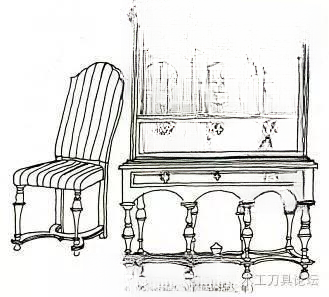
④ Queen Anna style furniture (1702-1750)
During the reign of Queen Anna, people paid more attention to the comfort of life, so the shape of furniture was mostly smooth curves, and the appearance became more beautiful. The most prominent features of the chairs were the curved feet and the piano-style high backrest. The seat was generally cushioned with cloth, and some of the cloth was also embroidered. Queen Anna's style was a form of "prominent curves" influenced by the Dongfeng style, especially Chinese furniture. The outline of the furniture was completely composed of the melody of curves, occasionally with a little inlay craftsmanship, but rarely with complicated carvings and decorations. The materials used were mainly walnut.
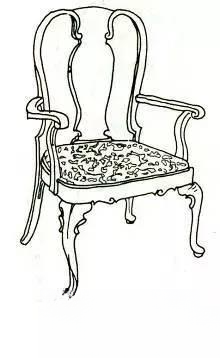
⑤ Chippingdale style furniture (1750-1830)
Chippingdale was one of the four great furniture designers of the Georgian dynasty in the mid-18th century. He absorbed the delicate and soft curves of the Rococo style in the simple and plain British style. He also liked to use Chinese patterns of wavy patterns and window panes as decorations for chair backs or other furniture, which made the openwork fine wood chair backs a typical feature of Chippingdale furniture. Chair backs can be divided into three typical styles: one is the vertical board openwork into a violin style or a winding curve style; the second is the Chinese lattice style; and the third is the trapezoidal horizontal style. The top of the cabinet is mostly made of mountain or vortex shapes as the brim, and decorated with delicate honeysuckle leaves or other carved patterns, but never used inlay technology. The materials used are mainly walnut and mahogany.
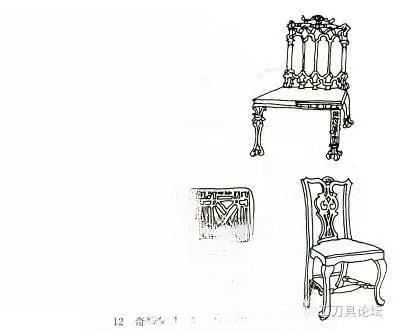
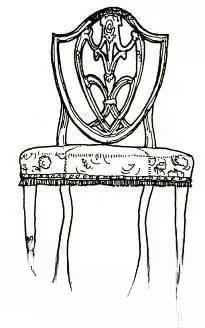
⑥ Hepplewhite furniture (1750-1830)
Hepplewhite is also one of the four great furniture designers of the Georgian dynasty. The characteristic of this style is that the outline of the chair back is made into a shield shape, a cross heart shape or an oval shape. There are ribbons, round flowers and harps in the middle of the chair back. In addition, the circle and oval shapes are often used on the mirror frame and tabletop of the dressing table. With the smooth and simple square legs, it forms a light and beautiful artistic style. The material used is mainly mahogany.
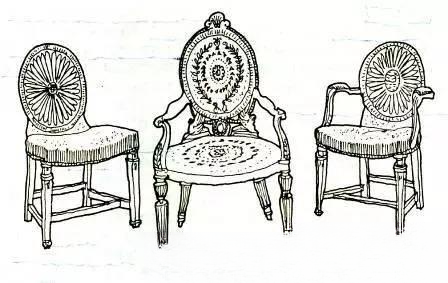
⑦ Adam style furniture (1705-1830)
Robert Adam is also one of the four great furniture designers of the Georgian dynasty. This style is characterized by straight lines. Chairs and panels are favored with square, hexagonal, octagonal or oval, cylindrical legs or straight legs with lower legs, often with hoe-shaped feet. Emphasis is placed on the application of decorative patterns, among which Roman hanging flower ornaments, ribbons, laurel branches, winged sphinxes, centaurs, and Greek ancient vases and wine glasses are the most common. The rich, exquisite and elegant appearance of Adam furniture reflects an extremely strong classical spirit. The main material is mahogany.
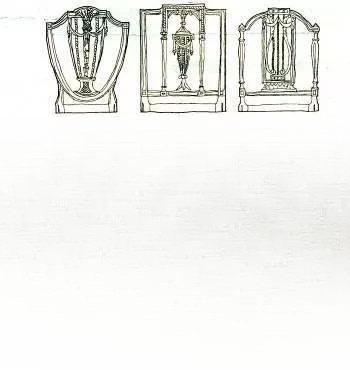
⑧ Sheraton furniture (1750-1830)
He is also a famous furniture designer in the UK. Influenced by the French Louis XVI style furniture, he simplified it to become the British style. The typical, dignified and concise straight lines are the keynote of his design. For example, the backs of the chairs are mostly square, with multiple straight vertical bars, harps and ancient vases in the middle. At the same time, he also pays attention to the configuration of the texture of various furniture materials, such as veneer parquet decoration, inlay decoration of different materials, and the decorative effect of masked fabrics. The materials are mainly mahogany and basswood.
c. French furniture in the early modern period (1515-1547)
① French Renaissance furniture:
The Renaissance movement originated in Italy in the 14th century and first spread to southwestern France, leading to the formation of French Renaissance furniture. Many caryatids, ancient Greek columns, various floral decorations and figure reliefs appeared in the decoration.
② Louis XIV style furniture (Baroque): 1643-1715
It is also a classic Baroque furniture. It refers to the art style popular in Western Europe from the late 16th century to the mid-18th century. It was originally produced in Italy. French Louis XIV furniture is a furniture style influenced and developed by Italian Baroque art. Baroque furniture has exaggerated passion, over-rendered magnificence, and dignified and civilized classical forms. Therefore, Louis XIV furniture is mainly characterized by its tortuous and changeable lines and free and unrestrained decoration. The main material is walnut. In terms of decoration, it is also influenced by China. Sometimes gold foil is pasted on the furniture to achieve a magnificent artistic effect.
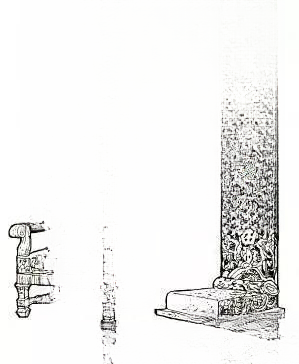
③ Louis XV style furniture (Rococo style):
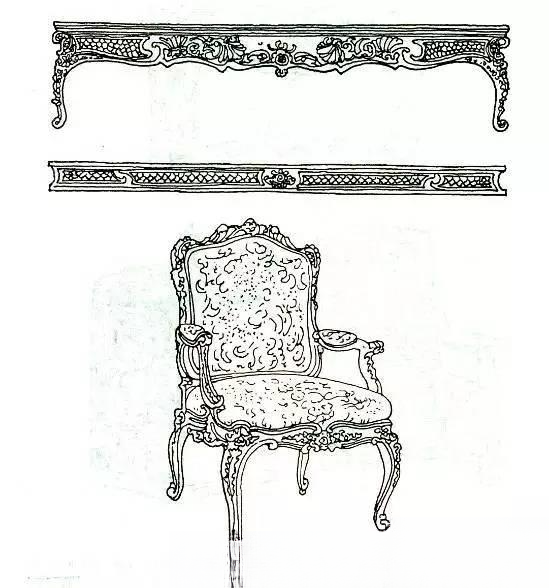
It was developed from Baroque art. It was first produced in France and soon became popular in Europe in the first half of the 18th century. Louis XV furniture completely shed the characteristics of Renaissance furniture and became an extremely luxurious style. Rococo furniture is mainly characterized by serpentine shell-shaped curves and delicate carvings, and the keynote of the shape is convex curves. Curved feet became the only form at that time, and cross braces were rarely used. In addition to seashells and eggs, decorative themes also used flowers, leaves, fruits, ribbons, scrolls and angels to form gorgeous and delicate patterns. The greatest achievement of Rococo furniture is to cleverly combine the most beautiful form with the most comfortable effect possible. The seat cover fabrics are mostly velvet or satin embroidered with patterns to coordinate with the entire piece of furniture. In terms of coating, the Chinese practice is imitated, and the paint is painted in bright black, red, green, white and gold, which produces a magnificent color effect, but there is also a practice of keeping the original color of the wood, with walnut being the majority.
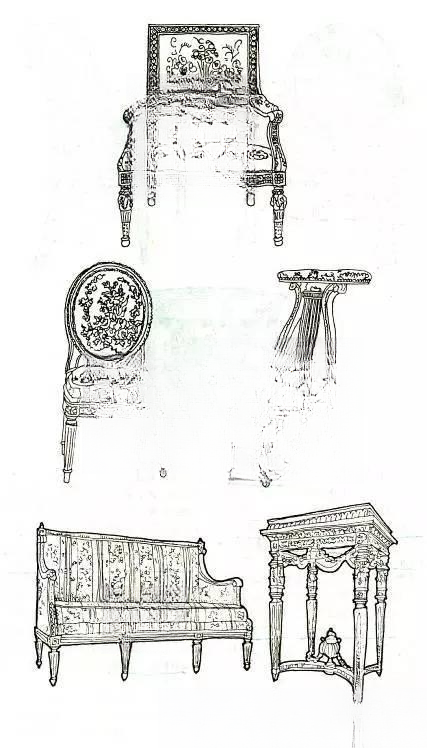
④Louis XVI style furniture (1774-1793)
The European revival of classical style is popular again. Classicists believe that Baroque and Rococo furniture abuse curves and completely violate the rational principles of classical style. Therefore, Louis XVI furniture gradually tends to be simple, solemn and pure. With straight lines as the keynote, without excessive detail decoration, the pursuit of the beauty of overall proportions shows the classical spirit of rationality, moderation, clear structure and rigorous context. It often has the characteristics of an architecture, with a square shape, and the feet are round or square columns with large upper and small lower parts, and long grooves are usually made on the columns. The back of the chair is often made of regular square or oval wooden frames.
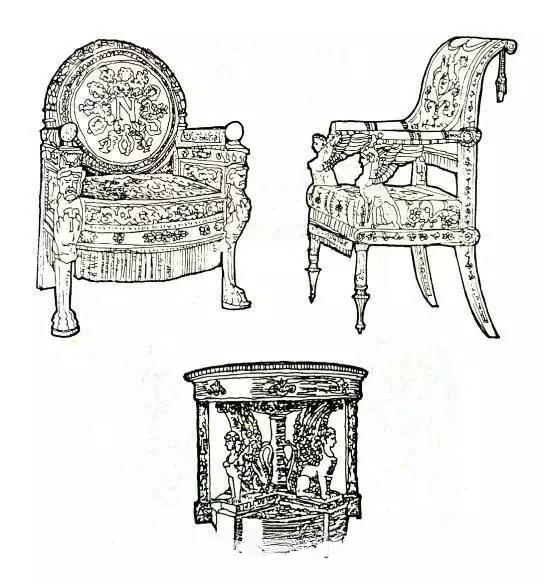
④ Imperial Antique Furniture:
This is the furniture style when Napoleon I of France became emperor. In order to show off military exploits and express the style of soldiers, Empire-style furniture adopts rigid lines and clumsy shapes, and uses almost all classical themes in decoration. Gilded copper is usually used for inlay or decoration. In terms of color, gold and silver are often used to embellish dark green, reddish brown and other colors. The color is gorgeous and calm. Mahogany is the most popular material; sandalwood and rosewood are also often used.
d. American Colonial furniture
Early American furniture came from early immigrants who came to the United States from Europe. They used the most readily available wood in the local area, such as pine and oak, to produce furniture that was simple, practical, and easy to process. As living conditions improved, they began to intentionally manufacture some slightly decorated furniture, which was called American Colonial furniture, and later Federal style. Influenced by French furniture, it still maintained the simple and rough characteristics of early American furniture. It is still very popular today.
e. Spanish and Mediterranean furniture
Reflecting the Roman state art of the 17th and 18th centuries, in addition to wood, leather, glass, metal and ceramics are widely used. Ancient Spanish knights are often embossed on the surface of the cabinet; the headboard is often arched; there are many decorative geometric patterns; the chairs are often covered with leather; they are relatively heavy, often made of walnut, and the coating is generally brown.
2. Foreign modern furniture
A. Early modern furniture (1850-1914)
a. Early art movements and schools
① Handicraft Movement:
It is mainly an art movement in the UK, initiated by Morris in 1888. The basic idea of this movement is to reform the past decorative art and meet people's needs with large-scale, industrially produced, cheap products. Therefore, it marks the first step for furniture to move from classical decoration to industrial design. With the pioneering work of Morris Decoration Company and its growing influence, this new idea spread to the entire European continent 10 years later, leading to the emergence of the "Art Nouveau Movement".
②Art Nouveau Movement:
It was a reform movement that started in France in 1895 and ended in 1905, spreading throughout Europe. It was committed to seeking a new style that was not at all subordinate to the past. It was a personal romantic art that focused on decoration. It used the beauty of natural forms as its own decorative style and was full of vitality. Representative figures of the movement included Hai Geyoumaat of France and Henri van der Velde of Belgium. Although their works were a bit too romantic and were eventually eliminated because they were not suitable for the requirements of industrial production, they made people understand that they should be liberated from imitating classics and constantly explore new design methods.
③ Vienna School of Decorative Arts:
In 1899, architects led by Wagner established the Vienna School of Decorative Arts. These famous Viennese architects believed that "modern forms must also be coordinated with the new requirements of contemporary life", and their works all have a simple and bright modern feel. Their theories and practices not only created new architecture in Austria in the 20th century, but also had a profound impact on the formation of modern furniture.
④ German Manufacturing Alliance:
This is an association proposed by German architect Moodysius and established in Munich in October 1907. Its members include artists, designers, critics and manufacturers. Moodysius had been to London and was deeply influenced by Morris Company and the "Crafts Movement". He advocated that "the goal of the association is to creatively integrate art, craft and industrialization, and thereby expand its role in industrial production". The practical activities of the "German Manufacturing Union" caused considerable repercussions in Europe, and led to the establishment of the Austrian Works Union in 1910, the Swiss Manufacturing Union in 1913 and the British Industrial Design Association in 1915. The "German Manufacturing Union" was closed by the Nazis in 1937 and resumed its activities in 1947.
⑤ Swiss Manufacturing Alliance: Founded in 1913, it is an association of the same nature as the "German Manufacturing Alliance".
b. Famous designers of early modern furniture and their works
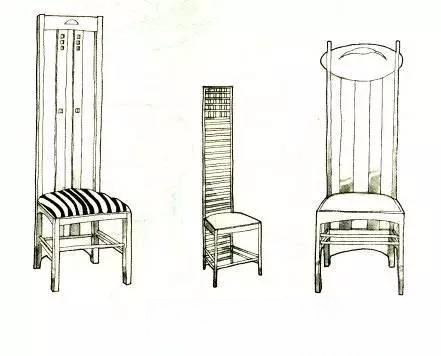
① McIntosh Charles:
Born in Glasgow, England in 1868 and died in London in 1928. In 1885, he attended night classes at the Glasgow School of Art. After graduation, he worked in an architectural firm mainly engaged in interior decoration and furniture design. Since he believed that furniture should mainly show vertical and beautiful features, he often used straight lines and right angles to emphasize his unique personal style. In 1913, he moved to London and became a leader of the British Art Nouveau movement as an architect, painter and interior designer.
②Maurice William:
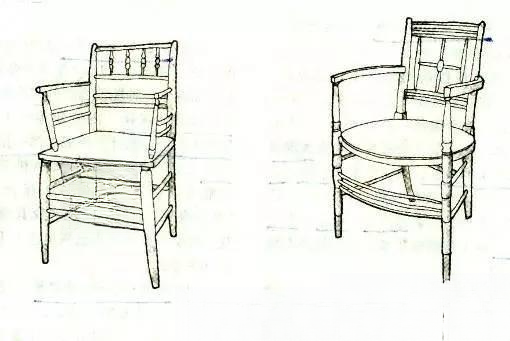
Born in Essex, England in 1834, he died in London in 1896. In 1861, he established a company with a large number of artists and craftsmen, engaged in wallpaper, stained glass, furniture, metal crafts and other businesses. In 1875, the company was renamed "Morris Decorating Company" and soon advocated the "Handicraft Movement". He is revered as the "Father of Modern Art Design".
③Sony Michel:
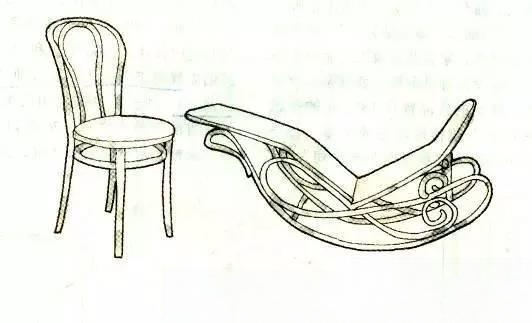
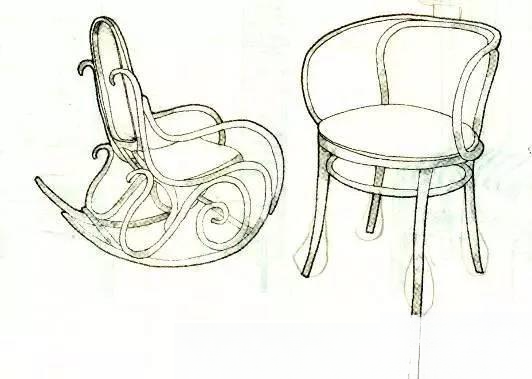
Born in Germany in 1796, died in 1871. In 1819, he opened a furniture factory and began to explore a style that could make the solid wood furniture of the time light and economical. In 1830, he finally invented the bending wood process, designed and made the first bent wood chair. In 1851, his "Vienna Chair" won the first prize at the World Furniture Fair in London. This chair has been sold for more than 50 million to date. He was the first pioneer to industrialize furniture production.
⑤ Henry van der Velde:
Born in Antwerp, Belgium in 1863 and died in Zurich, Switzerland in 1957.
Studied painting at the Academy of Fine Arts. Engaged in furniture and interior design in 1898. Founded the Weimar School of Arts and Crafts (the predecessor of the Bauhaus) in 1906. Was also one of the founders of the German Manufacturing Union.

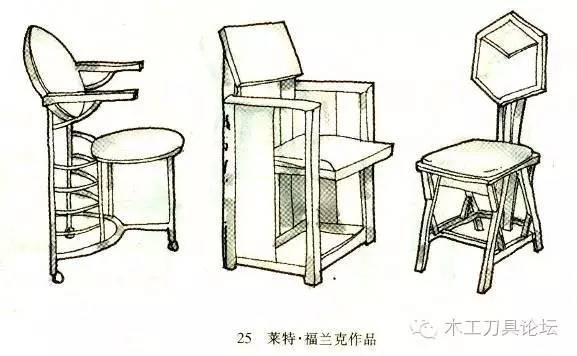
⑥ Wright Frank:
Born in Wisconsin, USA in 1867, he died in Arizona in 1959. He advocated the unity of form and function and emphasized the expression of individuality. The office chair he designed in 1904 illustrates his own views in practice.
B. Modern furniture between the two world wars (1914-1945)
a. Art movements and schools between the two world wars
① De Stijl:
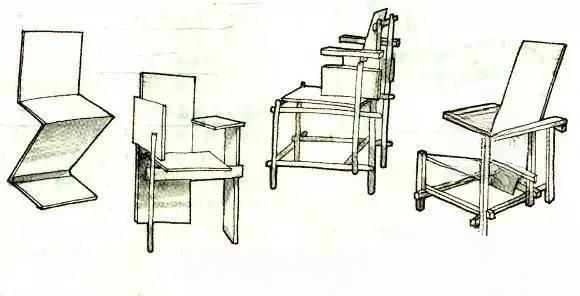
In 1917, a group of artists, architects and designers was formed in Leiden, the Netherlands. The group named its school after the art theory journal "Style" edited by the group's founder Vandue Tubourg. The school accepted the new arguments of Cubism, advocating the use of pure cubes, geometric shapes and vertical or horizontal surfaces to shape images, and the use of primary colors such as red, yellow and blue. In 1918, Reitveld joined and designed his masterpiece "Red and Blue Chair". The school was disbanded in 1931 due to the death of the founder.
② Bauhaus:
It is the abbreviation of a German architectural design school. Its predecessor was the Weimar Academy of Arts. It was reorganized and established by Gropius Walder in 1919. The school created a whole new set of teaching and creative methods of "using new technologies to economically solve new functions". The design characteristics of "Bauhaus" are focus on function and industrial production, and are committed to the unity of form, material and process technology.
b. Famous designers and their works during the two world wars
① Alto Alva:
Born in Finland in 1898, died in 1976. Aalto graduated from the Faculty of Architecture at the University of Helsinki in 1921. In 1929, he designed his first laminated wood chair with a wooden frame edging, and in 1933, he made a laminated bent wood chair without a wooden frame. In 1931, he founded Artek, which specializes in producing furniture, lamps and other daily necessities designed by himself. His works reflect the influence of the Finnish environment.
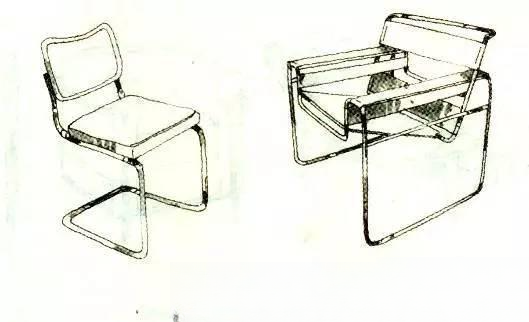
② Briar Marshall:
Born in Pécs, Hungary in 1902, died in 1981. In 1920, he entered the Bauhaus in Weimar to study industrial design and interior design. In 1925, he became the director of the academy's workshop. He designed his first steel pipe "Vassily Chair". In 1933, his aluminum alloy furniture won an award in Paris.
③ Gropius Walder:
Born in Berlin in 1883, died in the United States in 1969. Studied architecture in Munich and Berlin in his early years. In 1919, he merged the Weimar Polytechnic School and the Art Academy into the Bauhaus School, and served as its president. In 1937, he moved to the United States and served as the director of the Department of Architecture at Harvard University.
④ Le Corbusier:
Born in Switzerland in 1887 and died in France in 1965. His original name was Charles Ginarit. He studied at an art school in France in his early years. In 1929, he collaborated with Perriand Charlotte to design the interior furnishings of an apartment, including chairs, tables and standardized cabinets.
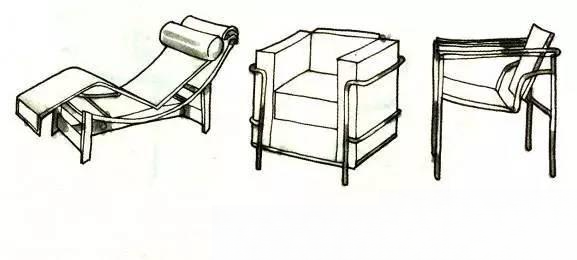
⑤ Bellion Charlotte:
Born in Paris in 1903, she first exhibited their standardized wooden storage modular furniture at the International Exhibition of Decorative Arts in 1925 with Le Corbusier and Pierre Ginarit. Perriand has always been committed to creating simple furniture that everyone can afford.
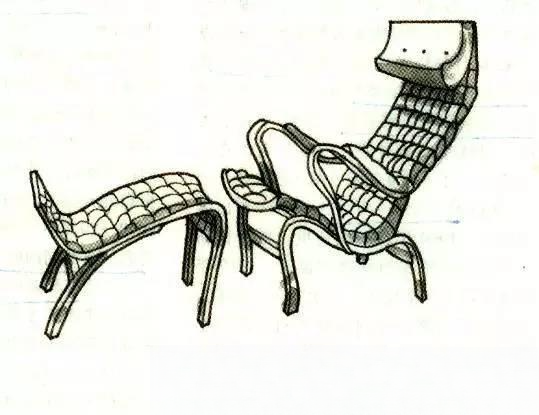
⑥ Matheson Bruno:
Born in 1907 in a Swedish carpenter family. When he grew up, he inherited his father's business and became a famous Swedish furniture designer and interior designer. Matheson was very interested in the craftsmanship and structure of furniture. After research, he successfully designed a group of chairs made of bent laminated wood. His works played a dominant role in the Swedish furniture industry from 1940 to 1950.
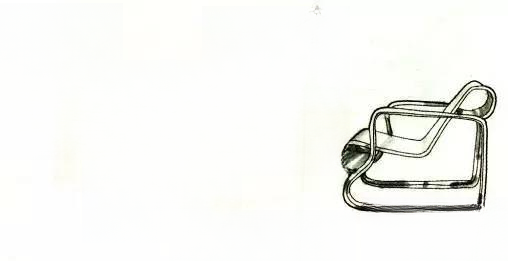
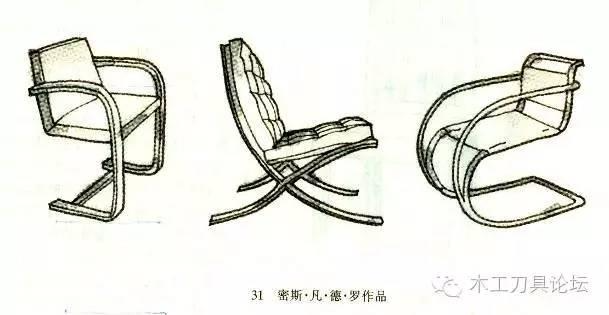
⑦ Ludwig Mies van der Rohe: Born in Germany in 1886, died in the United States in 1969, worked as a draftsman at the age of 15, and worked as a designer in 1908. He designed the cantilevered steel pipe chair in 1926 and the "Barcelona Chair" in 1929.
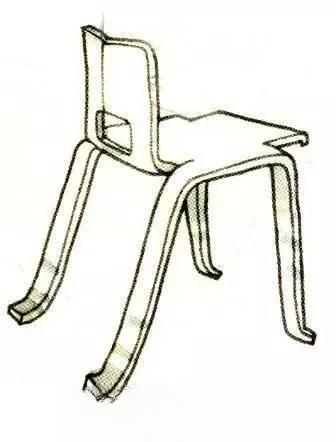
⑧Reitveld Gerrit:
Born in Utrecht, Netherlands in 1888, died in 1964. His early career was carpentry, and he taught himself architecture and furniture design in his spare time. In 1918, he designed and produced the "Red and Blue Chair", which is a representative work of the "De Stijl" theory. He has been exploring the design of cheap furniture that can be mass-produced.
Woodworking tool forum "zjwoodtools" [WeChat ID]
Woodworking Tool Network (http://www.) is the No. 1 website in the woodworking tool industry in China and the only professional forum in the woodworking tool industry in China. This website focuses on various related information and technical issues in the woodworking knife and saw industry, and is published to fans who follow this platform for reading. The graphic content is updated daily; it provides a harmonious platform for communication and discussion among people in the woodworking tool industry to meet the industry needs of visitors.